ECE520.427 Class #2
advertisement

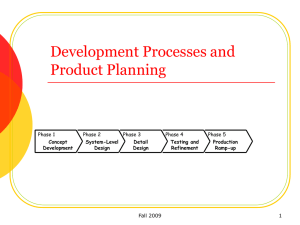
ECE520.427 Class #2 Product Development and Product Planning Outline: Class #2 Introduction to product design and development Product development process Intermission – get some popcorn Product planning Homework assignment #1 What is Product Design and Development? Product development is a set of activities starting with the perception of a market opportunity and ending with the sale of a product Product design is one aspect of the development process Engineering design specifies how the technical systems will work Industrial design specifies the aesthetics, ergonomics, and user interface Other development activities include marketing and manufacturing Success of the product typically depends on the success of all three development activities Successful Product Development Marketing (pre-design) Identification of market opportunities (pre-design) Identification of customer needs (pre-design) Identification of target pricing (post-design) Promotion of product Design Product quality Product cost (includes development cost) Development time Development capability Manufacturing Production system Supply chain Examples Good market research and bad design: Archos vs. Apple Archos 20GB Released October 2001 350 g, 1.3” thick File-based organization system Ugly interface iPod 5GB Released November 2001 184 g, 0.78” thick ID3-based organization system Pretty interface Examples Good design and marketing and bad manufacturing Example 1: Wii Example 2: Lenovo X61 Tablet Why Is Good Product Development Difficult? Trade-offs Dynamics Details Time pressures Economics Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Marketing Design Manufacturing Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Marketing Describe market opportunity Design Consider existing product platform (if any) Consider new technologies Manufacturing Identify production and/or corporate constraints Other Allocate project resources ¾ Mission statement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Market opportunity Æ product concept Marketing Identify customer needs Research competitive landscape Design Develop concepts Determine feasibility of design concepts Build and test prototypes Manufacturing Estimate manufacturing costs Other Investigate IP issues ¾ Product concept and proof-of-concept prototype Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Product Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Identify Customer Needs Product Specifications Concept Generation Concept Selection Concept Testing Product Architecture Industrial Design Design for Manufacturing Prototyping Robust Design Patents, IP, and Economics Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Proof-of-concept Æ complete product architecture Marketing Develop extended product family Develop marketing plan Design Describe all subsystems and components Develop software and firmware Create prototypes of each subsystem Select geometric layout and create industrial design Choose all parts and tolerances Manufacturing Identify suppliers Create assembly scheme Define assembly process and obtain tooling ¾ “Control documentation” Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Control documentation Æ prototypes Marketing Develop plans for field testing Design Create alpha and beta prototypes Performance and reliability testing Iterate and refine design Manufacturing Refine assembly and fabrication schemes Create quality assurance strategy Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Generic Design Process Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Prototypes Æ products Marketing Get first-run products to “preferred customers” Design Evaluate first-run output Relax a little Pray that everything works Manufacturing Start production Make sure you don’t use lead paint from China Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Isn’t This All Obvious? Yes and no Taken individually, you could probably think up most of the product development issues and tasks covered in this class Taken collectively, it takes experience to produce a thorough product development process from start to finish This class guides the process step-by-step with “structured methods” for each step Within each step, some items might be “obvious”, but combining all of the steps will produce a result greater than the sum of the parts Intermission ECE520.427 Class #2 Product Development and Product Planning Product Planning Phase 0: Planning Phase 1: Concept Development Phase 2: Phase 3: System-Level Detail Design Design Phase 4: Testing and Refinement Phase 5: Production Ramp-Up Corporations typically plan products many years in advance Product planning ensures that products support overall business strategy Determine mix of new products vs. upgrades Optimize past experience as leverage into new products Decide which market segments to target Example: Xerox Hodaka New Platforms Legend Lakes Project Product Release H-Net Derivatives L-Net Improvements 595 6010 Fundamentally New 1996 392 393 Astro 1997 1998 1999 2000 Types of product development projects: New product platforms, derivatives of existing platforms, incremental improvements to existing products, and fundamentally new products Evaluating Projects Step 1: Identify market opportunities Step 2: Evaluate opportunities Four perspectives for evaluation: Competitive strategy Market segmentation Technological trajectories Product platforms Competitive Strategy Defines the company’s approach to markets and competitors – “reputation” Technology leadership Cost leadership Customer focus Market Segmentation Technological Trajectories today Time Time Product Platforms and Technology Roadmaps Product Platforms and Technology Roadmaps Functional Elements Technologies Photoreceptor Cylindrical Drum Scanner Layout 2D CCD Array w/Optical Reduc. Toner Type High Temperature Output Modes Monochrome: Paper, Fax, Scan, Local Network, Internet 3-Pitch Belt Photoreceptor n-Pitch Belt Photoreceptor Full-Width, Linear Array without Optical Reduction Low Melting Point Low Melting Point, Low Emission Color: Paper, Fax, Scan, Local Network, Internet User Interface Keypad Touch Screen Image Processing 600 dpi Automatic Image Quality 600/1200 dpi 1200 dpi Diagnostics On-Board Diagnostics Touch Screen, Remote PC Remote-Dialup Diagnostics 1800 dpi Remote Repair Document Centre 220, 230 Document Centre 240, 255, 265 Document Centre 2XX Document Centre 3XX Hodaka Project Lakes Project Lakes Extensions Next Platform Time Product Platforms and Technology Roadmaps Product Platforms and Technology Roadmaps “In the course of the past several months, it has become clear that the right path for Palm is to offer a single, consistent user experience around this new platform design and a single focus for our platform development efforts. To that end, and after careful deliberation, I have decided to cancel the Foleo mobile companion product in its current configuration and focus all of our energies on delivering our next generation platform and the first smartphones that will bring this platform to market. We will, of course, continue to develop products in partnership with Microsoft on the Windows Mobile platform, but from our internal platform development perspective, we will focus on only one.” – Ed Colligan, CEO of Palm, Inc. Product Planning Process Multiple Projects Identify Opportunities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ¾ Evaluate and Prioritize Projects Portfolio of Projects Allocate Resources and Plan Timing Product Plan Complete Pre-Project Planning Identify opportunities Evaluate and prioritize products Allocate resources and plan timing Complete pre-project planning Reflect on the results and the process Product “Mission Statement” Mission Statements Product Development Process Mission Statement The Mission Statement provides a detailed definition of the assumptions under which the product will be developed, including: One-sentence description of the product (avoid implying a specific product concept) Benefit proposition Key business goals (time, cost, quality) Target market(s) Target price Assumptions and constraints Stakeholders Intermission Outline: Class #2 Introduction to product design and development Product development process Intermission – get more popcorn Product planning Homework assignment #1 Product Development Task #1: Opportunity Statement An opportunity statement is a one- or twosentence description of a product or market opportunity Should not imply the use of any particular technology Should not imply a specific product concept Example: “Create a simple bedside device that displays internet weather forecasts so you can see what the weather will be when you wake up in the morning.” Product Development Task #1: Opportunity Statement Make a “pitch” in three slides Explain problem, need, or motivation Explain necessary elements in solution Summarize with opportunity statement Assignment Schedule Monday (9/15) – email me your opportunity statement and your slides Tuesday (9/16) – be ready to make a short (< 5 minute) presentation with your slides At the end of class, everyone will vote for their preferred product. We’ll review votes and form teams. Thursday (9/18) – we’ll announce the product development teams by in-class and provide some feedback Monday (9/22) – each team will email me a team Mission Statement (HW #2) Review: Homework #1 Due (email) by September 15 Written opportunity statement Three (3) slides to make pitch Also due by September 15: take online Jung typology test and email me the results. Before student presentations and team selection, we’ll talk about teamwork and group dynamics The results of the online typology test will help us to customize the discussion to the students in the class Link to test is on course website How to Identify Opportunities Potential sources: Think about the frustrations and complaints your friends have about existing products Think about inefficiencies in your daily routine Read a recent issue of Wired or Popular Science and get inspired by new technologies Scan the TOC of Proc. IEEE for the past few months to get an idea of emerging trends Methods to keep track of opportunities: Keep an “opportunity database” on your computer; text-message or email yourself when you think of an idea Keep a running list of opportunities on your PDA Write ideas down on a small piece of paper that you keep in your wallet or purse Next Class In class: Guest lecture on teamwork and group dynamics Student presentations – product pitches Before class: Read U & E chapters 1, 2 & 3 Complete online typology test Submit opportunity statement, slides, and typology results via email