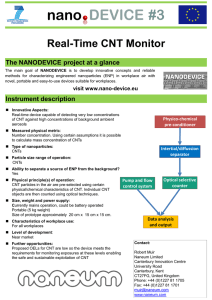
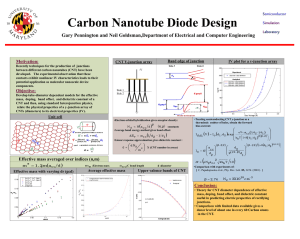
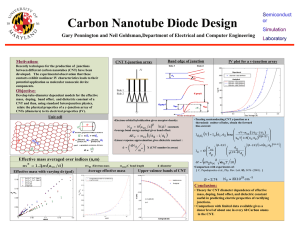
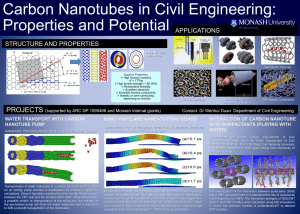
Electron Transport in Carbon nanotubes
advertisement

Numerical study of transport properties of carbon nanotubes • Dhanashree Godbole • Brian Thomas Summer Materials Research Training Oakland University 2006 Overview CNT: The material of the future Structure of Graphene and CNT’s Carbon nanotubes: bands and DOS Infinite CNT’s to quantum dots Quantum dots: what and why Numerical results: • Coulomb Blockade • Kondo effect Why Carbon nanotubes? Amazing electronic and physical properties • Space and mass saving • Strength and durability The Graphene Layer The graphene sheet and its band structure (n,m) CNT: band structure and DOS 1/ 2 a Eq q ka 2 ka (k ) t 1 4 cos cos 4 cos n 2 2 ka , q 1,...,2n , DOS An Infinite CNT to finite CNT Finite CNT to Quantum Dot Artificial atoms Transfer of a single electron charge Coulomb Blockade Increased resistance No conduction Conduction Kondo Effect Low-temp. increase in resistance Kondo resonance creates existence of a new state Numerical Results: One Level QD -2 0 1 2 1.0 1.0 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.0 0.0 2 for the electron G(e /h) One available state -1 -2 -1 0 1 2 1.0 1.0 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 -2 -1 0 1 2 2 G(e /h) Vg -3 0.0 0 Vg 1 -1 0 1 2 2 2 -1 G(e /h) -2 -2 0.0 0.0 -3 -2 -1 0 Vg 1 2 CNT as a Quantum dot Carbon nanotubes have two available states for electrons to propagate in 2.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.5 1.2 2 G(2e /h) G(2e2/h) 1.4 1.0 0.8 1.0 0.5 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.0 -1.6 -1.4 -1.2 -1.0 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0.0 0.2 Vg -3 -2 -1 Vg 0 1 CNT as Quantum dot B field kills Kondo effect…why? 1.0 2 G(2e /h) 2 G(2e /h) 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 0.0 -3 -2 -1 Vg 0 1 -3 -2 -1 0 Vg 1 2 Experimental Results b 0.0 U=U'=0.5 t'=0.2 t"=0.0 orb=0.2 a 2.0 1.5 1.0 1.0 1.5 3.0 B 0.5 G(2e2/h) sp=0.04 Esp U=U'=0.5 t'=0.2 t"=0.0 E=0.035 Eorb orb=0.2 0.5 sp=0.04 -2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 0.0 1.0 Vg Delft University - Netherlands Prof. Leo Kouwenhoven group -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 Vg 0.5 1.0 1.5 Conclusion What we learned • Basics of quantum mechanics and its applications in condensed matter physics • First time using computer code and programming with FORTRAN • Energy dispersion relations and their use in research of CNTs • Quantum Dots and the use of CNTs as QDs • Modeling and using numerical operations to represent real systems.