Organelle PowerPoint
advertisement

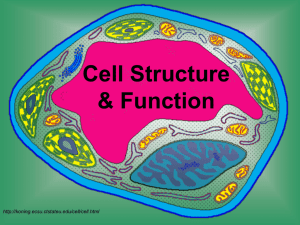
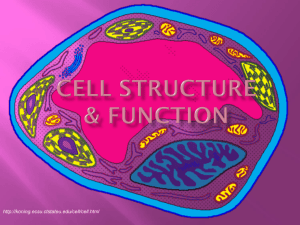
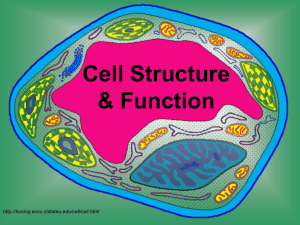
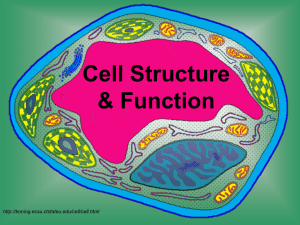
Cell Structure & Function http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html A Pretty Cool Video about Cells… • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFuEo2 ccTPA Learner Outcomes • I can list the three parts of the cell theory. • I can compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. • I can describe key characteristics of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit of life that is capable of performing life functions. Key Terms • Cytoplasm: jelly-like substance that contains all parts of the cell. • Organelles: structures within a cell that are specialized to perform certain functions. Discovery of Cells • The first cell was seen in 1665 by Robert Hooke using a simple light microscope. • He was looking at cork, the tough outer bark of a certain species of oak trees. – The plant cells he observed were dead and looked like small rooms so he called them cells. Cell Theory: work of several scientists • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the most basic units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. The Weird History of the Discovery of the Cell! • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4OpByl wH9DU Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Two Main Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic • Do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. • DNA is found floating in the cytoplasm. • All prokaryotes are bacteria. http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Eukaryotic • Have a nucleus and other organelles surrounded by membranes • All living organisms except bacteria. • Can be single-celled or multi-celled. Plant Animal http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Cell Parts Organelles Learner Outcomes • I can describe the function of the following organelles: – Mitochondria – Cell membrane – Ribosomes – Nucleus – Golgi Apparatus – ER – Nucleolus – Lysosomes -Vesicles Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane • Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell • Double layer http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cell Wall • Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria • Supports & protects cells http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Inside the Cell Nucleus • Directs cell activities • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane • Contains genetic material - DNA Nuclear Membrane • Surrounds nucleus • Made of two layers • Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chromosomes • In nucleus • Made of DNA • Contain instructions for traits & characteristics http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Contains RNA to build proteins http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture • Surrounded by cell membrane • Contains hereditary material Endoplasmic Reticulum • Moves materials around in cell • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins • Found on ribosomes & floating throughout the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Mitochondria • Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Bodies • Protein 'packaging plant' • Move materials within the cell • Move materials out of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Lysosome • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chloroplast • Usually found in plant cells • Contains green chlorophyll • Where photosynthesis takes place http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html