File
advertisement

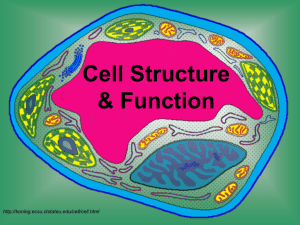
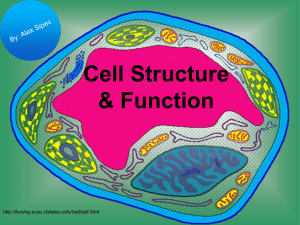
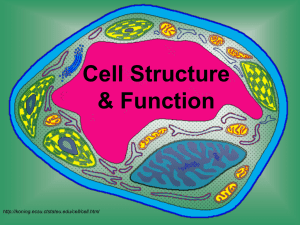
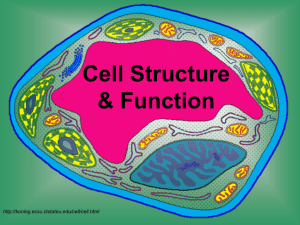
Cell Structure & Function http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Eukaryotic • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes • Most living organisms Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Cell Parts Organelles Cell Membrane • Outer membrane of cell –Contains the cell contents –Controls what gets in and out of the cell –Is selectively permeable http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Nucleus • Directs cell activities- the “Control Center” • Contains genetic material – DNA • Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope ADD THE LABELS Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture • Surrounded by cell membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum • Moves materials around in cell- the “Assembly line or Roads” • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): ribosomes attached to surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins • Found on RER & floating throughout the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Mitochondria • Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use • “Power plant” of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Bodies • Protein “packaging plant” or “shippers” • Coats proteins and other materials so they can move different location inside/outside of cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Apparatus Lysosome • The “Clean-up Crew” • Filled with enzymes that break apart molecules that are small enough for cell to use • Get rid of wastes “garbage disposal” • Destroy old cells/organelles; “suicide sacs” http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Lysosomes • Tay-Sachs disease occurs when the lysosome is missing the enzyme needed to digest a lipid found in nerve cells. – As a result the lipid accumulates and nerve cells are damaged as the lysosome swells with undigested lipid. Centriole • Aids in cell division • Only in animal cells Vacuoles • Large central vacuole in plant cells • Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells • “Storage container” for water, food, wastes, etc. Plant Cell Features • Unique Features of Plant Cells – Plant cells have three structures that animal cells lack: • a cell wall • Chloroplasts • Large vacuole Chloroplast • Found in plant cells • Capture energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy…PHOTOSY NTHESIS! • Green in color because of chlorophyll, a green pigment http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cell Wall • Found in plant and bacterial cells • Rigid, protective barrier that provides support • Located outside of the cell membrane • Made of cellulose (fiber) Quick Review • Which organelle is the control center of the cell? Nucleus • Which organelle holds the cell together? Cell membrane • Which organelles are not found in animal cells? Cell wall, chloroplasts • Which organelle helps plant cells make food? Chloroplasts • What does E.R. stand for? Endoplasmic reticulum Elodea Cells http://carnegieinstitution.org/first_light_case/horn/lessons/images/chlorop.jpg Cheek Cells Stained with Methyl Blue Plasma Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm http://faculty.kutztown.edu/friehauf/science_outreach/cheek_cells_005.jpg