Soil Texture & Fertility Lecture
advertisement

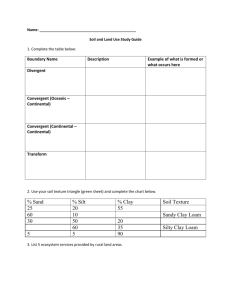
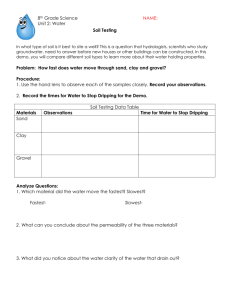
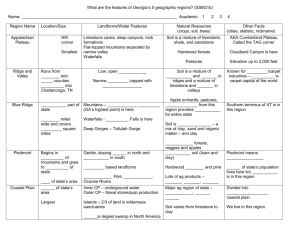
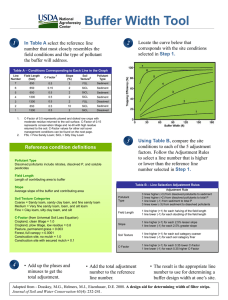
Material that supports plant life O= Organic layer= humus A= Topsoil, mixture of organic & minerals E= Eluvial (leached) mineral horizon B= Subsoil: accumulation of organic &/or inorganic matter C = Parent material, un-weathered Climate Topography(relief) Time Organisms Parent material Gravitational water: water that moves through soil under the influence of gravity. Field capacity: water held in the soil by capillary forces, available to plant Hygroscopic water: water that is adsorbed by soil particles, unavailable to plant Adsorbed: held in place, attached to Inorganic: Synthesized from minerals Organic: from plant and animals Quick release Slow release Short term plant growth Long term soil health Excess nutrients : Human harm: methemoglobinemia (Blue Baby Syndrome) Environmental harm: eutrophication 3 cm 1 cm Smaller particles have a 54cm2 162cm2 Higher chemical reactivity: clay is (-) attracts (+) Greater surface area: Nutrients: Mg+, Ca+, K+, Na+ Non-nutrients : H+ Higher water holding capacity: water is polar Is it 33% for all separates? What soil type is 18% clay, 40% sand, 42% silt? This point is where each separate has equal influence How much sand is required to get its name in a class? Last word is most important Does more clay mean Gravitational water: water that moves through soil more available water? under the influence of gravity. Plants can survive withField capacity: water held in the soil by capillary forces 50% of FC. Hygroscopic water: water that is adsorbed by soil particles Intensive monoculture farming Row crops, altering the landscape, weed free Physical damage: Erosion Compaction: reduce aeration Chemical damage Salinization Conversion Desertification Drummer Silty, clay loam Casa Grande Sandy Loam Houston Black Black clay Myakka Fine sand Drummer Silty, clay loam Casa Grande Sandy Loam Houston Black Black clay Myakka Fine sand What soil type would most likely need to have more fertilizer applied to it? Which farmer will need to irrigate their crops most often? Which farmer will most likely have to face salinization problems? Which farmer would most likely encounter gully or sheet erosion? Which farmer would most likely have waterlogged soil if there was a heavy rainfall? Which farmer has the best developed “O” horizon? Which farmer would most likely have the most acidic soil?