Business Plan
advertisement

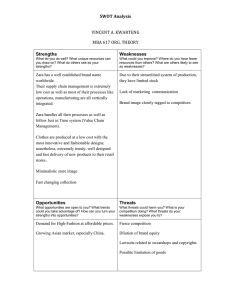
What goes into a business plan? What does it take to start a business? What kind of business would you want to start? We will talk about what goes into a business plan and talk about each part of it in depth. We will look at real life companies and different aspects of their business. You will get the chance to work alone or in a group to develop a business plan for a company you will create! What will your company do? Sell a product? Tom’s Shoes Home Depot Target Wal-Mart Apple Offer a service? Google Massage therapists Web Design You must decide what it is that your business is actually going to sell. It could be one product. It could be multiple. It could be several services, or it could be a blend of products and services. The Best Industries for Starting a Business Right Now There are some interesting companies out there… eNthem of San Francisco I Do Now I Don't Lucky Break Wishbone Prairie Tumbleweed Farm Sarah's Smash Shack A company obviously must have a name… Some cool company names I’ve come across: StumbleUpon Pinterest Google Hulu Sew Sew Lovely Yoforia Any cool names you’ve heard of? Business Name Examples Tips on Creating a Name This company actually comes up with business names for people A logo is just as important as a name….it’s something you put on a website, business card, business car or truck, and any advertisement you use! Most companies have a motto or 5 tips for writing an effective “Think Different” Apple “Have It Your Way” Burger King “Zoom Zoom” Mazda “Eat Fresh” Subway “Live in Your World, Play in Slogan Generator 10 Best Slogans according to catch phrase Ours” Sony Playstation “I’m Lovin’ It” McDonald’s “You Can Do It. We Can Help.” Home Depot slogan INC.com Every company has both! Your mission is what you do best every day, and your vision is what the founder ultimately envisions the business to be. Mission-daily focused. What’s your purpose? Vision-future focused. How high do we want to reach? Video: what's the difference? Mission Statement How To: 5 slides from Inc.com MissionStatements.com-examples of mission statements from real companies. Other examples: Mastercard PepsiCo A vision statement for a new or small firm spells out goals at a high level and should coincide with the founder’s goals for the business. Simply put, the vision should state what the creator(you) ultimately envisions the business to be, in terms of growth, values, employees, and contributions to society. Then, develop strategies for moving your business toward that vision. Video: Vision Statement How To Examples: Coca Cola Step #1 Write a list of facts about your business. List your goals, strengths, benefits and so on. Step #2 Now write a statement about what you want your business to become in the future. What does it look like? Is it global? What are you doing for your customers? Step #3 Combine your statement and the items in your list that stand out, create your vision statement. Remember, this is only an exercise, you may write and rewrite your vision statement ten times before you hit on one that resonates with you. Remember, your vision statement is an essential part of your business plan. Imagine creating a business without it. Many do and they’re short lived. Imagine trying to make a decision about hiring, about your business model, about marketing without knowing what it is exactly that you want your business to be and where you want it to go... You can’t. A business strategy encompasses many things. We will consider questions like: Is your company local or global? Small or big? Small staff, big staff? Who is your target market? How will your business meet customer needs and expectations? What is your competitive advantage? Intro Strategy! Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats A firm’s strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage. Examples: Patents Strong brand names Good reputation among customers Unique, differentiated product Low cost Exclusive access to high quality materials The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each of the following may be considered weaknesses: Lack of patent A weak brand name Poor reputation among customers Poor customer loyalty High costs Lack of access to high quality materials What could you potentially improve? What could lose you business? Unsafe environment Unfriendly employees The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities. Some examples: An unfulfilled customer need Arrival of new technologies Loosening of regulations Removal of international trade barriers Changes in the external environment also may present threats to the company. Examples: Shifts in consumer tastes away from your company’s product Tamagotchi’s anyone? Emergence of substitute products Netflix New regulations Increased trade barriers Some Real Examples Let’s do a SWOT analysis for Starbucks! So what do you do with a SWOT analysis? Answers the questions: How do we make the most of our strengths? How do we circumvent our weaknesses? How do we get the most out of our opportunities? How do we manage our threats? What’s the difference? MARKETING is the systematic planning, implementation and control of a mix of business activities designed to present products in such a way as to make them desirable. ADVERTISING is the public promotion of something such as a product, service, business or event in order to attract or increase interest in it. Simply put: Marketing is the umbrella, and advertising is underneath… THE FOUR P’s: Product: “Product” refers to the goods and services you offer to your customers. Apart from the physical product itself, there are elements associated with your product that customers may be attracted to, such as the way it is packaged. Other product attributes include quality, features, options, services, warranties, and brand name. Price: “Price” refers to how much you charge for your product or service. Determining your product’s price can be tricky. Place: “Place” refers to the distribution channels used to get your product to your customers. What your product is will greatly influence how you distribute it. If, for example, you own a small retail store or offer a service to your local community, then you are at the end of the distribution chain, and so you will be supplying directly to the customer. Businesses that create or assemble a product will have two options: selling directly to consumers or selling to a vendor. Promotion: “Promotion” refers to the advertising and selling part of marketing. It is how you let people know what you’ve got for sale. The purpose of promotion is to get people to understand what your product/service is, what they can use it for, and why they should want it. You want the customers who are looking for a product/service to know that yours will satisfy their needs. Website Business Card:cool cards Newspaper Commercial Radio jingle Poster/Flyer Facebook Twitter Every business needs money to get started and to keep running. We will cover what it takes to start up: Inventory Workers Capital And other stuff… Break-Even Analysis What it takes to make a profit You will get a chance to create a company and a business plan. Your business plan will require each element that we cover in class. I will give you a rubric so you know exactly what you need. You can work alone or in a group, and you will have class time to work on it. You will present your project to the class. The most viable business plan will win an award. And we just might have a class party to celebrate All images that appear on the PPT are copyright their respective owners and I claim no credit for them unless otherwise noted. If you own the rights to any of the images and do not wish them to appear on this PPT please contact me and they will be promptly removed.