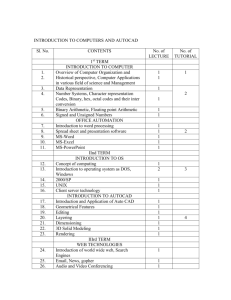
Introduction to AutoCAD 2007 Graphics Screen

Prepared by:
Nor Helya Iman Bt. Kamaludin
Starting AutoCAD 2007
1. AutoCAD 2007 is started: a) from the Windows ‘Start screen’ with a double left-click on the AutoCAD 2007 icon b) by selecting the windows taskbar sequence:
Start-Programs-AutoCAD 2007
2. Both methods will briefly display the AutoCAD 2007 logo and then: either a) the actual graphics screen or b) the Startup dialogue box.
3. If the Startup dialogue box is displayed, then select Cancel at present. This will allow the user access to the graphics screen.
4. Some users may also have the Workshop and New features screens displayed during start up. If these screens are displayed, cancel them.
The graphics screen
1 The AutoCAD title bar
2 The graphic screen menu bar
3 The Standard toolbar
4 The Styles toolbar
5 The Workspaces toolbar
6 The Layers toolbar
7 The Properties toolbar
8 The standard ‘windows buttons’
9 The Windows taskbar
10 The Status bar
11 The Command prompt window area
12 The Layout tabs
13 The Co-ordinate system icon
14 The on-screen cursor
15 The Drawing area
16 Scroll bars at right and bottom of drawing area
17 The Object Snap toolbar (floating)
18 The Sheet Set Manager palette
19 The Tool Palette for ALL tools
20 The Draw toolbar (docked)
21 The Modify toolbar (docked)
22 The Pickfirst/Grips boxes
Title bar
The title bar is positioned at the top of the screen and displays the AutoCAD 2007 icon, the AutoCAD
Release version and the current drawing name.
Menu bar
The screen menu bar displays the default AutoCAD menu headings. The full menu bar headings are:
File Edit View Insert Format Tools Draw Dimension Modify (Express)Window Help
The Standard toolbar
The Standard toolbar is normally positioned below the screen menu bar and allows the user access to several button icon selections including New, Open, Save,
Plot, etc.
Workspaces, Layers, Properties and Styles toolbars
These are normally positioned below and to the side of the
Standard toolbar. Icon selections are: a) Workspaces: Workspace settings, My Workspace b) Layers: Layer Properties Manager, Layer Control, Make
Object’s Layer Current, Layer Previous c) Properties: Color Control, Linetype Control, Lineweight
Control d) Styles: Text Style Control, Dimension Style Control,
Table Style Control.
The Windows buttons
The Windows buttons are positioned at the right of the title bar, and are: a) left button: minimise screen b) centre button: maximise screen c) right button: close current application.
The Windows taskbar
This is situated at the bottom of the screen and displays: a) the Windows ‘Start button’ and icon b) the name of any application which has been opened, e.g.
AutoCAD c) the time and the sound control icons d) other icons/information dependant on user requirements.
The Status bar
Positioned above the Windows taskbar, the Status bar gives the user: a) on-screen cursor X, Y and Z co-ordinates information at the left b) access to the drawing aid buttons, e.g. SNAP, GRID,
ORTHO, POLAR, OSNAP, OTRACK, DUCS, DYN, LWT c) access to the MODEL/PAPER space toggle.
Command prompt window area
1. The command prompt area is where the user
‘communicates’ with AutoCAD 2007 to enter: a) a command, e.g. LINE, COPY, ARRAY b) co-ordinate data, e.g. 120,150; @15<30 c) a specific value, e.g. a radius of 25.
2. The command prompt area is also used by AutoCAD to supply the user with information, which could be: a) a prompt, e.g. Specify first point b) a message, e.g. object does not intersect an edge.
3. The command area can be increased in size by
‘dragging’ the bottom edge of the drawing area upwards.
Layout tabs
Allows the user to ‘toggle’ between model and paper space for drawing layouts.
The co-ordinate system icon
1. This is the X–Y icon at the lower left corner of the drawing area.
2. This icon gives information about the co-ordinate system in use. The default setting is the traditional Cartesian system with the origin (0,0) at the lower left corner of the drawing area.
3. The co-ordinate icon display can be altered by the user.
The cursor cross-hairs
1. Used to indicate the on-screen position, and movement of the pointing device will result in the co-ordinates in the Status bar changing.
2. The ‘size’ of the on-screen cursor can be increased or decreased to suit user preference.
The drawing area
1. This is the user’s drawing sheet and can be any size required.
2. In general we will use A3-sized paper, but will also investigate very large and very small drawing paper sizes.
Scroll bars
1. Positioned at the right and bottom of the drawing area and are used to scroll the drawing area.
2. They are very useful for larger-sized drawings and can be ‘turned-off’ if they are not required.
Toolbars
1. By default, AutoCAD 2007 displays the Draw and Modify toolbars docked at the left and right of the drawing screen.
2. Users may positioned them differently.
Tool palettes
1. Figure above displays the AutoCAD 2007 default palettes, these being the Sheet Set Manager and all palettes.
2. The user’s screen may not display any tool palettes.
3. Palettes can be cancelled, minimised or repositioned by the user at any time.
The Pickfirst/Grips box
1. The user may have a small square box ‘attached’ to the cursor cross-hairs.
2. This box may be the Grips and/or the Pickfirst box, both aids to the user.
Terminology
Menu
A menu is a list of options from which the user selects
(picks) the one required for a particular task.
Picking a menu item is achieved by moving the mouse over the required item and left-clicking.
There are different types of menus, e.g. pull-down, cascade, screen, toolbar button icon.
Command
A command is an AutoCAD function used to perform some task. This may be to draw a line, rotate a shape or modify an item of text. Commands can be activated by: a) selection from a menu b) selecting the appropriate icon from a toolbar button c) entering the command from the keyboard at the command line
Objects
Everything drawn in AutoCAD 2007 is termed an
object (or entity) e.g. lines, circles, text, dimensions, hatching, etc. are all objects.
The user ‘picks’ the appropriate object with a mouse left-click when prompted.
Default setting
All AutoCAD Releases have certain values and settings which have been
‘preset’, these being essential for certain operations. Default values are displayed with <> brackets, but the actual value can be altered by the user as and when required. For example:
1. From the menu bar select Draw-Polygon and: prompt polygon Enter number of sides<4> respond press the ESC key to cancel the command.
2. Notes a) <4> is the default value for the number of sides b) polygon is the active command.
3. At the command line enter LTSCALE <R> and: prompt Enter new linetype scale factor<1.0000> (or other value) enter 0.5 <R>
4 . Notes a) <1.0000> is the LTSCALE default value on my system b) we have altered the LTSCALE value to 0.5.
The escape (Esc) key
This is used to cancel any command at any time. It is very useful, especially when the user is ‘lost in a command’.
Pressing the Esc key will cancel any command and return the command prompt line.
Icon
An icon is a menu item in the form of a picture contained on a button within a named toolbar.
Cascade menu
A cascade menu is obtained when an item in a pull-down menu with after it’s name is selected.
1. From the menu bar select the sequence Draw-Circle and the cascade effect as right figure will be displayed.
2. Cancel the cascade effect by: a) moving the pick arrow to any part of the screen and left-clicking b) pressing the Esc key – cancels the
‘last’ cascade menu, so two escapes are required.
Shortcut menu
1 . A shortcut menu allows quick access to commands that are relevant to the current activity.
2. Shortcut menus are displayed with a right-click: a) within the drawing area with or without any objects selected b) within the drawing area during a command c) within the text and command windows d) within areas and on icons in Design Center e) on a toolbar, tool palette, model or layout tabs f) on the Status bar or the Status bar buttons
3. Shortcut menus typically include options to: a) repeat the last command entered b) cancel the current command c) display a list of recent user input d) cut, copy, and paste from the Clipboard e) select a different command option f) undo the last command entered.
4. Right figure displays a typical shortcut menu with a cascade effect.
Dialogue boxes
A dialogue box is always displayed when an item with ‘…’ after it’s name is selected:
1. Dialogue boxes allow the user to: a) alter parameter values b) toggle an aid ON/OFF c) select an option from a list.
2. Most dialogue boxes display the options On,
Cancel and Help which are used as follows:
OK: accept the values in the current dialogue box
Cancel: cancel the dialogue box without any alterations
Help: gives further information in Windows format. The Windows effect can be cancelled with
File-Exit or using the Windows Close button from the title bar (the right-most button).
Toolbars
1. Toolbars allow the AutoCAD 2007 commands to be displayed on the screen in button icon form.
2. There are over 30 toolbars available for selection. The toolbars normally displayed by default when AutoCAD
2007 is started are Standard, Layers,
Properties, Styles, Workspaces, Modify and Draw.
3. Toolbars can be: a) displayed and positioned anywhere in the drawing area b) customised to the user preference.
Tool palette
1. A tool palette is an efficient method of organising and sharing various items.
2. Tool palettes can be customised by the user.
3. By selecting Auto-hide from the title bar, the tool palette can be minimised/maximised
4. Tool palettes can be: a) cancelled by selecting the Close (topmost) button from the title bar b) activated from the menu bar with Tools-Tool Palettes Window c) positioned by the user.
5. The objects which the user can add to a tool palette include: a) Geometric objects such as lines, circles, and polylines b) Dimensions c) Blocks, Hatches, Solid fills and Gradient fills.
Template
A template allows the user access to different drawing standards with different sized paper, each template having a border and title box.
AutoCAD 2007 supports several drawing standards including ANSI, DIN, Gb, ISO, JIS and Metric.
Templates will be used for our drawing work.
Toggle
This is the term used when a drawing aid is turned
ON/OFF and usually refers to: a) pressing a key b) activating a parameter in a dialogue box, i.e. a
tick/cross signifying ON, no tick/cross signifying OFF.
Function keys
Several of the keyboard function keys can be used as aids while drawing, these keys being:
F1 accesses the AutoCAD 2007 Help menu
F2 flips between the graphics screen and the AutoCAD Text window
F3 toggles the object snap on/off
F4 toggles the tablet on/off (if attached)
F5 toggles the isoplane top/right/left – for isometric drawings
F6 co-ordinates on/off toggle
F7 grid on/off toggle
F8 ortho on/off toggle
F9 snap on/off toggle
F10 polar tracking on/off toggle
F11 toggles object snap tracking off
F12 the dynamic input toggle
Help menu
AutoCAD 2007 has an ‘on-line’ help menu which can be activated at any time by selecting from the menu bar Help-Help or pressing the F1 function key. The
Help dialogue box will be displayed as two distinct sections: a) Left: with three tab selections – Contents, Index and
Search b) Right: details about the topic selected.
File types
When a drawing has been completed it should be saved for future recall.
All drawings are called files.
AutoCAD 2007 supports different file formats, including:
.dwg: AutoCAD drawing
.dws: AutoCAD Drawing Standard
.dwt: AutoCAD Template Drawing template file
.dxf: AutoCAD Data Exchange Format
Saved drawing names
Drawing names should be as simple as possible.
Finally
At this time, we have: a) started AutoCAD b) investigated the graphics screen c) discussed some terminology.
We are now ready to draw some AutoCAD objects.