iGCSE Biology Section 2 lesson 2
advertisement

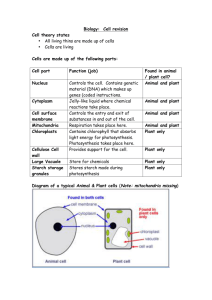
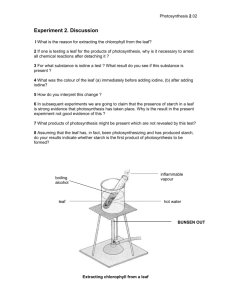
IGCSE BIOLOGY SECTION 2 LESSON 2 Content Section 2 Structures and functions in living organisms a) Levels of organisation b) Cell structure c) Biological molecules d) Movement of substances into and out of cells e) Nutrition f) Respiration g) Gas exchange h) Transport i) Excretion j) Coordination and response Content Lesson 2 e) Nutrition Flowering plants 2.15 describe the process of photosynthesis and understand its importance in the conversion of light energy to chemical energy 2.16 write the word equation and the balanced chemical symbol equation for photosynthesis 2.17 understand how varying carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity and temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis 2.18 describe the structure of a leaf and explain how it is adapted for photosynthesis 2.19 understand that plants require mineral ions for growth and that magnesium ions are needed for chlorophyll and nitrate ions are needed for amino acids 2.20 describe experiments to investigate photosynthesis, showing the evolution of oxygen from a water plant, the production of starch and the requirements of light, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll Content Lesson 3 e) Nutrition Humans 2.21 identify sources and describe functions of carbohydrate, protein, lipid (fats and oils), vitamins A, C and D, the mineral ions calcium and iron, water and dietary fibre as components of the diet 2.22 describe the structures of the human alimentary canal and describe the functions of the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and pancreas 2.23 understand the processes of ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion 2.24 explain how and why food is moved through the gut by peristalsis 2.25 understand the role of digestive enzymes, to include the digestion of starch to glucose by amylase and maltase, the digestion of proteins to amino acids by proteases and the digestion of lipids to fatty acids and glycerol by lipases 2.26 understand that bile is produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder, and understand the role of bile in neutralising stomach acid and emulsifying lipids Flowering plants AUTOTROPHS –organisms that can produce complex organic compounds from simple inorganic molecules. They are the PRODUCERS in a food chain. Flowering plants AUTOTROPHS –organisms that can produce complex organic compounds from simple inorganic molecules. They are the PRODUCERS in a food chain. HETEROTROPHS – organisms that cannot produce their own food, but acquire complex organic molecules by consuming plants or other animals. Photosynthesis LIGHT form the Sun CARBON DIOXIDE from the air WATER from the soil Photosynthesis LIGHT form the Sun CARBON DIOXIDE from the air WATER from the soil GLUCOSE for biomass and energy OXYGEN released to the atmosphere Photosynthesis LIGHT ENERGY CHEMICAL ENERGY Photosynthesis Light Carbon dioxide + water Glucose + oxygen Chlorophyll Photosynthesis Light 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Chlorophyll Photosynthesis Light 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Chlorophyll Some of the glucose produced is used in respiration by the plant itself, but most of it is converted into insoluble STARCH for storage in stems, roots and leaves. Factors affecting photosynthesis Factors affecting photosynthesis 1. Temperature 2. CO2 concentration 3. Light intensity Factors affecting photosynthesis Rate of photosynthesis Temperature Temperature Factors affecting photosynthesis Temperature Rate of photosynthesis As temperature rises, so does the rate of P/S. Here temperature is limiting the rate. Temperature Factors affecting photosynthesis Rate of photosynthesis Temperature As temperature approaches 45oC, enzymes start to denature and rate of P/S falls to zero Temperature Factors affecting photosynthesis Carbon dioxide concentration Rate of photosynthesis As CO2 increases, so does the rate of P/S. At this point [CO2] is the limiting factor. CO2 concentration Factors affecting photosynthesis Rate of photosynthesis Carbon dioxide concentration Increasing [CO2] has no further effect. The limiting factor must now be sunlight or temperature. CO2 concentration Factors affecting photosynthesis Light Intensity Rate of photosynthesis As light intensity increases, so does the rate of P/S. At this point light intensity is the limiting factor. Light intensity Factors affecting photosynthesis Rate of photosynthesis Light Intensity Increasing light intensity has no further effect. The limiting factor must now be [CO2] or temperature. Light intensity Plant mineral requirements Plant mineral requirements • For healthy growth plants also need certain minerals Plant mineral requirements • For healthy growth plants also need certain minerals • Farmers use fertilisers to add minerals to soil. Plant mineral requirements • For healthy growth plants also need certain minerals • Farmers use fertilisers to add minerals to soil. • Natural fertiliser = dead plants and animals and organic waste. Plant mineral requirements • For healthy growth plants also need certain minerals • Farmers use fertilisers to add minerals to soil. • Natural fertiliser = dead plants and animals and organic waste. • Artificial (manufactured fertiliser) = made in factories from chemicals. Plant mineral requirements Element Needed for Nitrogen (in nitrates) Proteins for growth of stems and leaves Phosphorus (in phosphates) Healthy roots Potassium Healthy leaves and flowers Healthy growth of new stems Making chlorophyll Calcium Magnesium Plant mineral requirements Fastgro fertiliser NPK 20:50:30 Elements- Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium Ratio of the elements in the fertiliser Leaf adaptations Leaf adaptations Leaf adaptations Broad Thin Flat Internal air spaces Leaf adaptations Large surface area Broad Thin Flat Internal air spaces Leaf adaptations Leaf adaptations Stomata (stoma) on the undersurface of leaves that allow CO2 to diffuse in and O2 to diffuse out. Water is also lost through the stomata by transpiration. Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Waxy cuticle – stops too much water from just evaporating away from the leaf. Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Waxy cuticle – stops too much water from just evaporating away from the leaf. Plants in hot, dry or windy conditions have a thicker wax layer. Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Palisade layer– most of the chloroplasts are found here, containing chlorophyll, the pigment needed for photosynthesis Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Spongy mesophyll layer – less chloroplasts here. Note the large number of air spaces. Leaf adaptations Cross section through a leaf Lower epidermis – note the presence here of stomata (tiny pores surrounded by guard cells). Photosynthesis experiments Light source Photosynthesis experiments Bubbles of oxygen gas being produced Light source Variable: distance of the light source (= intensity) away from the pond weed. Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Variegated leaves Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Chlorophyll No chlorophyll Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Photosynthesis experiments Testing leaves for starch Positive starch result where the chlorophyll has been extracted (the green parts) Negative starch result in variegated (white) part of leaf where chlorophyll is absent. Photosynthesis experiments Carbon dioxide requirements Geranium plant Soda lime Photosynthesis experiments Carbon dioxide requirements Leave the plant for a couple of days – the soda lime should absorb all the CO2 in the jar Geranium plant Soda lime Photosynthesis experiments Carbon dioxide requirements After a couple of days there should be no starch in the leaves. Geranium plant Soda lime End of Section 2 Lesson 2 In this lesson we have covered: Nutrition – flowering plants