New Product Development_3501

New Product Development
What is product development all about?
“
Product development is the set of activities beginning with the perception of a market opportunity and ending in the production, sale, and delivery of the product”
Ulrich & Eppinger, 2002
Some products…
And their development efforts..
Annual Production volume
Sales lifetime
Sales price
Number of unique parts
Development time
Internal development team
(peak size)
External development team
(peak size)
Development cost
Stanley Tools
Jobmaster
Screwdriver
Rollerblade In-
Line Skate
HP DeskJet
Printer
VW New Beetle
Automobile
Boeing 777
Airplane
Product Development Strategy
Task: Define a well-defined product development process and propose a product development organization that will allow your company to compete effectively over the next decade.
• Is there a standard development process that will work for every company?
• What milestones will be used to divide the overall product development process into phases?
• What role do experts from different functional areas play in the development process?
• Should the development organization be divided into groups corresponding to projects or to development functions?
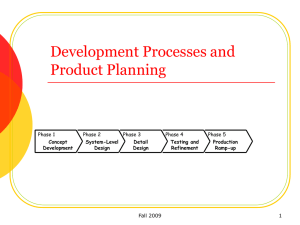
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Generate mission statement
(target market, business goals, key assumptions and constraints)
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Ulrich and Eppinger 2004
Example
Mission: “design a better hand-held roofing nailer”
Assumptions:
The nailer will use nails (as opposed to adhesives, screws, etc.)
The nailer will be compatible with nail magazines on existing tools
The nailer will nail through roofing singles into wood
The nailer will be handheld.
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Identify needs of target market;
Select several product concepts for further development and testing
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Ulrich and Eppinger 2004
Example
Needs of target market:
The nailer inserts nails in rapid succession.
The nailer is lightweight.
The nailer has no noticeable nailing delay after starting tool.
Product concepts:
Rotary motor with spring and single impact
Rotary motor with spring and multiple impacts
Linear motor with a moving mass and single impact
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Define product architecture
Decompose product into subsystems and components
Define final assembly scheme
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Ulrich and Eppinger 2004
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Ulrich and Eppinger 2004 Complete specification of geometry, materials and tolerances of all parts
List of standard parts to be purchased
Detailed drawings
Process plans for fabrication and assembly
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Building of alpha- and beta- prototypes alpha: same material and geometry
- does it work?
- does it satisfy customer needs?
beta: parts supplied by production process
- tested internally and by customers
- tested for performance and reliability
Product Development Process
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Small volume production to train workforce and work out any remaining problems.
Finally…
LAUNCH!!
Variations to Product Development Process
• Market pull products
– Market opportunity to technology, e.g. sporting goods, furniture
– Uses generic process
• Technology push products
– Technology to market opportunity, e.g. teflon, gore-tex
– Concept development takes technology as given
• Platform products
– Built around existing platform, e.g. consumer electronics, printers
– Concept development assumes proven technology platform
• Process intensive products
– Product constrained by production process, e.g. semiconductors, chemicals
– Product and process developed from start
• Quick build products
– Rapid modeling and prototyping, e.g. software, cell phones
– Many design-build-test cycles
• Complex systems
– System includes many subsystems and components, e.g. airplanes, jet engines
– System and subsystems developed by many teams working in parallel
Some products…
And their development efforts..
Annual Production volume
Sales lifetime
Sales price
Number of unique parts
Development time
Internal development team
(peak size)
External development team
(peak size)
Development cost
Stanley Tools
Jobmaster
Screwdriver
Rollerblade In-
Line Skate
HP DeskJet
Printer
VW New Beetle
Automobile
Boeing 777
Airplane
Some development efforts
Stanley Tools
Jobmaster
Screwdriver
Rollerblade In-
Line Skate
Annual Production volume 100,000/year 100,000/year
HP DeskJet
Printer
4M/year
Sales lifetime 40 years 3 years 2 years
Sales price
Number of unique parts
Development time
$3
3
1 year
Internal development team
(peak size)
External development team
(peak size)
Development cost
3 people
3 people
$150,000
$200
35
2 years
5 people
10 people
$750,000
$300
200
1.5 years
100 people
75 people
$50M
VW New Beetle
Automobile
Boeing 777
Airplane
100,000/year
6 years
$17000
10,000
3.5 years
800 people
50/year
30 years
$130M
130,000
4.5 years
6800 people
800 people
$400M
10,000 people
$3B
Food for thought..
• Plot development cost against the other rows and see if there is any correlation. Why or why not?
What drives product development costs?
development cost
3500000000
3000000000
2500000000
2000000000
1500000000
1000000000
500000000
0
-20000
-500000000
0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000 120000 140000
# parts
What drives product development costs?
development cost
3500000000
3000000000
2500000000
2000000000
1500000000
1000000000
500000000
0
-500000000
0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000
Internal team size x duration
What drives product development costs?
development cost
3500000000
3000000000
2500000000
2000000000
1500000000
1000000000
500000000
0
-20000
-500000000
0 20000 40000 60000 80000
Total team size x duration
Market issues…
“
Rather than compete with the super jumbo (a 550-seat cruiser by
Airbus), Boeing has decided to concentrate on a smaller, faster
‘sonic cruiser’. So the petty snipping of old has been replaced by a genuine battle of philosophies: on one side is size, on the other speed ”
The Economist, July 2001
Technical issues…
… “ advance fuel cell-vehicles, could have a profound effect on vehicle manufacturing - perhaps setting the stage for the reinvention of the automobile business. One of the biggest hurdles is the development of safe and effective on-board hydrogen storage.
”
L. D. Burns
Vice President of R&D, General Motors
Resource issues…
“AstraZeneca has to rein in some of its most promising drug candidates because of lack of resources to develop them simultaneously ”
Claes Wilhelmsson
Head of R&D, AstraZeneca
Who is Involved in Product Development?
• Marketing
– Mediates interactions between firm and customers
– Identifies product opportunities
– Defines market segments
– Identifies customer needs
– Oversees launch and promotion of product
• Design
– Lead role in defining physical form of product to best meet customer needs
– Includes engineering design and industrial design
• Manufacturing and supply chain
– Designs and operates the supply chain in order to produce the product from procurement to distribution
Characteristics of Successful Product
Development
• Product quality
– How good is the product?
• Product cost
– What is the capital equipment cost and unit production cost?
• Development time
– How quickly did the team complete the effort?
• Development cost
– How much did the firm have to spend to develop the product?
• Development capability
– Are the team and firm better able to develop other products?
Challenges of Product Development
• Trade-offs
– Lightweight vs costly
• Dynamics
– Technologies, customer tastes, competition change environment
• Details
– Screws vs snap fits on enclosure of computer
• Time pressure
– Decisions made quickly and without complete information
• Economics
– Large investment – will it pay off?
• Organizational realities
– Team composition, empowerment, functional allegiance, resources
Design Changes over Time
Quality Function Deployment
• A method to translate customer requirements into engineering specifications
• Aims to get design, engineering and production people involved early on in the process
Quality Function Deployment
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Organizational challenges
• How should the product development team operate?
Project-Based Organization
Marketing Engineering Operations
Project Manager Project 1
Project
Managers have more power
“Heavy Weight”
Project Manager Project Manager Project 2
Functional-Based Organization
Marketing manager Engineering Operations manager
Project 1
Project 2
Project 3
Project 1
Project 2
Project 1
Project 2
Project 3
Project 4
Functional managers have more power
Matrix Organization
Marketing manager R&D manager Engineering
Project 1
Project 2
Pros and cons
Functional
Strength
Weakness
Example
Major issue
Matrix Project
Fosters specialization and expertise
Coordination among groups can be slow
Slight variations to custom design
How to integrate different functions to achieve a common goal.
Provides integration and speed benefits
Optimal resource allocation, quick trade-off resolution
Requires more managers and administrators
Difficulty maintaining functional capabilities
Many recently successful projects in automobile, electronics, aero
How to balance functions and projects. How to evaluate project & functional performance.
Start-up companies, dynamic markets, to achieve breakthroughts
How to maintain functional expertise over time
Final Word…
Phase 0
Planning
Phase 1
Concept
Development
Phase 2
System-level
Design
Phase 3 Phase 4
Detail Design Testing and
Refinement
Phase 5
Production
Ramp-Up
Product development is a process and it can be managed!!