Tetrapods & Amniotes
advertisement

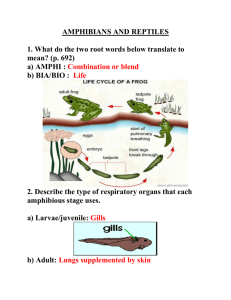
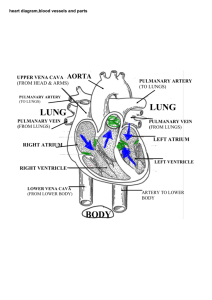
Tetrapods & Amniotes Amphibians + Reptiles Tetrapods (gnathostomes that have limbs)= amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals • Derived from the lung-fish branch of lobe-finned fish Characteristics of Tetrapods: • 2 pairs of limbs WITH DIGITS – Support weight, provide mobility on land Amphibians: --Reproduction is tied to water --Activity is restricted to aqueous or humid/damp/moist environments 3 clades: • Urodeles = salamanders • Anurans = frogs and toads • Apoda = ceacilians – – – – Legless, almost blind, Look segmented like earthworm (but with distinct head) Live in soil (tropical) From legged ancestor Amphibian: common characteristics • damp habitats • External fertilization in most • Eggs require moisture (sometimes retained) – Susceptible to drying out • Lungs + Skin for gas exchange – Positive pressure/buccal breathing • 3 chambered heart with double circulation Gas Exchange Lungs: • Infoldings with many pockets – Localized w/in body circulatory system – Thin layer of tissue between blood and air SKIN • Significant contribution to gas exchange • Permeable to gas (good) = permeable to water (bad) • Very vascular • Relative importance of skin varies with activity/O2 demand of individual. Ventilation (i.e., breathing) Inhalation: 1. Oral Cavity Expansion w/ nares open – “sucks” air into oral cavity 2. Oral cavity contracts w/ nares closed – Air “pumped”/pushed into lungs Exhalation 1. Elastic recoil of lungs + compression of muscles of body wall – Air pushed out Double Circulation • Two circuits/loops of blood pumped by a single heart – Lungs (pulmonary) • Picks up O2, removes CO2 – Rest of body (systemic) • Delivers O2, picks up CO2 • Single pump ensures ‘evenness’ of both circuits • Repressurizes blood after it has picked up O2 in the pulmonary circuit Amphibians: Heart and Blood Flow • 3 Chambered heart = 2 atria + 1 ventricle • R atrium = venous blood from muscle and organs/systemic • L atrium = venous blood from lungs and skin (pulmocutaneous circuit) – Ventricle pressurizes blood/pumps out • Ridge (spiral valve) in ventricles prevents most mixing of blood. • Blood flow to lungs “stops” during diving Osmoregulation: • • • • Freshwater Net gain of water Large quantities of dilute urine water can be re-absorbed across the urinary bladder wall. Amniotic Egg • • • • • Amnion: encloses embryo in fluid that cushions/protects, Chorion: gas exchange Yolk sac: stores/transfers nutrients Allantois—waste storage and some gas exchange These are extraembryonic (i.e., not part of the embryonic tissue) Amniotes • Amniotic Egg – Egg can be retained – Egg can be retained and no shell, but still has 4 layers • Also ribs that assist in negative pressure breathing Reptile Clade: Tuataras, lizards, snakes, turtles, crocodilians, & birds • Scales w/ keratin (makes skin relatively impermeable) • Shelled, amniotic eggs • Internal fertilization • Clawed • Mostly ectothermic – Regulate body temp – 10% of the calories required by endotherms • Birds are endothermic 3 Clades TURTLES: • Shell (carpace + plastron), fused to ribs and clavicles • Can breath through GI tract LEPIDOSAURS (tuataras + lizards + snakes, later two are squamates) Crocodilians (alligators, crocodiles, and caimen) • Breath air through upturned nostrils • Warm regions Reptile Heart Double Circulation Typically • 2 atria + 1 partially divided ventricle – Very little mixing of blood In crocodiles • ventricle is completely divided – aorta are joined by a passageway – allows blood to be shunted/bypass pulmonary circuit when diving Ventilation • Negative pressure • Expansion of ribcage