Eukaryotic Cells Note Outline
advertisement

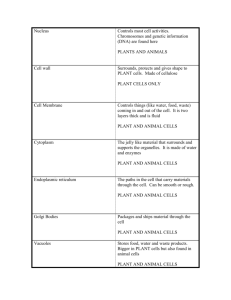
Levels of cellular organization Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Cells Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic Animal Plant Division of Cells Eukaryotic Cells Literally means “True nucleus” Have a ________ _______ Cells Have membrane-bound __________ Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are called “________” Examples: Animals, Plants, Fungi, Unicellular organisms like paramecium and amoeba Cellular Components Cytoplasm ___-_____ substance ______ the cell where organelles are found Cytoskeleton “Cell skeleton” Network of _______ fibers that maintain the ______ and structure of cell Composed of three networks of fibers 1. 2. 3. Microtubules: _______; hollow tubes made of protein; determine cell shape; scaffolding ______________ Filaments: Provide strength of cell Actin Filaments: ________; contractile string-like proteins that allow for cell ________ Cellular Components Cell Membrane ______-permeable barrier that _________ the cell Regulates what _____ and ______ the cell Provides protection Found in ____ types of cells Cell Wall Porous, ______ barrier found _________ the ____ ________ Adds additional layer of support and protection _____ found in _______ cells Organelles Nucleus Houses the ______ material (DNA) needed for replication of the cell “______ Center” of the cell Contains the instructions for the creation of proteins (made from DNA) Exterior: Surrounded by nuclear envelope: double-layered ________ that encloses the DNA; contains nuclear pores: small ________ that allow for the passage of molecules between the _________ and the _______ Interior: DNA in the form of ___________ (string-like) • Nucleolus: where ribosomes are made; very _______ region Organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum A grouping of sac-like structures _____ types of ER: ______ ER: contain ribosomes (creating ‘rough’ appearance); involved in the process of _______ synthesis ______ ER: no ribosomes; involved in ______ synthesis Ribosomes Location where _______ are made (protein synthesis) Organelles Golgi Apparatus Looks like a stack of membranes (pancake-like appearance) Modifies, ____, and _______proteins received from the ER. Break off from the golgi apparatus; float ________ in the cell or travel to _______________where it will eventually___the cell. Creation of _____________ Organelles Lysosomes Contain _______ necessary for_______ of cell food or waste Can break down lipids, carbs, proteins Digest non-functional organelles, ‘_______ ___’ the cell Organelles Vacuoles Sac-like structure responsible for _______ of various materials (e.g. water, carbs, proteins, etc.) Organelles Mitochondria The “___________” of the cell Convert _____ energy into energy that is used by the _____ itself (for growth, development, movement, etc.) via cellular respiration ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) _________ structure Organelles Chloroplast Site of _____________ Energy from ____ is captured and converted into chemical energy Contain the pigment ________ which absorbs solar energy used in photosynthesis Responsible for the ______ color of plants Organelles Centrioles Made of ______________ Located ______ nucleus ___________ microtubules within the cytoskeleton prior to cell division