17 3 Domains and Kingdoms
advertisement

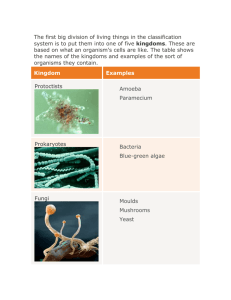
Domains and Kingdoms 17.3 pages 499-503 Today’s Essential Question: What are the similarities and differences among the 6 kingdoms of life? What are the two broadest categories of the classification system???? Domain Kingdom How many domains are there? 3 Domains 1.Bacteria 2.Archea 3.Eukarya Domains are based on the characteristics of 1. Cell Type 2. Cell Structure What are the 2 cell types again??? Domains Archaea and Bacteria are made up of unicellular prokaryotes Eukarya are made up of multiicellular and unicellular organisms that have eukaryotic cells. The difference between Domain Bacteria and Domain Archaea is the cell structure. Domain Bacteria - the cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. Domain Archaea - the cell wall DOES NOT have peptidoglycan Peptidoglycan=Cell wall component. Quick check!! What are the 3 Domains? Bacteria are made up of what kind of cells? Eukarya are made up of what kind of cells? What's the difference between Domain Bacteria and Domain Archaea? How many kingdoms are there??? 6 kingdoms BrainPOP 3 Domains 6 Kingdoms 3 DOMAINS Bacteria Archaea Eukarya 6 KINGDOMS Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi PlantaeAnimalia Take out your graphic organizer and check your answers as we go through the next slides!! Kingdom Archaebacteria Cell Type: Prokaryote # of Cells: Unicellular Cell Wall is Present: NO peptidoglycan Nutrition/Food: Most are heterotrophs, but some are autotrophs Reproduction: Asexual Location: Extreme environments (hot springs, acidic water, salt flats, the Dead Sea) Examples: extremophiles, thermoacidophiles Kingdom Eubacteria Cell Type: Prokaryote # of Cells: Unicellular Cell Wall Present: With Peptidoglycan Nutrition/Food: Most are heterotrophs, some autotrophs Reproduction: Asexual Location: EVERYWHERE!!! Example: Bacteria are on most surfaces. Some cause human diseases, some are helpful. E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus What are the kingdoms of Eukarya??? 1. Protista 2. Fungi 3. Plantae 4. Animalia Kingdom Protista Cell Type: Eukaryote # of Cells: Some are unicellular and some are multicellular Cell Wall: SOME have cellulose in cell wall; some don’t have a cell wall. Nutrition/Food: Some get nutrients by absorption, ingestion, or photo-synthesis; some heterotrophs; some autotrophs Reproduction: Sexual or asexual Examples: Amoeba, green algae, diatoms, euglena, and slime molds Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Fungi Cell Type: Eukaryote # of Cells: Some are unicellular and some are multicellular Cell Wall: Contains chitin Nutrition/Food: all are heterotrophs; digestion takes place outside the body Special Characteristics: Not mobile Reproduction: Asexual and sexual Examples: Mushrooms, yeasts, and molds which grow in shady places. Kingdom Plantae Cell Type: Eukaryote (multicellular) Cell wall: Cellulose Nutrition/Food: Autotrophs Reproduction: Sexual, asexual, or both Location: Land and water Examples: Flowering plants mosses and ferns Land Plants Water Plants Kingdom Animalia Cell Type: Eukaryote Cell Wall: No Cell Wall!! Nutrition/Food: All are heterotrophs; digestion takes place inside the body Special Characteristics: Organized into complex organ systems. Examples: Sponges, anemones, jellyfish, lobsters, insects, spiders, squid, worms, dogs cats, humans Viruses Are they alive?? Viruses are not living so they are not placed in the classification system. Activity!! Take out 4 sheets of paper Stack two sheets of paper so that the back sheet is one inch higher than the front sheet Repeat with two more sheets of paper so that the back sheets are each one inch higher than the sheet in front of it. Bring the bottom of the sheets upward and align the edges so that all of the layers or tabs are the same distance apart. When all tabs are an equal distance apart fold the papers and crease. Open the papers and staple them along the top “mountain” crease. Label the 8 Flaps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Similarities and Differences Among the 6 Kingdoms of Life An Overview of Domains and Kingdoms Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Animalia When you are done put your foldable away and work on the concept map till the bell rings!!