Istation - DPS ARE
advertisement

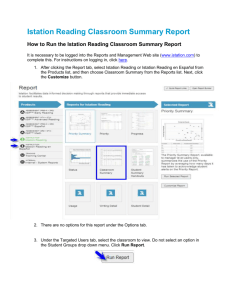
2015-16 SAL Administration Training ISIP Early Reading ISIP Advanced Reading ISIP Español August 2015 HOUSEKEEPING, INTRODUCTIONS AND WELCOME • Rochanda Jackson - Manager of Assessment Administration Rochanda_jackson@dpsk12.org 720-423-3758 • Ashley Jakubowski – Assessment Coordinator (ANet and Istation) Ashley_jakubowski@dpsk12.org 720-423-2197 • Peter Tardif - READ Act Coordinator (DRA2/EDL2, Istation, STAR) Peter_tardif@dpsk12.org 720-423-3766 AGENDA • Let’s review! GENERAL SAL RESPONSIBILITIES Let’s review! (http://dpsare.com/site-assessment-leaders/) 1. Be familiar with all aspects of federal, state, and district tests 2. Coordinate the administration of federal, state, and required district assessments. 3. Assume an assessment leadership role at the school. 4. Communicate assessment information with school and district staff 5. Use all available sources of information in role as SAL. ROLES AND GENERAL RESPONSIBILITIES Administrators will: check in with READ Act SAL to ensure all necessary staff are trained by Sept. 25th provide time in professional development calendar for READ Act SAL to administer necessary training check audit reports in School Folders to ensure 100% of compliance and follow up when necessary ROLES AND GENERAL RESPONSIBILITIES (CONT.) The SAL will: train teachers (literacy and special education), literacy interventionists, administrators, and ELA support staff on the READ Act and assessment administration prior to administering the test Submit sign-in sheets to ARE by Sept. 25th Identify teachers administering assessment for first time ensure school has all required assessment materials distribute necessary testing materials to teachers maintain test security ensure that all testing procedures are followed ensure that all READ Act deadlines are met check audit reports to ensure 100% of compliance and follow up when necessary Set up testing schedule with admin Show teachers how to access OASIS Data Entry to review READ Plans at the beginning of the year Walk teachers through available resources on ARE website Meet with STR to ensure device readiness ROLES AND GENERAL RESPONSIBILITIES (CONT.) The teacher will… be responsible for directly administering the assessment and entering data in Assessment Applications, be trained prior to any assessment administration, be trained in any specific accommodation they are providing, manage each assessment administration and ensure all required students complete testing, contact the READ Act SAL or building administration if a testing irregularity occurs, actively proctor test sections, create all required READ plans with student’s parents, progress monitor and update READ Plan as a living document until the student is reading on grade level. and create a testing environment allowing students to perform to the best of their ability. ROLES AND GENERAL RESPONSIBILITIES (CONT.) The STR will… work with administration and SAL to ensure technology readiness updates software according to specifications provided by DoTS conduct System Check on all devices work with SAL to ensure training for test administrators includes familiarity with technology aspects of testing be available to provide onsite support to troubleshoot technology issues that arise during testing. SCHEDULING GUIDELINES: READ ACT ASSESSMENTS Assessment Paper/pencil Istation (online) Grade level # Students tested at one time K-8 1 Kindergarten Individually No more than 5 per small group 1st Small group (1-5) Half class (1-12/15) Whole class in Spring only(20-30) 2-8 Whole class (20-30) •Each SAL in collaboration with your principal and STR will create a testing schedule within the testing windows that includes regular sessions, make-ups, and accommodations. •Your testing schedule will be determined by 5 factors: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Type of assessment (paper/pencil or online) Number of students requiring assessments One-on-one administrations vs. whole class • Number of available testing devices (online) Time per assessment Your school schedule SCHEDULING GUIDELINES: ADMINISTRATION TIME When creating your testing schedule, add approximately 30 minutes for activities prior to and at the end each unit for other activities (see chart below). Task Recommended minutes allotted for an Administration Preparing for testing (includes reading instructions to students and answering questions) 10 minutes (recommended) Distributing test materials (Student login cards) 5 minutes (recommended) Testing Times Logging off computers, collecting test materials, and setting up testing environment for next session/student. Assessment DRA2/EDL2 Istation SRI Minutes 20-50 30-40 30-50 5–15 minutes (recommended) 10 QUESTIONS? UPDATES FOR 2015-2016 • • • • • New READ Plan format to support DDI Flexibility for Assessments for K-3 Extended Kindergarten Fall Window Shortened READ Plans for Students with IEPs Continued 3rd Grade Advancement/Retention Policy • New website (www.dpsare.com) • Updated READ Act Guidebook WHAT IS THE COLORADO READ ACT? • The Colorado Reading to Ensure Academic Development Act (READ Act) was passed by the Colorado legislature and went into effect on July 1, 2013. • The READ Act… – focuses on literacy development through interventions AND – includes: • requirements for assessment, • the creation of individualized READ Plans for students performing Significantly Below Grade Level, and • specifics around parent involvement and communication. READ ACT ASSESSMENT FLEXIBILITY OPTIONS DPS sponsored assessments K-5 Alternate Assessments K-5 o DRA2/EDL2 and STAR o Istation (ISIP ER, ISIP AR, ISIP Español) Grades 6-12 o SRI College & Career • • o Use of CDE approved assessments only Grades 6-12 o Choice of reading assessment as part of a body of evidence. o Must meet minimum requirements in READ Act Guidebook Schools that do not opt-in to DPS assessment paths must notify ARE of assessment(s) to be used. Reference the Requirement & Timelines Document for your assessment path on the ARE READ Act website for detailed information. WHAT DOES SIGNIFICANTLY BELOW GRADE LEVEL (SBGL) MEAN? • For K-3 SBGL is defined by state provide cut scores on reading assessments. • For grades 4-12 SBGL is defined as a student who is reading more than one year below grade level based upon a body of evidence that includes one recent reading assessment score. • Cut Score and Proficiency Level documents can be found on the ARE READ Act website and in the READ Act Guidebook. HOW ARE STUDENTS IDENTIFIED AS SIGNIFICANTLY BELOW GRADE LEVEL? Kindergarten – 3rd Grade Process Initial Screener (Fall) If student scores at or below state cut scores, move to the next box. If not, no further testing. 30 Day Verification (Fall) If at or below SBGL cuts on second assessment, create READ Plan and move to next box. If above cut, teacher makes SBGL decision in OASIS Data Entry. Progress Monitoring Continuous progress monitoring must occur throughout the year with updates to READ plan. Spring Testing Student reassessed in Spring window. READ plan continues until a body of evidence shows grade-level reading. CONFLICTING ASSESSMENT DATA: K-3 TEACHER DECISIONS Due to conflicting assessment data, there will be times when teachers need to make a determination to create a READ Plan or not. To make this determination, ARE recommends: • teachers use all available data points, anecdotal notes/observations of student, and professional judgment • being conservative by creating plans for students where data is not conclusive so they do not fall further behind. This determination must be entered in OASIS Data Entry. HOW ARE STUDENTS IDENTIFIED AS SIGNIFICANTLY BELOW GRADE LEVEL? 4th – 12th Grade Process Fall Assessment Student takes reading assessment. Teacher uses body of evidence to determine if student is reading at grade level. If no, READ Plan continues. READ Plan Update Teacher updates READ Plan and continues reading interventions until student reaches grade-level reading. Progress Monitoring Continuous progress monitoring must occur throughout the year with updates to READ plan. Spring Testing Student reassessed in Spring window. READ plan continues until a body of evidence shows grade-level reading. Example #1 of Identifying SBGL Fall (Initial Screener) – 1st grader John scores 180 on ISIP ER. Does John need to take a 30 Day Verification Assessment? Yes and one week later he scores a 177 on ISIP ER. Is John SBGL? Yes! John’s teacher will contact his parents/guardians to create a READ Plan with them. Example #2 of Identifying SBGL Fall (Initial Screener) – 3rd grader Nayeli scores 870 on ISIP Español. Does Nayeli need to take a 30 Day Verification Assessment? Yes and she scores a 884 on ISIP Español. Is Nayeli SBGL? • Conflicting Data! Nayeli’s teacher must decide SBGL status due and enter decision into OASIS Data Entry. • Teacher must use all available evidence to make this determination. Example #3 of Identifying SBGL Midyear – 2nd grader Roscoe transferred into DPS in December and scores 229 on ISIP ER. Does Roscoe need to take a 30 Day Verification Assessment? No. Is Roscoe SBGL? • No. • Even though Roscoe is below grade level, he is not significantly below. Creation of a READ Plan is optional, but Roscoe will need some reading interventions to improve his reading skills. PARENT COMMUNICATION AND INVOLVEMENT • The READ Act requires a high level of parent participation and communication. Parents of students who are performing Significantly Below Grade Level must be notified in writing within 30 days of verification. By law, specific information must be mentioned in this notification, so teachers MUST use the form letter on the ARE website for this purpose. This letter will require both the teacher’s and principal’s signatures. Before the form letter goes home, teachers should attempt to contact the parent over the phone to discuss the student’s status, as this may be a difficult topic for parents. The READ Act requires that teachers contact the parents and partner with them to jointly create the READ Plan. Only after THREE attempts documented on the READ Plan in OASIS can teachers create the READ Plan without the parent and share that information with him/her upon completion. PARENT COMMUNICATION AND INVOLVEMENT When teachers meet with parents to create the READ Plan and discuss the student’s status, several points must, by law, be discussed. Teachers MUST use the Parent Talking Point Document to guide them in this discussion and provide parents with the Parent READ Act Information brochure. (Both docs on ARE website) In this session, the law requires that the teacher mention retention among other intervention options. It should be noted that though retention could be considered, it is recognized as a drastic measure that is not appropriate for most children. SUPPORT DOCUMENTS FOR COMMUNICATING WITH PARENTS • DPS has created documents that will help teachers meet the state requirements for communicating with Parents. (http://dpsare.com/read-act/) QUESTIONS? o Questions on the READ Act, Parent involvement, or how to determine SBGL? THE READ PLAN 1. Online Wizard in Assessment Apps 2. Paper/Pencil (must input info online) WHAT IS A READ PLAN AND WHO CREATES THEM? A READ Plan is… • …a general education intervention plan that is available to all students reading significantly below grade level. • …an individual student reading intervention plan focused on a student’s most necessary areas of reading development. • …a living document and remains open until the student is reading on grade level as evidenced through a body of evidence and one reading assessment score indicating grade level reading. Who creates the READ Plan? • The general education teacher, special education teacher, and other appropriate school personnel will collaboratively work to create the READ Plan with the parent/guardian. WHO IMPLEMENTS THE READ PLAN? The most qualified teacher (general education or special education) or reading interventionist (who regardless of licensure has the specific expertise in research–based reading instruction) provides the reading instruction and interventions in order to meet each student’s learning needs. • For students with disabilities: Schools should take into account both professional expertise in literacy instruction and knowledge of the impact of disability on learning to read when deciding the best method for implementing the READ Plan. READ PLAN COMPONENTS • • • • Student Information Language Development Body of Evidence – Presents all of the assessment information that is collected at the district and State level. Teachers enter additional assessment information, classroom observations, and other information/considerations. Analysis of Body of Evidence Teachers choose ONE OR TWO areas of focus that will most impact the student’s reading achievement. Teacher completes narrative boxes identifying skills to improve upon in area of focus and explanation of how this focus/skill will bring the student to grade-level reading. READ PLAN COMPONENTS • Intervention Plan(s) The teacher will write a separate intervention plan for each area of focus selected. Each intervention plan includes: A goal based on area of focus Description of the instructional techniques, strategies, and/or approaches the teacher will use (Example: “make and break” sight words) The reading program to be used in conjunction with techniques, strategies, and/or approaches (Example: Guided Reading Plus) How teacher will progress monitor the student Parent strategies being done at home to assist in the student achieving grade-level reading. READ PLAN COMPONENTS • Results of Intervention Plan(s) Explanation if the intervention plan helped or did not help the student meet/move towards their goal? Explanation whether the intervention plan should or should not continue as part of the READ Plan If it does not, new intervention plan will be created. READ PLAN COMPONENTS Signatures: Teacher and parent/guardian will sign the plan electronically. A copy must be provided to the parent/guardian. READ Plans can be downloaded and printed in English or Spanish directly from Assessment Apps. *Note: Info entered into a plan will print exactly as it was typed. No translation occurs. If you want the plan in another language, then enter the info in that language. After three documented attempts to have the parent help in creating the READ Plan, the teacher can complete the plan and present it to a parent/guardian for a signature. Document each attempt in the separate boxes on the signature page. READ PLAN COMPONENTS Discontinue READ Plan: Does a body of evidence that includes one recent reading assessment score indicate the student is reading at grade-level? If yes, teacher enters score to discontinue this READ Plan. ARE will audit these scores and confirm whether plan can be discontinued. READ PLAN CREATION Since READ Plans focus on data driven instruction for a specific school year, a new READ Plan must be created each year for each student. • • • Interventions/strategies within plans are specific to teacher, grade-level, and school. When these change, the plans must change. – Example: Teacher use of scripted lesson plans. Nothing should be automatically copied over, but modified by the teacher Previously created READ Plans for each student are available in OASIS. UPDATES THROUGHOUT THE YEAR Since a student’s READ Plan is a living document… …teachers update and modify the READ plan as necessary throughout the year or whenever changes need to be made based on progress monitoring. – For example, if a student reaches their goal or succeeds in their area of focus as demonstrated through a body of evidence, then a new goal or area of focus should be created. – Similarly, if a particular strategy is not helping a student make progress another strategy should be implemented and then documented in the Review and Recommendations page of the READ Plan. • …updates occur through OASIS Data Entry on the Assessment Applications website. REMOVAL FROM A READ PLAN Two necessary requirements… 1. student achieves a grade level score on a READ Act assessment 2. a body of evidence also indicates grade-level reading. *Please refer to each assessment’s grade–level expectations and DPS Body of Evidence Guidance document on ARE’s READ Act webpage. To Remove: Open READ Plan Navigate to final screen Click “yes” to question Enter recent grade level assessment score Notify the parent/guardian that a READ plan is no longer necessary as the student is now reading on grade-level. Teachers may use the DPS Removal from a READ Plan on the ARE’s READ Act webpage for this purpose. NEW PLANS IN THE SPRING The intent of the READ Act is to provide our most struggling and vulnerable readers with the supports needed to reach grade level proficiency, including a READ Plan that provides appropriate targets and strategies, as soon as possible after a teacher becomes aware that a student is reading SGBL. Sometimes this is not possible due to timing at the end of the school year. Schools should assess students they suspect are reading SBGL early enough in the window to be able to implement a READ plan if needed. NEW PLANS IN THE SPRING CONT. Is there a reasonable amount of time before the end of the school year to meet with parents, create, administer, and monitor a READ plan? If yes then the teacher… creates READ Plan with parents, implements, and monitors the READ plan through the remainder of the school year. If no then the teacher… creates the Bridge Plan in Assessment applications notifies the parent of: SBGL status, a confirming assessment will be given next fall, and their child may be put on a READ plan at that point. discusses home reading strategies that the parent can do to help their child improve their reading skills over the summer. (Use “DPS Spring Bridge Letter to a READ Plan”) QUESTIONS? o Questions on READ Plans. THE READ ACT & RTI Response to Intervention (RtI) should be used hand-in-hand with… • the READ Act to help students get the interventions that are most appropriate for them. • students who are below grade level, but are not SBGL. • RtI Resources : – Getting Started: http://rti.dpsk12.org/get-started/ – Provides information and guidance for teachers on the RtI process – RtI Appendix: http://rti.dpsk12.org/appendix/ – Provides DPS RESOURCES to guide you, DPS FORMS to empower you, and TOOLS to implement for each step in the RtI DATA INQUIRY PROCESS after selecting GRADE, FOCUS, and SUBJECT. READ PLANS & SPECIAL EDUCATION While the law allows for READ Plans and IEPs to be combined, DPS has decided it is in the best interest of the district to create separate READ plans for students who have IEPs. New Shortened READ Plan for Students with IEPs • If IEP addresses literacy, much of the required READ Plan documentation is already incorporated into the IEP. • Prior to a parent meeting, review student’s IEP to ensure it addresses literacy. • Follow steps on next page. READ PLANS & SPECIAL EDUCATION Steps for students with an IEP that address literacy Log into Assessment Applications Click on OASIS Data Entry On the Student Summary tab, under column Create READ Plan, select the Create Plan button. In the Student Information section of the READ Plan, teachers will select the “IEP with Literacy focus” button. Teacher confirms necessary READ Plan info is in IEP Teacher completes the rest of the READ Plan READ PLANS & SPECIAL EDUCATION Review the Special Education and READ Act document to check to ensure IEP can be used as the READ plan. READ ACT & ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEARNERS • • • • Teachers will assess English Learners based on their primary language of instruction. – If instructed in both languages, choose language in which majority (more than 50%) of the student’s literacy instruction occurs on a daily basis. Use the Language of Assessment document to help make this determination. Students are not required to be tested in both languages. If students are reading SBGL in their primary language of instruction, a READ Plan will be required. Primary language of Initial Assessment instruction is… 30 day verification to confirm SBGL status English ISIP ER ISIP ER Spanish ISIP Español ISIP Español EXEMPTIONS Exemptions from Testing Exemptions from READ Plans 1st year Enrolled Exemption Language Exemption Special Accommodations Exemption Grade-level Exemption Entering Exemptions: All exemptions will be entered individually in the Assessment Applications. Follow these steps: 1. Log in to Assessment Apps 2. Click OASIS Data Entry 3. Under Exemption column, Click “Create Exemption” 4. Select the correct exemption. STUDENT EXEMPTIONS FROM TESTING: 1ST YEAR ENROLLED 1st Year Enrolled – to qualify students must meet all 3 requirements: 1. English Learners 2. scored Non-English Proficient (NEP) on W-APT assessment 3. in first year of enrollment in a US school. Please note: Infinite Campus data should be used for this decision. Please check that an EL’s data in IC is updated on the summary page at the bottom. STUDENT EXEMPTIONS FROM TESTING: SPECIAL ACCOMMODATIONS Special Accommodations Exemption–Due to limited allowable accommodations on CDE approved assessments, some students with disabilities cannot access the assessment. This unintended exclusion of some students reading SBGL is currently being addressed by a state-wide task force. • • • • All students should be assessed using approved accommodations to receive a valid and reliable score as outlined by the author of the assessment. If this is not the case, students may be exempt from testing. – Schools can use non-approved accommodations to obtain instructional information even though the score will not be reported to the ARE department. This decision should be made on a student-by-student basis. DPS recommends testing students when appropriate. STUDENT EXEMPTIONS FROM READ PLAN: LANGUAGE ISSUE VS. READING ISSUE Language Exemption (Only applies to ELA-E students) If an ELA-E’s assessment score is SBGL and the teacher determines it is related to the student’s language development, then the student can be exempt from a READ Plan. • ARE recommends a READ Plan focused on Language Development to help these students. • Teachers should use the following student info to help make this determination: • ELL designation • English Proficiency based on W-APT • ACCESS scores and ACCESS Trajectory Status • Classroom observations • Other standardized assessments (CMAS, DRA2, SRI, etc.) *Please note: there are some cases where a teacher will have to make the decision with limited data. *More detailed information is available in the READ Act Guidebook. STUDENT EXEMPTIONS FROM READ PLAN Grade-Level Exemption • After fall testing, a student who previously was on a READ Plan has an assessment score that indicates grade-level reading and a body of evidence supports this score, the student does not need a READ Plan. • Enter the grade-level exemption in Assessment Applications. 3RD GRADE ADVANCEMENT/RETENTION POLICY DPS will not retain any student solely based on Significantly Below Grade Level (SBGL) identification in reading, but continue to use current Policies IKE and IKER. DPS highly recommends retention only be used in extreme cases when all other interventions/strategies have been exhausted because of the decades of research that shows retention as ineffective and harmful. • • Policy IKE: (Click here) provides grade retention depends on several factors including all of the following: – Academic skills, – maturity, – satisfactory completion of assigned work, and – likely success in completing the academic work at the next grade level. Policy IKE-R: (Click here) provides specific timeframe beginning 4 months before end of year and if parents and principal do not agree, the student will not be retained. Exemptions from the retention/advancement conversation by law: • • • students with disabilities eligible to take alternative statewide tests or the student’s disability impacts progress in developing reading skills, students with limited English proficiency, students previously retained in 3rd grade. 3RD GRADE ADVANCEMENT/RETENTION POLICY (CONT.) TIMELINE Month Action Steps January (early) ARE provides list of required students in School Folders. January –by end of month 1. Schools send Meeting Notification letters to parents 2. Schools call parents to set up meetings. February through end of year 1. Meetings occur 2. READ Plans updated by teacher March 1st If retention is seriously considered, academic interventions to address the student's needs will be developed and implemented by the first school day of the month. March through end of school If retention is seriously considered, continue to thoroughly year follow Policy IKE-R Anytime after meeting Complete and send Post-Meeting letter to parent informing of decision and rationale. For retained students, a copy of letter must be put in student’s permanent record. *More information on ARE’s website SUMMER ACADEMY 2015 All K-3 students on READ Plans will be required to attend the DPS READ Summer Academy in June. • For more information visit the Summer Academy website: http://ela.dpsk12.org/instruction/dps-summer-academy/ • Contact: – Alejandra Estrada – Alejandra_Estrada@dpsk12.org or DPSSummerAcademy@dpsk12.org – 720-423-3523 ASSESSMENT APPLICATIONS & OASIS DATA ENTRY • All READ Plans are created and data is entered through https://are.dpsk12.org/assessapps/ or https://aresecure.dpsk12.org/assessapps/ Let’s watch how I access OASIS Data Entry in Assessment Apps. ASSESSMENT APPLICATIONS & OASIS DATA ENTRY ASSESSMENT APPLICATIONS & OASIS DATA ENTRY QUESTIONS? READ ACT ASSESSMENT WINDOWS, REQUIRED STUDENTS, AND ASSESSMENTS TO USE READ Act Windows Fall (Initial Screener) Fall (30 Day Verification) Midyear Spring Kindergarten 8/24 – 10/23 10/26 – 12/14 12/14 – 2/3 4/6 – 5/17 Grades 1-3 8/24 – 10/5 10/6 – 11/19 12/14 – 2/3 4/6 – 5/17 Grades 4-12 8/24 – 10/5 N/A 12/14 – 2/3 4/6 – 5/17 Let’s take a look at the Timeline and Requirements Document. (Under General Resources http://dpsare.com/read-act/) QUESTIONS? 5 MINUTE BREAK Istation specific training next! WHAT IS ISTATION? Istation… • is a web-delivered Computer Adaptive Test (CAT) that diagnostically assesses student ability in critical domains of reading, • provides web-based reports detailing student strengths/areas of need and links to teaching resources, • allows teachers to make informed decisions to target reading instruction and intervention strategies. Istation is designed to… • identify children at risk for reading difficulties, • provide continuous progress monitoring of skills that are predictors of later reading success, and • provide immediate data linked to student learning needs. The entire assessment… • requires 40 minutes or less • can be administered individually, small group, whole class, to an entire school, and even an entire district in a single day - given adequate computer resources. WHAT IS A COMPUTER ADAPTIVE TEST (CAT)? CAT tests… • adjust to the ability of the child • replace the need for multiple test forms How does a CAT test work? CRITERIA FOR SELECTING APPROPRIATE ISTATION TEST By Grade level: • K-3 = ISIP Early Reading. • 4-8 = ISIP Advanced Reading. • K-3 students receiving the majority of their literacy instruction in Spanish = ISIP Español. (ARE is working with the ELA department to provide a decision-tree to help teachers/school staff make these decisions). PROGRESS MONITORING WITH ON DEMAND ASSESSMENTS What are On Demand Assessments? Teachers will have the ability to assign shortened forms of the assessment that focus on the areas of reading selected. – ARE recommends specific Subtests (5-10 minutes) throughout the intervention cycle to measure progress. – Be mindful not to over assess. Availability of On Demand Assessments Month Website defaults to… On Demand Assessment Availability August to October Full assessment Only after full assessment taken by student November to March On Demand Anytime, but must assign all subtests for each student April to May Full assessment Only after full assessment taken by student June On Demand Anytime, but must assign all subtests for each student How to schedule On Demand Assessments? Use the one page document on the ARE READ Act website. ISIP EARLY READING ISIP EARLY READING DOMAINS AND SUBTESTS Domain Subtest Item Types Phonemic Awareness Phonemic Awareness • • Beginning Sound Phonemic Blending Phonics Letter Knowledge • • Letter Recognition Letter Sound Alphabetic Decoding • Alphabetic Decoding Spelling • Spelling Vocabulary Vocabulary • • Picture Items Synonym Items Comprehension Listening Comprehension* • Listening to story, question read aloud, and picture answers. Reading Comprehension • • Matching sentences and pictures Sentence Completion Text Fluency* • 2-minute maze task where every fifth or sixth word is blank Fluency *Text Fluency and Listening Comprehension use parallel forms that measure end-of-grade level expectations and are not CAT items. ISIP ADVANCED READING ISIP ADVANCED READING DOMAINS AND SUBTESTS Subtest Item Types Word Analysis • Vocabulary Select the word that: • best matches the definition • Is most similar in meaning to the following word • Best describes the following picture • Is most similar in meaning to the underlined word Reading Comprehension • • • Timed passage with 4 MC questions. Not allowed to go back to passage Narrative and expository texts that measure: o Main idea o Cause/effect or problem/outcome o Inferences o Critical judgment of the text Text Fluency* • 2 ½ minute maze task where every seventh word is blank; choose from 3 words. Spelling ISIP ESPAÑOL • Aligned to Spanish Language Arts & Reading standards including… – WIDA (World-class Instructional Design and Assessment) – Estandares del desarrollo de la lectura (Reading Development Standards) from United States, Puerto Rico, Columbia, Mexico and Spain Ministries of Education • • • Developed in Spanish by native speakers of Spanish Not a translation Assessment items include cultural references to Spanish speaking countries Why is this important? Research shows… • “Teaching beginning Spanish Literacy is different than teaching beginning English literacy because the linguistic nature of the two languages is different (Myer, 2010).” • “It is important that teachers know how reading in Spanish is similar to and yet different from, teaching reading in English (Escamilla, 1999).” FOUNDATIONAL DIFFERENCES IN TEACHING ENGLISH VS. SPANISH READING SKILLS - MYER, 2010 English Spanish Phonemic awareness taught in pre-reading stage Phonemic awareness taught concurrently with reading and writing Not a direct sound to symbol correspondence Direct sound to symbol correspondence Consonants before vowels Vowels before consonants Letter names taught before/ in conjunction with initial sounds Letter names taught after initial sounds 16 vowel sounds 5 vowel sounds Key phonological structure: Onset and Rime Key phonological structure: Syllable unit Monosyllabic words common and typically used in beginning reading instruction Very few monosyllabic words; 2 and 3 syllabic words common in beginning reading instruction Words sounded out by individual Words sounded out by syllables ISIP ESPAÑOL ISIP ESPAÑOL READING DOMAINS AND SUBTESTS Domain Subtest Conciencia Fonológica Item Types Destreza fonológica y fonética Phonemic and phonological awareness Letter sounds, beginning rhyme, rhyming and blending Comunicación escrita Written Communication Grapheme-phoneme correspondences and syllabic awareness Vocabulario Vocabulario Vocabulary Vocabulary Oral and academic vocabulary including derivatives, associatives, prefixes, and suffixes. Comprensión Comprensión auditiva* Comprehension Listening Comprehension Phonemic Awareness Conversión Grafemafonema Grapheme-phoneme conversion Comprension de lectura Reading Comprehension Lectura con Fluidez Lectura con fluidez* Fluency Text Fluency Listening to one narrative and one expository passage; question read aloud, and answered. Narrative and expository texts paired up with inferential and evidential questions Receptive fluency with text comprehension (Maze task where every seventh word is blank) *Lectura con fluidez and Comprensión auditiva use parallel forms that measure end-of-grade level expectations and are not CAT items. WHAT DOES ISTATION MEASURE BY GRADE LEVEL? ISIP Early Reading/ISIP Advanced Reading ISIP Español NUMBER OF ITEMS PER SUBTEST To ensure Istation presents reliable, valid data for instruction, students will see a minimum number of items per subtest: Assessment Number of items per subtest Overall Reading Ability Index Score Range ISIP Early 5 to 20 Reading/Advance d Reading ISIP ER: 0 – 290+ ISIP AR: 0 – 2240+ ISIP Español 0 – 985+ Information not provided in technical manual. We are following up with Istation. ISTATION SCORES Ability Index • a measurement scale that aligns student performance levels with test question levels of difficulty on the same scale. ISIP determines the difficulty level at which the student is able to perform and An ability index is assigned for overall reading and individual subtests. • Since ISIP is adaptive and the test questions are displayed based on student performance, not age or grade, identical ability indices across grades mean the same thing. For example, a first grader who receives a score of 215 and a third grader who receives a score of 215 are performing at the same level. Grade Level Equivalencies • Based on 2010–2011 norming group, the grade level equivalent (GE) represents the grade level and month of the typical score. If a student receives a GE of 2.4, this means that the student earned a score similar to the 50th percentile students in the test’s norming group who were in their fourth month of Grade 2. • The grade level equivalent does not represent the appropriate level of instructional material with which a student should be placed. Grade level equivalencies should never be interpreted literally, but rather as a rough estimate of a student’s grade level performance. ISTATION SCORES (CONT.) • Difference Between Ability Index Scores and Grade Level Equivalencies – There are basic differences between Ability Index Scores and Grade Level Equivalencies. The Ability Indices represent a student’s performance on a measurement scale of skill and reading ability. In contrast, the grade level equivalent represents a student’s performance in comparison to students who were in the norming group. • Lexile® Reader Measures – Istation has partnered with MetaMetrics®, developer of the widely adopted Lexile® Framework for Reading to link student comprehension scores from ISIP to the Lexile scale. Students are given a Lexile reader measure every time they take the ISIP Early Reading comprehension subtest. The comprehension subtest is typically given to students in Grade 1 through Grade 8. – Because Lexile measures place readers and texts on a common scale, teachers and parents are able to match students with appropriately challenging reading materials. ISTATION INSTRUCTIONAL TIERS Istation Proficiency Levels Tier 3 DPS Proficiency Levels 0 – 20th percentile SBGL – Significantly below grade level 21st – 39th percentile Tier 1 40th – 100th percentile GL/AG – Grade Level or above grade level INSTRUCTIONAL TIER GOALS FOR EACH ASSESSMENT • • Istation provides Instructional Tier Goal Charts by month located on the website. Updated scores will be available in early September based on a new norming study. ISIP Early Reading Sample: CONNECTION TO OTHER ASSESSMENTS Reading Level Correlations • Istation completed empirical studies for DRA2 and Lexile levels. These are reliable data points, but ARE always recommends teachers use a body of evidence to truly represent a student’s ability. • Istation provides a Disclaimer for connections to other assessments on these documents. • Let’s take a look! QUESTIONS? GETTING STARTED GUIDES 1. Getting Started with Istation 2. Assisting Young Students with Technology 3. Assessment Day Script in English and Spanish Click on the pictures to download a PDF. TEST ENVIRONMENT AND SECURITY Testing environment… • provides best opportunity for student to succeed. • does not distract nor assist student in any way. • has excellent lighting and temperature. • is free of clutter. • is always actively proctored by teacher whose students are being assessed. Security Student login cards are not distributed until moments before start of test. TEACHER/SAL GETTING STARTED WEBINAR • • • Go to www.dpsare.com/read-act/ Select Elementary / K-8 Under Training Istation Getting Started Webinar LOGIN INFORMATION Teacher/SAL/Admin login Username – DPS Active Directory Login Password – Emailed directly from vendor, will have to change after logging in for the first time. *We recommend that teachers use the same password as their DPS username. Student login Username – 6-digit DPS Student ID, 123456 Password – 8-digit birthday, MMDDYYYY Teacher dashboard access – www.istation.com Student assessment access – via application installed on device BEFORE THE FIRST ASSESSMENT: SAL CHECKLIST Istation app is downloaded and ready for student use. Verify correct student data is imported into Istation to create user accounts. Reliable headsets are connected to student technology where Istation will be used. Student login cards are printed and ready for student use. Active monitoring of students is planned to ensure fidelity of program results. Teachers become familiar with student assessment by logging in with their own account information. STR Check-in: Programs installed and computers are rebooted daily and/or between sessions. Have technical issues come up? Have administration issues come up? Have appropriate contacts been notified? Set up testing schedule for school with proper accommodations for qualifying students. DURING THE ASSESSMENT: ACTIVE PROCTORING Why do teachers need to actively proctor the assessment? • To collect accurate assessment data that provides accurate picture of student performance • To maximize instructional time What does Active Proctoring look like? The teacher… actively monitors students during the test (i.e., walk around the room). does not interact with students while they are responding to a question. does nothing (verbally or nonverbally) that may impact a student’s answer. keeps the computer monitors in view. (i.e., students SHOULD NOT browse the web during the test) makes students aware that computer-based assessments are formal assessments with no talking or looking at another’s computer screen. cannot use their own computer during assessment. verifies the student logs off the computer after completing the assessment and sits quietly until the testing session is complete. allows students to read, but not to get back on the computer. AFTER THE ASSESSMENT Train teachers how to… identify useful reports to help drive instruction group students and identify focus for instruction administer linked and recommended Istation Teacher Directed Lessons. create required READ Plans for identified students schedule On Demand Assessments to determine if student is responding to intervention TEACHER SAMPLE TESTS • • Teachers can take a sample test by starting the student application and entering login credentials. Assessment defaults to grade level of teacher’s classroom. – This can be changed in Edit Manager after searching for your name and clicking the button below: WHAT ARE ASSESSMENT ACCOMMODATIONS? • Changes made to assessment procedures that provide students with an equal opportunity to demonstrate knowledge and skills • Changes that do NOT: – affect the reliability or validity of the assessment – alter the instructional level, content, or the performance criteria WHAT ACCOMMODATIONS ARE AVAILABLE FOR ISTATION? Accommodation What does the accommodation look like? Scribe • While a scribe is not an approved accommodation for an adaptive test, the test proctor can use the mouse or keyboard to respond for students with physical limitations that prevent students from answering independently • Must be tested individually in a separate test environment. Untimed assessments • Only available for students with extended time built into their IEP. Otherwise, it is not available. Oral Instruction • Oral instruction may be provided for the activities if necessary, including instructions in sign language. More TBD • We are still working with Istation to figure these out. Presentation accommodations such as braille are not available for a computer adaptive assessments, in these cases please use an alternate literacy assessment to measure student reading achievement and progress. QUESTIONS? HOW CAN ISTATION REPORTS SUPPORT INSTRUCTION? • • • • • Assessment reports automatically group students according to the level of skill and support needed. Teachers are provided links to teacher-directed plans of instruction, downloadable lessons, and materials appropriate for each group. Data is provided in both graphical and detailed numerical formats on every measure and at every level of a district’s reporting hierarchy. Data can be pulled at the student, teacher, classroom, school, and network level. Individual student information can be provided to parents or guardians of students tested. SUMMARY OF REPORTS AVAILABLE TOP REPORTS USED BY TEACHERS • • • Summary Report Priority Report Student Summary Report Each report allows teachers to drill down to each iteration of the assessment that shows: – Questions answered – Student selected response – Correct answer – Time spent on each question SUMMARY REPORT The ISIP Summary Report shows the number and percentage of students at each instructional tier for the current month. Individual students broken out here After ISIP, students are automatically classified by tiers Scroll over the data for a more in-depth look PRIORITY REPORT The Priority Report alerts teachers of students needing additional support, and provides lessons based on demonstrated weaknesses. Student’s are grouped according to specific need Lessons are prescribed here (PDF) Teachers can document the intervention creating an audit trail! STUDENT SUMMARY HANDOUT The Student Summary Handout provides student performance data from the most recently completed ISIP assessment. Each Dot is a Data Point WHAT RESOURCES ARE AVAILABLE ON THE ISTATION WEBSITE? • • • • • Access to all reports and data – Customize and save reports – Editing/printing/exporting reports in various formats Teacher Resources – Teacher Directed Lessons – Reading Level Correlation Chart – Instructional Tier Goals – Percentile Rank Charts – Glossary of Terms Help Center – Teacher/Administrator, Tech/STR, and PD Training Videos Interactive User’s guide Lexile – Find a Book QUESTIONS? TECHNOLOGY REQUIREMENTS • • To take the assessment, every student needs: – Device (desktop, laptops, or tablets) • Headphones (regular headphones can be used; same type used for CMAS) • Mice • Tablet keyboards needed for ISIP Advanced Reading for grades 4-8 Runs on Windows, Macintosh, Chromebook, iPads, and other tablets. HARDWARE/SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS • • • STRs will set up all devices to administer the assessment. Istation runs on several platforms and has very modest hardware requirements. Especially important to note is that Istation products run easily on iPads and MacBook Airs. You can run Istation from a small client app installed on your desktop or you can run the program as a completely web-based program. If you run products as an installed app, the following requirements apply: WHO TO CONTACT WHEN THINGS GO WRONG? Start with… 1) READ Act SAL, then the.. 2) School Technology Representative (STR), then either… 3) Issues with Technology Issues with Administration (network connectivity, hardware, etc.) (logins, misadministrations, missing students, etc.) • DoTS Hotline - 720-423-3888 • READ Act SAL (Peter Tardif, 720-423-3766) • Istation Assessment Coordinator (Ashely Jakubowski, 720-4232197) • ARE Hotline 720.423.3736 4) Istation Customer Support: (Open Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM to 7:30 PM) E-mail – support@istation.com Phone – 866-883-7323, press 2 ACCESSING ISTATION’S WEBSITE Let’s take a look! • • • • www.istation.com Select Customer Login Type in your login info – Username = DPS Active Directory Login – Password = Unique emailed from Istation Use top bar to navigate the webpage QUESTIONS? CLOSING • Rochanda Jackson - Manager of Assessment Administration Rochanda_jackson@dpsk12.org 720-423-3758 • Ashley Jakubowski – Assessment Coordinator (ANet and Istation) Ashley_jakubowski@dpsk12.org 720-423-2197 • Peter Tardif - READ Act Coordinator (DRA2/EDL2, Istation, STAR) Peter_tardif@dpsk12.org 720-423-3766