Grade 9 Biology Study Guide: Cells, Systems, Reproduction & More
advertisement

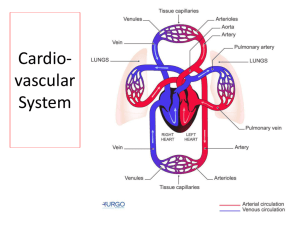
Grade 9 Detailed Study Guide If you can answer these questions, you will be in great shape for the exam! Note: You should be able to label diagrams, like the human heart, male reproductive system, etc. I will note what you should be able to label for each subject in the study guide. Chapter 5 Cells, tissues, organs and systems Label: a cell (3 main parts) 9. What are the processes used by cells to divide? Specify which method is used for what purpose, along with the stages of each division. 1. What is a cell? 10.What are gametes? 2. What are the three parts of the cell that you can see using a conventional microscope? List the functions/characteristics of each part. 11.What is tissue? List the 4 different types. 3. What is DNA? What is its shape? Where is it located in the cell? 4. What is a gene? 12.What is the difference between an organ and a system? The Reproductive System Label: Male and female reproductive systems 5. What is a chromosome? 1. What is fertilization? 6. What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells? 2. What are the stages of human development? 7. What is a genome? 3. What is puberty and what age does it occur in humans? 8. What is genetic diversity? 4. What is a hormone? Which hormones are responsible for puberty? 13.What is semen made of? 14.What is ejaculation? 5. Which gland secretes the hormones that are responsible for puberty? Where is it located? 15.What are menopause and andropause? Chapter 6 6. What are the primary and secondary sexual characteristics of males and females? 7. Which hormones are responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females? In males? 8. What is oogenesis? Where does it occur? 9. What are the different stages of the ovarian cycle? 10.What are the different stages of the menstrual cycle? Be sure to note the changes in hormone levels and endometrium thickness during each stage. 11.What is spermatogenesis? Where does it occur? 12.What is an erection? Nutrition Label: Nutrition label (be able to understand one) 1. Define nutrients, list the six types of nutrients and their uses. 2. Which nutrients provide energy to the body? 3. List different foods that are rich in each of the six nutrients. 4. Which units do we use to measure energy from food? 5. For each nutrient, list how much energy is given per gram, in each of the different units of measure. 6. What are the four food groups? What are the recommended servings for each group for people your age? 8. How is fecal matter expelled from the body? 7. What types of foods are best for peak athletic performance? Respiratory system Digestive system Label: The digestive system (complete), digestive tract 1. What is digestion? 2. How is food moved along the digestive tract? 3. What is mechanical transformation of food? Where and how does this occur? 4. What is chemical transformation of food? Where and how does this occur? 5. Name the organs and secretions that play a part in chemical transformation. 6. What is absorption? Where does this happen in the body? 7. What happens in the large intestine? Label: Respiratory system, respiratory tract, inside of the lung (bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli) 1. What is respiration? 2. What is the chemical equation of respiration? 3. What is the difference between external and cellular respiration? 4. Through what process does gas exchange happen in the blood? 5. Explain the process of inhalation and exhalation using terms such as diaphragm, intercostal muscles, volume, pressure and diffusion. 6. Where does gas exchange occur in the lungs? Explain the process Blood Label: Blood (formed elements and plasma) 1. What are the different parts of the blood? List percentages of blood volume as well as functions for each. 2. What determines your blood type? Be as specific as possible. 3. What are the rules of blood transfusions in terms of donors and recipients? 4. In relation to blood transfusions, what is a universal donor? What is a universal recipient? 4. Describe the path of the blood as well as what happens to it as it moves from the right side of the heart. 5. What are pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation? Which side of the heart is responsible for each? 6. What are the diastole and systole phases of the heart? Lymphatic System Label: Lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes Cardiovascular System Label: cardiovascular system, heart (especially circulation route through the heart), pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation. 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. What are the three categories of blood vessels? Note important characteristics or each, as well as whether each type of blood vessel moves blood to or from the heart. 3. What are the four cavities of the heart? 1. What is extracellular/interstitial fluid? 2. How do water and other substances get into extracellular fluid from the capillaries? 3. What is lymph? 4. What type of vessels transport lymph around the body? 5. Where do these vessels take the lymph to be cleansed? 6. What role do the lymph nodes play in defending our bodies from infection? 7. What two ways do white blood cells fight invaders? 8. What are antigens? 9. What is an antibody? Give two important features of antibodies. Elimination of waste Label: the urinary system 1. What role does sweat play in our bodies? 2. What are the parts of the urinary system? What is the function of each? 3. How does the kidney regulate the levels of certain substances in our bodies? 4. What is urine made of? Be sure to mention the amount of each component.