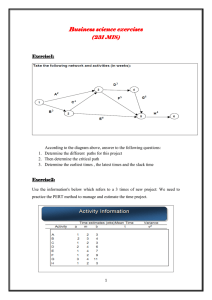
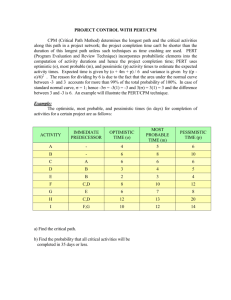
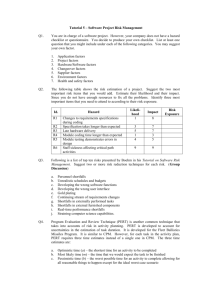
Activity Network Diagram
advertisement

Activity Network Diagram Brian McAluney OISM 470W PowerPoint Training Presentation Overview • • • • • • • • Definition of an Activity Network Diagram History Basic Terms How can it be used in your organization? How the diagram works Example Activity Network Diagram Exercise Summary Definition of an Activity Network Diagram • • • Also known as the Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) or Critical Path Diagram Tool used to control the length of projects Takes into account many aspects of projects: task times, slack times, critical tasks, etc. Definition of an Activity Network Diagram (cont.) • • Designed for research and developmenttype projects Determines a probability distribution for a project History • • • Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense First used as a management tool for military projects Adapted as an educational tool for business managers Basic Terms Basic Vocabulary of the PERT Diagram: • Activity – part of the project represented by an arrow or line • Best Estimate(B) – earliest completion time • Critical path(CP) – the most time consuming path through the diagram with no slack time • Earliest Start Time(EST) – earliest possible time for an activity to begin • Network – the project shown graphically • Most likely estimate(M) – length of time probably needed Basic Terms (cont.) • • • • • Expected Time(ET) – the average duration time Event – represents the start or finish of one or more events (shown as a circle, square, or other symbol) Latest Start Time(LST) – latest time an activity can begin and still be completed before the next activity Slack Time – latest start time minus earliest start time for an activity Worst estimate(W) – pessimistic time estimate How can it be used in your organization? Brainstorm ideas of where activity network diagrams could be utilized in your business practices… How can it be used in your organization? • • • Finding minimum completion times Determining maximum completion times Value of time for each step in the project • • Assigning specified times for parts of the project Creates a realistic schedule for the company How the diagram works Basic Rules: • • All preceding activities must be completed before the project can begin The arrows represent the logical precedence of the project How the Diagram Works (Cont.) Procedure for development: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify all activities and relationships among them Sketch the diagram Estimate the times for each activity, or node, in the diagram Determine the critical path Evaluate the diagram for milestones and target dates in the overall project Example Activity Network Diagram A D C B F E Exercise Given the following formula, data, and diagram, determine the critical path and the expected time of the project. Time is represented in days ET = 4(M) + 1(B) + 1(W) / 6 A = 2, B = 3, C = 1, D = 4, E = 3, F = 2, G = 2, H = 1, and I = 3 Exercise (cont.) A D C B G F E I H Begin the Analysis Remember your steps for PERT diagrams: Using the given diagram, list all the steps Determine task times Determine relationships between the tasks Find the earliest start time Find the latest start time Determine slack and the critical path Summary Review the exercise Advantages of PERT Disadvantages of PERT Odds and Ends Review the Exercise Did you arrive at the correct answer? Do these answers make sense? Advantages of PERT Diagrams • • • • • Projecting plans before they begin Helps to separate planning and scheduling functions of a project Controls projects Clarifies maintenance of the plan Shows dependency of different aspects of the project Advantages of PERT Diagrams • • • • Allows for concentration on the steps themselves and not the time required for each Represents a realistic schedule Focuses attention on critical aspects of the plan Changes can be made easily in the project Disadvantages of PERT Diagrams • • Cannot handle all specific problems that arise in each step of the project Different graphical representations can be made easier in other types of control processes Odds and Ends Activity Network Diagrams have many more advantages than disadvantages They are used in all types of businesses The topics that were covered should act as the key in helping you lead your company in their next business project Works Cited Bedworth, David D. and James E. Bailey. Integrated Production Control Systems. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1987. “PERT”. Internet. http://www.uwf.edu/coehelp/studentaccount s/rnew/perthome.html. 12 February 2001. Stamatis, D.H. TQM Engineering Handbook. New York: Marcel Decker, Inc. , 1997.