Ch.11
advertisement

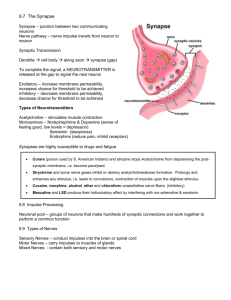
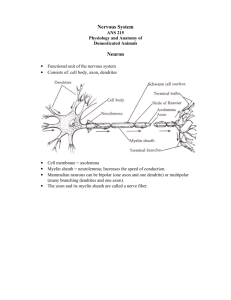
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 11 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 11-1 Chapter 11 Nervous System II Meninges • membranes surrounding CNS • protect CNS • three layers • dura mater – Hard mother, outer most layer •Double layer with fluid and blood vessels •Contains large veins – dural sinuses • arachnoid mater – weblike •Subarachnoid -CSF • pia mater – inner, delicate mother 11-2 Meninges of the Spinal Cord 11-3 Ventricles • interconnected cavities • within cerebral hemispheres and brain stem • continuous with central canal of spinal cord • filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) • lateral ventricles • third ventricle • fourth ventricle • cerebral aqueduct 11-4 Cerebrospinal Fluid • secreted by choroid plexus- within the lateral ventricles, interventricular foramen, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, and fourth ventricle. Then flows to the central canal of spinal cord, and subarachnoid space. CSF is reabsorbed by granulations that penetrate the inner dura mater ( Dural Sinus). • completely surrounds brain and spinal cord • clear liquid • nutritive and protective • helps maintain stable ion concentrations in CNS 11-5 Spinal Cord Structure • extends foramen magnum to 2nd lumbar vertebra 11-6 Cross Section of Spinal Cord 11-7 Spinal Cord Functions • center for spinal reflexes • conduit for nerve impulses to and from the brain 11-8 Reflex Arcs Reflexes – automatic, subconscious responses to stimuli 11-9 Knee-jerk Reflex • helps maintain posture 11-10 Withdrawal Reflex • protective 11-11 Crossed-Extensor Reflex • flexor muscles contract • flexor muscles on opposite side inhibited • extensor muscles on opposite side contract for balance 11-12 Tracts of the Spinal Cord • Ascending tracts conduct sensory impulses to the brain • Descending tracts conduct motor impulses from the brain to motor neurons reaching muscles and glands 11-13 Ascending Tracts • fasciculus cuneatus • lateral spinothalamic 11-14 Corticospinal Tract 11-15 Brain Functions • interprets sensations • determines perception • stores memory • reasoning • makes decisions • coordinates muscular movements • regulates visceral activities • determines personality Major Parts • cerebrum • two cerebellar hemispheres • diencephalon • brain stem • cerebellum 11-16 Brain Development Three Major Vesicles 1. Forebrain 2. Midbrain 3. Hindbrain Forebrain (prosencephalon) • anterior portion (telencephalon) • cerebrum • basal ganglia • posterior portion (diencephalon) • thalamus • hypothalamus • posterior pituitary • pineal gland 11-17 Brain Development Midbrain (mesencephalon) • midbrain Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) • anterior portion (metencephalon) • cerebellum • pons • posterior portion (myelencephalon) • medulla oblongata 11-18 Structure of Cerebrum • corpus callosum • connects hemispheres • convolutions • bumps or gyri • sulci • grooves • longitudinal fissure • separates hemispheres • transverse fissure • separates cerebrum from cerebellum 11-19 Lobes of Cerebrum • Frontal • Parietal • Temporal • Occipital • Insula 11-20 Functions of Cerebrum • interpretation • initiating voluntary movements • storing memory • retrieving memory • reasoning • center for intelligence and personality 11-21 Functional Regions of Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex – thin layer of gray matter that constitutes the outermost portion of cerebrum; contains 75% of all neurons. 11-22 Motor Areas • Primary Motor Areas • frontal lobes • control voluntary muscles • Broca’s Area • anterior to primary motor cortex • usually in one hemisphere • controls muscles needed for speech • Frontal Eye Field • above Broca’s area • controls voluntary movements of eyes and eyelids 11-23 Motor Areas 11-24 • Auditory Area – temporal lobe – interprets hearing • Visual Area – – – – occipital lobe interprets vision Cutaneous Sensory Area interprets sensations on skin Sensory Areas 11-25 Sensory Areas 11-26 Association Areas • regions of cortex that are not primary motor or primary sensory areas • widespread throughout the cerebral cortex • analyze and interpret sensory experiences • provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment, emotions 11-27 Association Areas Frontal Lobe Association Areas • concentrating • planning • problem solving • judging Temporal Lobe Association Areas • remember visual scenes • remember music • remember complex patterns Parietal Lobe Association Areas • understanding speech • using words to express thought Occipital Lobe Association Areas • combine visual images with other sensory experiences 11-28 Hemisphere Dominance • In over 90% of population, left hemisphere is dominant • Dominant hemisphere controls • speech • writing • reading • verbal skills • analytical skills • computational skills • Nondominant hemisphere controls • nonverbal tasks • motor tasks • understanding and interpreting musical and visual patterns • provides emotional and intuitive thought processes 11-29 Memory Short Term • working memory • closed circuit • circuit is stimulated over and over • when impulse flow stops, memory disappears Long Term • changes structure and function of neurons • enhanced synaptic transmission 11-30 Basal Nuclei • masses of gray matter • deep within cerebral hemispheres • caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus • produce dopamine • control certain muscular activities 11-31 Diencephalon • between cerebral hemispheres and brainstem • surrounds third ventricle • thalamus • hypothalamus • optic tracts • optic chiasm • infundibulum • posterior pituitary • mammillary bodies • pineal gland 11-32 Diencephalon Thalamus • gateway for sensory impulses heading to cerebral cortex • receives all sensory impulses (except smell) • channels impulses to appropriate part of cerebral cortex for interpretation Hypothalamus • maintains homeostasis by regulating visceral activities • links nervous and endocrine systems 11-33 Limbic System Consists of • portions of frontal lobe • portions of temporal lobe • hypothalamus • thalamus • basal nuclei • other deep nuclei Functions • controls emotions • produces feelings • interpret sensory impulses 11-34 Brain Stem Three Parts 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata 11-35 Midbrain • between diencephalon and pons • contains bundles of fibers that join lower parts of brainstem and spinal cord with higher part of brain • cerebral aqueduct • cerebral peduncles – bundles of nerve fibers • corpora quadrigemina – centers for visual and auditory reflexes 11-36 Pons • rounded bulge on underside of brainstem • between medulla oblongata and midbrain • helps regulate rate and depth of breathing • relays nerve impulses to and from medulla oblongata and cerebellum 11-37 Medulla Oblongata • enlarged continuation of spinal cord • conducts ascending and descending impulses between brain and spinal cord • contains cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory control centers • contains various nonvital reflex control centers (coughing, sneezing, vomiting) 11-38 Reticular Formation • complex network of nerve fibers scattered throughout the brain stem • extends into the diencephalon • connects to centers of hypothalamus, basal nuclei, cerebellum, and cerebrum • filters incoming sensory information • arouses cerebral cortex into state of wakefulness 11-39 Types of Sleep Slow Wave Rapid Eye Movement (REM) • person is tired • some areas of brain active • decreasing activity of • heart and respiratory rates reticular system irregular • restful • dreaming occurs • dreamless • reduced blood pressure and respiratory rate • ranges from light to heavy • alternates with REM sleep 11-40 Cerebellum • inferior to occipital lobes • posterior to pons and medulla oblongata • two hemispheres • vermis connects hemispheres • cerebellar cortex – gray matter • arbor vitae – white matter • cerebellar peduncles – nerve fiber tracts • dentate nucleus – largest nucleus in cerebellum • integrates sensory information concerning position of body parts • coordinates skeletal muscle activity • maintains posture 11-41 Peripheral Nervous System • Cranial nerves arising from the brain • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera 11-42 Structure of a Peripheral Nerve 11-43 Nerve Fiber Classification • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into CNS • Motor Nerves – conduct impulses to muscles or glands • Mixed Nerves – contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers; most nerves General somatic efferent fibers • carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles General somatic afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to CNS from skin and skeletal muscles General visceral efferent fibers • carry motor impulses away from CNS to smooth muscles and glands General visceral afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to CNS from blood vessels and internal organs 11-44 Nerve Fiber Classification Special somatic efferent fibers • carry motor impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing, swallowing, speaking, and forming facial expressions Special visceral afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to brain from olfactory and taste receptors Special somatic afferent fibers • carry sensory impulses to brain from receptors of sight, hearing, and equilibrium 11-45 Cranial Nerves 11-46 Cranial Nerves I and II Olfactory (I) • sensory • fibers transmit impulses associated with smell Optic (II) • sensory • fibers transmit impulses associated with vision 11-47 Cranial Nerves III and IV Oculomotor (III) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that • raise eyelids • move the eyes • focus lens •adjust light entering eye Trochlear (IV) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes 11-48 Cranial Nerve V Trigeminal (V) • mixed • opthalmic division • sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, and upper eyelids • maxillary division • sensory from upper teeth, upper gum, upper lip, palate, and skin of face • mandibular division • sensory from scalp, skin of jaw, lower teeth, lower gum, and lower lip • motor to muscles of mastication and muscles in floor of mouth 11-49 Cranial Nerves VI and VII Abducens (VI) • primarily motor • motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes Facial (VII) • mixed • sensory from taste receptors • motor to muscles of facial expression, tear glands, and salivary glands 11-50 Cranial Nerves VIII and IX Vestibulocochlear (VIII) • sensory • sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear • sensory from hearing receptors Glossopharyngeal (IX) • mixed • sensory from pharynx, tonsils, tongue, and carotid arteries • motor to salivary glands and muscles of pharynx 11-51 Cranial Nerve X Vagus (X) • mixed • somatic motor to muscles of speech and swallowing • autonomic motor to viscera of thorax and abdomen • sensory from pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and viscera of thorax and abdomen 11-52 Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, neck, and back Hypoglossal (XII) • primarily motor • motor to muscles of the tongue 11-53 Spinal Nerves • mixed nerves • 31 pairs • 8 cervical (C1 to C8) • 12 thoracic (T1 to T12) • 5 lumbar (L1 to L5) • 5 sacral (S1 to S5) • 1 coccygeal (Co) 11-54 Spinal Nerves Dorsal root • axons of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglion Dorsal root ganglion • cell bodies of sensory neurons Ventral root • axons of motor neurons whose cell bodies are in spinal cord Spinal nerve • union of ventral root and dorsal root 11-55 Dermatome • an area of skin that the sensory nerve fibers of a particular spinal nerve innervate 11-56 Cervical Plexus Nerve plexus – complex networks formed by anterior branches of spinal nerves; fibers of various spinal nerves are sorted and recombined Cervical Plexus • C1-C4 • lies deep in the neck • supply muscles and skin of the neck • contribute to phrenic nerve 11-57 Brachial Plexus • C5-T1 • lies deep within shoulders • musculocutaneous nerves • supply muscles of anterior arms and skin of forearms • ulnar nerves • supply muscles of forearms and hands • supply skin of hands • radial nerves • supply posterior muscles of arms and skin of forearms and hands • axillary nerves • supply muscles and skin of superior, lateral, and posterior arms 11-58 Lumbosacral Plexus • T12 – S5 • extend from lumbar region into pelvic cavity • obturator nerves • supply adductors of thighs • femoral nerves • supply muscles and skin of thighs and legs • sciatic nerves • supply muscles and skin of thighs, legs, and feet 11-59 Autonomic Nervous System • functions without conscious effort • controls visceral activities • regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • efferent fibers typically lead to ganglia outside CNS Two Divisions • sympathetic – prepares body for fight or flight situations • parasympathetic – prepares body for resting and digesting activities 11-60 Autonomic Nerve Fibers • all are motor (efferent) • preganglionic fibers • axons of preganglionic neurons • neuron cell bodies in CNS • postganglionic fibers • axons of postganglionic neurons • neuron cell bodies in ganglia 11-61 Sympathetic Division • thoracolumbar divison – location of preganglionic neurons • preganglionic fibers leave spinal nerves through white rami and enter paravertebral ganglia • paraverterbral ganglia and fibers that connect them make up the sympathetic trunk 11-62 Sympathetic Division • postganglionic fibers extend from sympathetic ganglia to visceral organs • postganglionic fibers usually pass through gray rami and return to a spinal nerve before proceeding to an effector • preganglionic fibers to adrenal medulla do not synapse with postganglionic neurons 11-63 Sympathetic Division 11-64 Parasympathetic Division • craniosacral division – location of preganglionic neurons • preganglionic fibers of the head in III, VII, and IX • ganglia are near or within various organs • preganglionic fibers of thorax and abdomen in X • short postganlionic fibers 11-65 Parasympathetic Division 11-66 Autonomic Neurotransmitters Cholinergic Fibers • release acetylcholine • preganglionic sympathetic fibers • preganglionic parasympathetic fibers • postganglionic parasympathetic fibers Adrenergic Fibers • release norepinephrine • postganglionic sympathetic fibers 11-67 Actions of Autonomic Neurotransmitters • depend on receptor Cholinergic receptors • bind to acetlycholine • muscarinic • excitatory • nicotinic • excitatory Adrenergic Receptors • bind to norepinephrine • alpha • different responses on various effectors • beta • different responses on various effectors 11-68 Actions of Autonomic Insert figure 11.39 Neurotransmitters 11-69 Control of Autonomic Activity • Controlled largely by CNS • Medulla oblongata regulates cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory activities • Hypothalamus regulates visceral functions • Limbic system and cerebral cortex control emotional responses 11-70 Life-Span Changes • Brain cells begin to die before birth • Over average lifetime, brain shrinks 10% • Most cell death occurs in temporal lobes • By age 90, frontal lobe has lost half its neurons • Number of dendritic branches decreases • Decreased levels of neurotransmitters • Fading memory • Slowed responses and reflexes • Changes increase risk of falling • Sleep problems common 11-71 Clinical Application Cerebral Injuries and Abnormalities Concussion • brain jarred against cranium • loss of consciousness • temporary loss of memory • mental cloudiness • headache • recovery usually complete Cerebrovascular Accident • stroke • sudden interruption in blood flow • brain tissues die Cerebral Palsy • motor impairment at birth • caused by blocked cerebral blood vessels during development • seizues • learning disabilities 11-72