Contact Lenses 2013

Contact Lenses
Clinical Function and Practical Optics
Outline
Basic optics
Soft Lenses
RGP Lenses
Hybrid
Lens Calculations
An optical interlude……
The corneal reflex is brighter in a person with contacts- WHY?
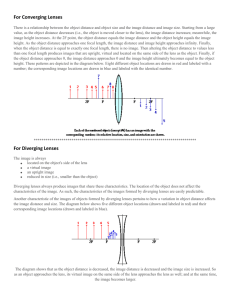
The corneal reflex with a contact lens is a superimposition of reflections from the air/tear interface, the anterior and posterior tear/lens interfaces and the tear/corneal reflex. Because RGP lenses have a higher n, the reflex off of these will be greater (2.5% versus 2.3%).
R={n’-n/n’+n} 2
Air/tear interface
Tear/lens interface
For practical purposes think of each layer as a separate lens in air
AIR
Prelens tear film
Post-lens tear film
Tear/epithelial interface
Nuances of CL power
CLS are treated as thick lenses
– Anterior and posterior surfaces
– Center thickness
– Index of refraction
– Saggital depth/extreme curvatures
F f
Contacts are THICK
LENSES (!)
H H’ fFVP fBVP n n’ t
A1 A2 fT f’T
F’
Tx this way b/c curves are so great….
CL Optics – Effective
Power
Remember to consider vertex distance for all powers > +/- 4.00 D
– Myopes need less power in cls
– Hyperopes need more power in cls
Also have to vertex the cylinder component
– Use optical crosses
Vertex of toric Rx’s
Rx:
+4.00+3.00X180
Fsp= K/ (1+dK)-use this to convert to spectacles
Where d= vertex distance in meters
K= power at the cornea
K= Fsp/1-dFsp- use this to convert from specs to contacts
CL Optics- changes in accommodative demand
Hyperopes have more accommodative demand with glasses
– Pre-presbyopes love cls! (more plus with
CLS)
Myopes have less accommodative demand with glasses
– Pre-presbyopes do not do well (more minus to overcome with CLS)
CL optics –Changes in accommodative convergence
Myopes = increased accommodation with cls , thus will use MORE accommodative convergence
– An esophoric myope will have to use more
NEGATIVE fusional vergence
Hyperopes = decreased accom with cls, will use LESS accommodative convergence
– An exophoric hyperope will have to use more
POSITIVE fusional vergence
CL Optics- Prismatic effects
Correctly fitted cls are always centered on the eye, where glasses induce prism
Plus lenses induce BO prism
–An esophoric hyperope is at a disadvantage with cls b/c there is no prismatic effect to counterbalance
CL Optics- Prismatic Effects
Minus lenses induce BI prism
–An exophoric myope is at disadvantage with cls b/c there is no prism
The lack of prism effect is a benefit for anisometropes.
Prescribing prism in cls
BD prism reduces rotation
toric lenses
- bifocal lenses
The lens thickness is increased toward the base w/o alteration in surface curvature, thus power is more plus towards the base
– Exploited in bifocal designs (rgps)
CL Optics- cl/eye system
Lenses can alter the shape of the cornea
(warpage)
Cornea can alter the shape of lenses
(soft cls)
RGP lenses can mask corneal astigmatism
CL optics-
Magnification Effects
Occurs because the cl is touching the cornea
The power factor of SM formula includes the distance from lens to entrance pupil, changing this to zero causes a change in magnification
Myope will get larger retinal image
Hyperope will get smaller retinal image
The opposite of what happens in glasses !
Magnification Effects
Mag=Original power/vertex power
What is change in RIS switching from glasses to cls for -5.00D at 12mm?
-5/1-.012(5)=-4.72 (vertex)
-5/-4.72=1.06
%change is 6% larger with cl.
CL optics –aberrations and field of view
CL wearers have greater field of view
– No glasses rim!
Spectacles suffer from oblique astigmatism, curvature of field and distortion
– CLS eliminate OA and CF because the lenses are always centered
– CLS eliminate D because they are directly on the eye
Wavefront guided contacts are available now!
Visual Optics – corneal transparency
The air/tear interface has the most refractive power because of change in index, although optically the TF has no power
The stroma is optically significant
The tear film, epithelium, Bowman’s and
Decemet’s are optically insignificant b/c of their CT and parallel surfaces
Corneal Transparency
200 lamellar sheets arranged in parallel, stacked in an anteroposterior direction.
Regular spacing 65nm apart in a lattice
Lattice theory states that the spacing between collagen is sufficiently small that light scattered by individual fibers is mutually destroyed by destructive interference
Loss of Corneal
Transparency d/t CLS
Edema
Infiltrates
Microcysts
Vacuoles
Calcium
Lipid
Dry spots/ dellen
Scarring
Salzmann’s nodules
Vascularization
Dimple Veil
Inclusions (epi)
Trauma
Mechanical
Chemical
Toxic
Osmotic
Hypoxic
Alterations to eye optics
Myopic creep –unexplained
– edema (rgp < scl)
– Steeper k’s and altered pachy readings
– Lowered stromal n (more +)
– endothelium
Change in anterior corneal curvature
– Spectacle blur
Lens flexure and warpage
CLS in vivo variably conform to the cornea
Function of material, K’s and the lens/cornea fitting relationship
Flexure – soft lenses
The most extreme example
– As cornea steepens, net minus power increases for all lenses
Topography shows inferior steepening
Soft lenses cannot be assumed to provide the labeled power
– OR varies depending on flexure
– Dehydration raises n, increasing power
– Steepens with dryness, increasing power
– Cannot confirm power in office
– Tear fluid tonicity/pH/temperature/heat/humidity
Flexure RGPs
Flex to the steepest meridian
– Wtr cornea, lens steepens in the vertical and slightly flattens in the horizontal.
– Measured as toricity with over-K’s
– Calculated effect is to lessen the minus power of the LL in the steepest meridian
Outline
Optics of contacts
Soft Lenses
RGP Lenses
Bifocal Lenses
Fitting procedures
Types of soft lenses
Spherical
Toric truncated prism ballast thin ballast
Aphakic
Extended wear
Bifocal
Bandage lenses
High dK/l
Different polymers
– Ionic high water
– Ionic low water
– Non-ionic high water
– Non-ionic low water
Newer silicone FDA proposal:
Same as above plus sihi designation
Types of soft lenses
Conventional (sphere/toric)
– Keep for a year
– Bifocals
– Higher powers
Disposable (sphere/toric/bifocals)
– Quarterly http://oculuseyehospital.com/images/toric.jpg
– Monthly
– Weekly or Two week
– Daily
Some optical considerations
Fitted flatter than the cornea
– Parallels the periphery and drapes over apex
– 1 or 2 radii of curvature (base curves) only per type of lens are generally available
Why/Why not soft lenses?
Advantages
– Comfortable
– Available
– Easy to fit
– Good for social use
– Better for internal cyl
Disadvantages
– More risk of infection
– Dry out
– Prone to rotation (toric)
– Get dirty quickly
– Noncompliance
– Poor Oxygenation
(older lenses)
– GPC
D
N
I
Bifocals – soft lenses
D
N
D
N aspheric
Simultaneous vision
Soft CL problem
Patient’s Rx is -4.00 -1.00 x 090 all cyl is corneal
Patient cannot afford toric lenses- what do you prescribe?
Soft CL problem
Patient’s Rx: -6.50+2.00x045
K readings: 45.00/46.00@135
-What power CL?
- What bc? (choice is 8.7 or 8.2)
- Say CL OR is -1.00 – 0.50 x 040 what do you do?
- what if lens is rotating 20 degrees nasal
(lars)
- what if the OR is -1.00-1.00 x 090?
Outline
Optics of contacts
Soft Lenses
RGP Lenses
Bifocal Lenses
Fitting procedures
Rigid Gas Permeable
Sphere
Toric
– Bitoric
– Front surface toric
– Back surface toric
Bifocals
– Aspheric
– Segmented
– “Pinhole”
Anatomy of RGP CL
RGP why/why not?
Advantages
– More Oxygen
– Cheaper
– Less surface area
– Better for dry eye
– Masks corneal cyl
– Compliance
– Rare sleeping
– Rare infection
– Superior optics
Disadvantages
– Adaptation
– Chair time
– Misconception
Lacrimal Lens
An rgp interacts with the tears
– Has less effect on the curvature of the cornea (unless poor fit)
– As long as rgp maintains it’s bc, the interface between the lens and the tears is spherical (elimiates astigmatism)
Rgp does not affect internal astigmatism!!
Lacrimal Lens
Steeper contact creates a + power LL
Flatter contact creates a – power LL
For every BC change, and equal and opposite change of power is needed .05mm=0.25D
Lacrimal Lens Problem
CL parameters:
7.50/-6.00/95
Need to steepen BC .5D what is new power?
Need to flatten BC by
.75D what is new power?
Fitting Philosophies
Lid Attachment
– Fit is under the lid
– Moves with blink
– More comfortable
– Less GPC
Interpalpebral
– Wide eyes
– Must have good recovery
Fluorescein Patterns
l l t t t t i i
: : o n
B
C
3 l l l c a i i i r
S p h e i i i t t t s
D
W
T
R a t t t e n g n m i i i l l l
A t t t t t t p a e r n t t t t t t p a e n
E v
Observe apical clearance and insufficient peripheral clearance
On K 95/84
More alignmet with greater
Peripheral clearance
On K 95/76 Bicurve design with a
10.0mm PCR; .5mm wide
Bicurve design with a
10.0mm PCR; 1.0mm wide
Bicurve design with a
9.0mm PCR; .8mm wide
12mm PCR, .8mm wide
Good edge, bit narrow
An increase in edge clearance can be observed
Insufficient edge clearance can be observed
Observe greater clearance
RGP Problem
Rx: -8.50DS
K: 44.50/46.00@78
What power?
What BC?
RGP Problem
Rx:
-3.00 + 6.00 X 090
K:
42.50/47.75@180
What bc?
What power?
Therapeutic RGP fits
Use topography and SLE to assess K
Goal is to fill in irregular part with tears
Pick steepest K as starting point
Just fit the lens and then OR to get power
Bifocal RGP
n http://www.hroptical.com/images/bifocal-contact-design.jpg
d aspheric aspheric
Bifocal RGP fitting
Many different brands
Proprietary v custom
Fitting is specific to brand/ type
Many potential changes
Set realistic expectations
Acknowlegde time investment
THE BASICS
Details of previous cl wear
What are the problems?
When/how do you wear them?
Careful refraction (vertex over +/-4D)
Keratometry or topography
Examination of the cornea, lids, lashes
Dryness…..?
Pupil size (dim/light)
Palpebral Apeture/ characteristics –tight/loose etc.
Iris Diamter
The Basics
Technicians are key to profitability
Insertion/removal training
Lens hygiene teaching
Patient follow up- phone calls
FOLLOW UP IS IMPERATIVE…