015_MLP_ENG
advertisement

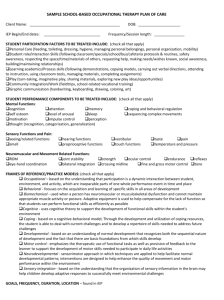
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems Instructor Serial/Semester Location Start/Finish Time Date LESSON OBJECTIVE Performance: Describe the meaning, levels and components of a sensation. Conditions: The student will be presented a powerpoint presentation by the instructor and will have all necessary references made available to him/her. Standard: 1. The student will be expected to describe the below information included within the teaching points to the instructor at the end of the lesson and in a written exam. TEACHING POINTS 1. Define sensation. 2. Describe somatic sensations. 5. 6. 3. Describe the motor cortex maps in the cerebral cortex. 7. 4. Describe the somatic sensory pathways. 8. Describe the somatic motor pathways. Describe the integrative functions of the cerebrum. Describe the homeostatic imbalances associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Define the medical terminology associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGY Interactive Lecture Method: Instructor and Print (including PowerPoint Presentation) Media: Classroom Environment: OTHER LESSON SPECIFICATIONS Knowledge Lesson Type of Lesson: 1/50 Ratio: Resources: Power point handouts. End of Lesson Test: None Minutes Instructional Time: 290 Reference(s): Tortora, Grabowski: Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition. Chapter 15. LESSON PLAN APPROVAL Signature of Standards Officer Date AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems INTRODUCTION Allocated Time: Review: 5 Minutes You have had previous lectures on anatomy and physiology during the Combat medic course, this lecture will built upon what you have already learned. Objective: This chapter introduces the meaning, levels and components of a sensation. Receptors are studied in terms of classification and adaptation. The somatic sensations examined include tactile sensations, thermal sensations, pain sensations, and proprioceptive sensations. The study of the somatic sensory pathways follows with the spinal sensory tracts examined in detail. Somatic motor pathways are covered with a comparison of direct and indirect motor pathways. The chapter concludes with a discussion of the integrative functions of wakefulness, sleep, learning and memory. Homeostatic imbalances included are spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and Parkinson's disease. Clinical applications included are analgesia: relief from pain, tertiary syphilis, paralysis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and damage to basal ganglia and the cerebellum. Importance: Nurses work in different health care setting so it is important to gain an understainding of this subject as it will apply to clinical setting. Fit: This is the fifteenth chapter on anatomy and physiology. Approach: You will be presented the subject in a lecture format and will be tested using a written exam at a later date. Control Statement: If you have any questions during the lesson please feel free to ask. BODY 1. Teaching Point: Define sensation. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over sensation. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 1. Provide an overview of the three basic functions of the sensory, motor, and integrative systems of the nervous system. 2. Define and compare sensation and perception. Sensory Modalies 1 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems 3. Define sensory modality, give examples, and indicate the unique relationship to impulses transmitted along specific pathways. The Process of a Sensation 4. Generally examine the four requisite events for a stimulus to become a sensation. Sensory Receptors Types of Sensory Receptors 5. Describe the types of receptors in terms of association with general or special systems, location, and stimulus type. Adaptation in Sensory Receptors 6. State what is meant by adaptation of receptors and provide examples of slow and rapidly adapting receptors. 2. Teaching Point: Describe somatic sensations. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over the somatic sensations. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 7. Note the general location and nature of somatic receptors. 8. Identify the cutaneous sensation modalities. Tactile Sensations 9. 10. 11. 12. Identify the tactile sensations, how they are detected, and the receptors involved. Describe the touch receptors and how they respond to a stimulus. Define and compare the sensations of pressure and vibration. Define and compare the sensations of itch and tickle. Thermal Sensations 13. Identify the thermal sensations, their receptors, and the receptor locations. Pain Sensations 14. Describe the function of pain. 15. Identify the pain receptors, their location, and what stimulates them. Types of Pain 2 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems 16. Distinguish between fast and slow pain and among superficial somatic, deep somatic, and visceral pain. Localization of Pain 17. Discuss the localization of pain, including referred pain and phantom limb pain. 18. Describe how analgesic drugs provide relief from pain. Proprioceptive Sensations 19. Identify the types of proprioception and indicate their neural pathways, areas of CNS processing, and function. Muscle Spindles 20. Describe the architecture and reflexive operation of the muscle spindle apparatus with their neural links to the CNS and skeletal muscle. Tendon Organs 21. Describe the architecture and reflexive operation of the tendon organs with their neural links to the CNS and skeletal muscle. Joint Kinesthetic Receptors 22. Discuss the location, nature, and purpose of joint kinesthetic receptors. 3. Teaching Point: Describe the motor cortex maps in the cerebral cortex. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over the motor cortex maps in the cerebral cortex. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 23. Examine the somatic sensory and somatic motor maps in the cerebral cortex. 24. Demonstrate the relationship of the proportion of sensory representation on the cortical surface with receptor density on the body surface. 25. Describe the relationship between the number of motor units going to an area of the body and the amount of surface area of the primary motor cortex that controls that body part. Knowledge Lesson: Skill Lesson: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 4. Teaching Point: Describe the somatic sensory pathways. Minutes Allocated Time: 3 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems We will now go over the somatic sensory pathways. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 26. Discuss the general neuronal components of the somatic sensory pathways from receptors to cerebral cortex. Posterior Column-Medial Lemniscus Pathway to the Cortex 27. Discuss the neuronal components and functions of the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway. Anterolateral Pathways to the Cortex 28. Discuss the neuronal components and functions of the anterolateral pathway. Somatic Sensory Pathways to the Cerebellum 29. Describe the neural paths that lead from receptors to the cerebellum and how they are structurally different from the spinothalamic tracts. 30. Discuss how Treponema pallidum impacts the operation of the spinocerebellar tract. 5. Teaching Point: Describe the somatic motor pathways. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over the somatic motor pathways. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 31. List the neural circuits termed the somatic motor pathways. Organization of Upper Motor Neuron Pathways 32. Differentiate between direct motor pathways and indirect motor pathways. 33. Describe the difference in paralysis symptoms with damage to upper versus lower motor neurons. Direct Motor Pathways 34. Illustrate the neural pathway segments of three major representations of the descending pyramidal-corticospinal tract and indicate their distinctive functions. 35. Describe the effects of ALS on the motor pathway neurons. Indirect Pathways 4 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems 36. List the central nervous system components that are involved with processing of motor information of the extrapyramidal pathways and the tracts of the spinal cord where they connect. Modulation of Movement by the Basal Ganglia 37. Explain how the basal ganglia are involved in motor responses. 38. Examine the effects of Parkinson disease and Huntington disease on the basal ganglia. Modulation of Movement by the Cerebellum 39. Discuss the four principle operations of the cerebellum in the coordination of conscious and subconscious skilled muscle movements. 40. Describe ataxia and intention tremors as symptoms of damage to the cerebellum. 6. Teaching Point: Describe the integrative functions of the cerebrum. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over the integrative functions of the cerebrum. Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 41. List the major integrative functions of the cerebrum. Wakefulness and Sleep 42. Describe the role of the hypothalamus in the wakefulness and sleep cycle. The Role of the Reticular Activating System in Awakening 43. Describe the role of the reticular activating system in arousal and consciousness. Sleep 44. Discuss the characteristics of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and the difference compared to the stages of non-REM sleep. Learning and Memory 45. Show how learning and memory are related and the areas of the brain that are though to be involved. 46. Examine the theoretical mechanisms of short-term and long-term memory. 7. Teaching Point: Describe the homeostatic imbalances associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Minutes Allocated Time: 5 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems Introduction: We will now go over the homeostatic imbalances associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson Powerpoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 47. Discuss spinal cord injury and Parkinson disease in terms of cause, symptoms, and prognosis. 8. Teaching Point: Define the medical terminology associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Minutes Allocated Time: We will now go over the medical terminology associated with the sensory, Introduction: motor and integrative systems. Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Please follow along with your handouts and take notes. Skill Lesson PowerPoint presentation with associated handouts. Learning Support: 48. Define the medical terminology associated with the sensory, motor, and integrative systems. Knowledge Lesson: Skill Lesson: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. END OF LESSON TEST Allocated Time: Instructions: Test Questions or Performance Expected: Test Key: 0 Minutes You will tested on this subject at a later date. You will be expected to review and study the material taught in this section in order to pass the associated written test. If you have difficulty with the material please see me so we can review together. CONCLUSION Allocated Time: Summary: 5 Minutes Review and re-emphasize the difficult Teaching Points below. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6 Define sensation. Describe somatic sensations. Describe the motor cortex maps in the cerebral cortex. Describe the somatic sensory pathways. Describe the somatic motor pathways. AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Sensory, Motor and Integrative Systems 6. 7. 8. Describe the integrative functions of the cerebrum. Describe the homeostatic imbalances associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Define the medical terminology associated with the sensory, motor and integrative systems. Closing Statement: Nurses work in different health care setting so it is important to gain an understainding of this subject as it will apply to clinical setting. Re-motivating Statement: You will be able to utilize this information taught today in all clinical settings. 7