Coral Reef Biome
advertisement

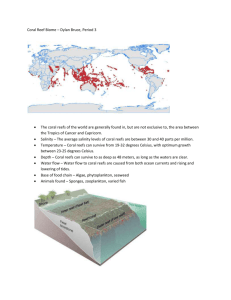
The Coral Reef Biome A Look at a Marine Biome © Terri Street, 2002 What Is a Coral Reef? A structure formed by coral polyps, tiny animals that live in colonies. Coral polyps form a hard, stony, branching structure made of limestone. New polyps attach to old coral and gradually build the reef. Types of Coral Reefs Fringing reefs Submerged platforms of living coral extending from the shore into the sea Barrier reefs Follow the shore but are separated from it by water Great Barrier Reef is world’s largest Types of Coral Reefs Atolls Ring-shaped islands of coral in open sea Form on submerged mud banks or volcano craters Surround a seawater lagoon Channels connect lagoon to the sea A World of Coral Reefs = Coral Reef Coral Reef Climate Usually found near land in shallow, warm salt water Lots of light Tropical temperatures, averaging 70°-85° F Most coral cannot survive below 65° F Coral Reef Plants Phytoplankton Microscopic Basis for all ocean food chains Coral Reef Plants Algae Green Red Brown algae takes many forms Coral Reef Plants Seaweed and Sea grasses Brown seaweed Sea grass Shoal grass Turtle grass Fascinating Fact: The Great Barrier Reef World’s largest coral reef Over 1257 miles long Off the northeast coast of Australia Only grows about one inch per year The Great Barrier Reef: Home to… 1500 species of fish 400 different types of coral 4,000 mollusks 500 species of seaweed 215 species of birds 16 species of sea snake 6 species of sea turtle Whales visit during winter Coral Reef Creatures Coral polyps Tentacles Digestive sac Connecting filaments Skeletal body Coral Reef Creatures Symbiotic relationships Coral with algae Clown fish with sea anemones Coral Reef Creatures Tropical fish Angel fish John Dory Butterfly fish Sea horse Octopus Reef shark Fascinating Fact: The Sea Horse Very weak swimmers Female lays eggs, male carries them in pouch till birth Only animal in which the father gives birth Body covered with armored plates Sample Food Chain Starfish Coral Octopus Zooplankton Moray Eel Phytoplankton Endangered Coral Reefs Major threats to coral reefs include: Ocean pollution Dredging off the coast Endangered Coral Reefs Other dangers: Careless collection of coral specimens Sedimentation Inhibits growth of coral polyps Inhibits algae growth Upsets balance of the biome Saving Coral Reefs Oceanguard (Australia-based) Focus is preserving the Great Barrier Reef Fight invasions of Crown of Thorns starfish Education Saving Coral Reefs Reef Relief (Florida-based) Coral Nurseries Education Promote reef conservation legislation References “Coral Reefs.” World Book. Chicago: World Book, 1998. Vol. 4, p. 257. “Coral Reefs.” http://kidscience. about.com/kids/kidscience/cs/ coralreefs/