America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition)
advertisement

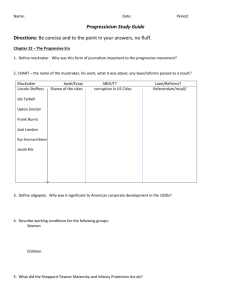
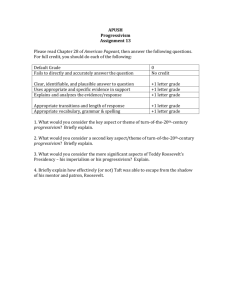
America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Tindall/Shi Chapter 23 - "Making the World Over": The Progressive Era I. Elements of reform o A. Diverse goals of progressivism 1. An element of conservatism in progressivism 2. Urban industrial ills required government responses o B. The varied sources of progressivism 1. Populism 2. The Mugwumps 3. Socialism o C. The muckrakers II. The main features of progressivism o A. Greater democracy 1. Direct primaries 2. The initiative, referendum, and recall 3. Popular election of senators o B. The “gospel of efficiency“ 1. Frederick W. Taylor and The Principles of Scientific Management 2. Shorter ballots 3. New ideas for municipal government—commission system and the city-manager plan 4. Robert La Follette and the “Wisconsin idea“ o C. Corporate regulation 1. Alternative solutions to the problems of big business 2. The trend toward regulation o D. Social justice 1. Labor laws a. Child labor b. The Supreme Court and state labor laws 2. Prohibition o E. Public service functions of government o F. Progressivism and religion III. Roosevelt’s progressivism—first term o A. Trusts 1. Roosevelt thought effective regulation better than attempts to restore competition 2. Decision in United States v. E. C. Knight and Company (1895) held manufacturing to be intrastate activity 3. Supreme Court ordered the Northern Securities Company dissolved o B. Coal strike of 1902 1. Workers struck for more pay and fewer hours 2. Mine owners closed mines 3. Roosevelt threatened to take over the mines o C. More trust cases 1. Overall, brought about 25 anti-trust suits 2. Swift and Company v. United States (1905) o D. Anti-trust and regulatory legislation of 1903 1. Creation of the Bureau of Corporations 2. The Elkins Act IV. Roosevelt’s progressivism—second term o A. The election of 1904 o B. The Hepburn Act of 1906 o C. Food and drug regulations 1. Campaign against patent medicines 2. Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle and meat packers 3. The Meat Inspection Act (1906) 4. The Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) o D. Conservation 1. Origins tied to the sportsman-naturalist a. Roosevelt a model 2. Effect of state conservation laws 3. Gifford Pinchot 4. Reclamation Act o E. The election of 1908 1. Roosevelt handpicked Taft 2. Taft’s victory over Bryan America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Tindall/Shi V. Taft’s progressivism o A. Taft’s early career o B. Tariff reform 1. Taft wanted lower tariff 2. Tariff raised many rates 3. Fearful of party split, Taft backed new tariff o C. Ballinger-Pinchot controversy 1. Chief of Forestry Pinchot went public with accusations against Secretary of the Interior Ballinger 2. Pinchot fired by Taft for insubordination 3. Taft’s image as progressive tarnished o D. The Taft-Roosevelt break 1. United States Steel suit 2. Review of accomplishments of Taft’s administration 3. In Republican primary for 1912, Taft controlled party machinery 4. Roosevelt and the Progressive party VI. The election of 1912 o A. The rise of Woodrow Wilson o B. Campaign 1. Roosevelt shot 2. Taft had no chance 3. Roosevelt’s New Nationalism a. Influence of Herbert Croly b. Hamiltonian means to achieve Jeffersonian ends 4. Wilson’s New Freedom a. Influence of Louis Brandeis b. Restoration of an economy of small-scale competitive units o C. Election figures—victory for Wilson o D. Significance of the election of 1912 1. A high-water mark for progressivism 2. Brought Democrats back into effective national power 3. Brought southerners back into national and international affairs 4. Altered the character of the Republican party VII. Wilsonian reform o A. Relied more on party politics than popular support to pass reforms o B. Underwood-Simmons Tariff (1913) 1. Lowered average duty by about one-fifth 2. To replace lost revenue, began income tax o C. The Federal Reserve Act (1913) 1. Allowed reserves to be pooled 2. Made currency and bank credit more elastic 3. Lessened concentration of reserves in New York o D. Wilson and trusts 1. The Clayton Anti-Trust Act of 1914 a. Outlawed price discrimination, “tying“ agreements, interlocking directorates in large corporations b. Prevented corporations from buying up stock of competitors to gain control of the market c. Exempted farm labor organizations 2. Federal Trade Commission o E. Wilson and social justice 1. Little legislation before 1916 o F. Progressivism for whites only 1. Wilson’s racial attitudes 2. Spread of uncompromising racists in Wilson’s government o G. A resurgence of progressivism 1. Wilson added to his progressive record to form broad base of support for 1916 election 2. Farm reforms (credit and education) 3. Federal Highways Act (1916) subsidized state highway departments 4. Labor reform a. Keating-Owen Act (1916) excluded from interstate commerce goods manufactured by children under fourteen b. Adamson Act (1916) provided for eight-hour day for railroad workers o H. Under Wilson, progressivism became a movement for positive government VIII. The limits of progressivism o A. Disenfranchisement of blacks o B. Decisions made more by faceless policy makers o C. Decline in voter participation