Stethoscopy_files/Final Project 639 stethoscopy
advertisement

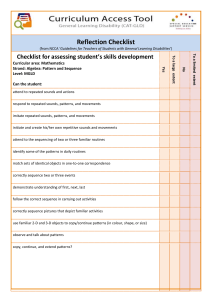
Final Project Stethoscopy for Dummies Session Bob Page EDAE 639 12-13-2014 Introduction: This class is designed to be a supplemental course that current paramedics, EMT’s, and nurses can take for continuing education credit. Audience analysis polling revealed that most providers do not have the fundamental knowledge required to use a stethoscope properly. The basic assumption is that the learners have had some introduction in the use of the stethoscope. The overall objectives for the course is that the learner will be able to use their stethoscope in a clinical setting and can correctly identify various normal and abnormal breath sounds. Audience analysis: The purpose of this audience analysis is to determine the knowledge level and confidence level of prospective students to take a stethoscopy class. The first section is a self-assessment (a 5 point Likert scale) to determine a baseline of how they feel they grasp the skill. The second part is actual assessment of their knowledge. I do it this way because some students will say they know something but indeed they do not. By doing this I can gauge the level of interest and the genuine knowledge gap and needs of the student. The questions will be anonymous using an audience response system and the students will have clickers to respond to the questions that appear on the screen. This will allow for quick and measurable feedback. The Likert scale will appear on the screen with each question to prevent confusion in answering. The second set of questions featured a real breath sounds played aloud and the participants hear them and select the correct answer. Here is an example of the question that appeared on the screen. Results The audience was informed that the study was to determine their needs and interest in a class on stethoscopy. I asked the participants to be honest and open with their answers. I polled a total of 104 students in two separate venues: Gunnison, Colorado and Panama City, Florida. Overall I was surprised that there was a difference between their perceived knowledge and their actual knowledge of procedures and performance in identifying sounds; A big difference. The perception questions were presented first before the learners were actually tested. I did this to gauge their perception of their own skills. When asked to respond to the statement: “I feel I am completely competent is my skills in using a stethoscope.” Only 20% disagreed with the statement meaning they did not feel competent at all. However 80% thought they were confident. When asked about their initial training on a stethoscope, 59% thought they didn’t receive sufficient initial training. This was intriguing because it did not correspond with their perception of their skill. They must have learned through experience. I asked a pure clinical question that was used to gauge the perceived value of breath sounds. “I listen to breath sounds on every patient.” 92% disagreed, which tells me that the providers are only listening when they think the patient has a condition that the need to listen. The questions about their perceived need for more training was very telling as most agreed they needed more training. That was also apparent because a large majority voiced they did not have a way to train on this themselves. Then when put to the test to actually identify sounds that were played aloud, the results were very clear that more training in sound identification was needed. When all sounds that were played, less than 30% correctly identify any one sound. The raw results from all of the questions are in appendix B. Conclusions Based on the data in this audience analysis, there is strong evidence that the class is not only needed but is also desired but the audiences polled. I also learned the students may not value the information gained by the stethoscope as they do not listen on every patient. This is not promising as experience is only gained by practice and valuable information is being lost. In developing this course, I will include several cases where routine breath sound assessment reveals unexpected results. I also think that the lack of doing lung sounds assessments may also be due to their not being at all confident on how to use a stethoscope. Although I did not poll the learners after they were assessed on their ability to identify the sounds. It was apparent to me that they struggled to identify the sounds. This class is going to be a real success and a much-needed offering that should fill in a learning gap that exists. Appendix A: Question List Section 1 Audience instructions. After carefully considering the following statements, please respond with your clicker with the number that corresponds with your answer. 1. Strongly Agree 2. Agree 3. Neither agree or disagree 4. Disagree 5. Strongly disagree Statements 1. I feel I am completely competent is my skill in using a stethoscope. 2. I received sufficient training in using a stethoscope in my primary EMS course. 3. I listen to breath sounds on every patient. 4. I can easily recognize normal breath sounds by location heard 5. I can easily recognize and name adventitious breath sounds. 6. I am aware of the proper procedure for auscultating breath sounds. 7. I have access to a lab that I practice listening to breath sounds. 8. I need more practice in using a stethoscope. 9. I need more practice in identifying the various breath sounds. 10. I would take a class on stethoscopy if one were offered. Assessment: 1. When auscultating breath sounds, which of the following statements are true? a. They are high pitched sounds heard with a bell b. They are high pitched sounds heard with a diaphragm c. They are low pitched sounds heard with a bell d. They are low pitched sounds heard with a diaphragm 2. Blood pressures should be taken with a. The bell of the stethoscope b. The diaphragm of the stethoscope Listen to the following sounds and select the correct answer to these questions 3. Identify the following breath sound. a. Normal vesicular b. Normal broncho-vesicular c. Normal tracheal d. Normal bronchial 4. Identify the following breath sound a. Monophonic wheeze b. Polyphonic wheezes c. Stridor d. Crackles 5. Identify the following breath sound a. b. c. Normal vesicular d. Course crackles e. Fine crackles f. Rales 6. In using a stethoscope with a tunable diaphragm, which of the following techniques will result in the user hearing low frequency sounds. a. Diaphragm lightly held b. Diaphragm firmly held c. Bell lightly held d. Bell firmly held With this information in mind, I have developed the following course designed to address the needs and requests of EMS medical professionals Course Proposal: “Stethoscopy for Dummies” Time Frame: 60-75 minutes or 2 hour hands on Skills Session Audience: All, BLS, ALS CEU category: Assessment Web Page Link: http://www.multileadmedics.com/www.multileadmedics.com/Stethoscopy.html How much did you pay for your stethoscope? How much training did you get on how to use it? This will fill the gap. In this session, participants are provided down to earth “for dummies” information on various types of stethoscopes and how to use them to get the most out of patient assessment. In this “Ear Opening” session, new and improved methods and techniques are presented and you will get the chance to practice this on others. Breath sounds are also played aloud so all participants can hear the sounds rather than hear a “description” of the sound. Stethoscopy with Skills Session: 2 hours In this session, participants must bring heir own stethoscopes with them. Bob brings simulators for all participants to use their own stethoscopes to hear the various sounds. There is even a test at the end of class to see who earns the right to wear the stethoscope! Objectives By the end of this session, the participant will be able to 1. Describe the parts of the stethoscope and the proper way to wear it 2. Describe the difference in the bell vs the diaphragm and the use for each 3. Identify by sound, common normal and abnormal breath sounds 4. Describe a technique for identifying consolidated lung tissue 5. Value the use of a stethoscope as a primary assessment tool on every patient contact. Sub-objectives: 1. Given a stethoscope, correctly identify the bell, diaphragm, tubing, earpiece and yolk with 100% accuracy 2. Describe the difference between the bell and the diaphragm. 3. Demonstrate on another person or simulator, each of the proper locations for a 6 point breath sound assessment. 4. Demonstrate the proper use of a tunable diaphragm stethoscope on another person for both high frequency and low frequency sounds. 5. Correctly identify by sound all of the following: normal tracheal, bronchial, broncho-vesicular, and vesicular breath sounds. 6. Correctly identify by sound all of the following adventitious breath sounds of narrowed airways such as wheezes and stridor. 7. Describe the difference between polyphonic and monophonic wheezes. 8. Correctly identify by sound all of the following adventitious breath sounds of mechanical obstruction: course and fine crackles and consolidated tissue. Lesson Plan: Stethoscopy for Dummies Materials needed: Stethoscope, sounder, handout/course syllabus, clicker, alcohol wipes Time needed for lesson: 2 hours Time Index Prior to start Objective Baseline assessment History and why use a stethoscope 0 -15 minutes 15 – 30 minutes Describe the parts of the stethoscope and the proper way to wear it SO - 1 Describe the Content On screen poll Sounds overhead Brief history How a stethoscope works Methods Clickers, Q and A The parts of the scope Hands on wearing and seating the scope in your ears Lecture Powerpoints Photos and old stethoscope tacticle Photos of proper ways to wear in a PowerPoint. In seat practice in small groups How to adjust the Students pair up Instructor B. Page B. Page B. Page 30 – 40 minutes 40-50 minutes 50-60 minutes 60-75 minutes 75 – 90 minutes 90 -100 minutes 100-110 minutes 110–120 minutes difference in the bell vs the diaphragm and the use for each SO 2,4 SO 3 Demonstrate on another person or simulator, each of the proper locations for a 6 point breath sound assessment. touch to hear different frequency sounds Respite Ears on Lab, Normal Breath Sounds OB - 3 SO - 5 Respite Normal Tracheal Bronchial Bronchovescicular Vesicular sounds Ears on Lab Abnormal breath sounds- Abnormal Sounds Stridor Monophonic and polyphonic sounds OB 3 SO – 6 -7 Ears on Lab Abnormal Sounds OB 3 SO 8 Review game show assessment Reflection and evaluations OB 5 How to do a methodical assessment of breath sounds using correct anatomical landmarks Abnormal sounds Crackles Consolidation All sounds Class discussion after a period of processing and practice. Show them quick, Show them slow, Let them practice, Let them go! Students pair up and practice. Show them quick, Show them slow, Let them practice, Let them go! Respite Live use of stethoscope on sounder. Play sounds three times for 15 seconds each Live use of stethoscope on sounder. Play sounds three times for 15 seconds each Live use of stethoscope and sounder Use stethoscopy final challenge game with clickers, scope and sounders Final evaluations with clickers and on screen questions B.Page B. Page B. Page B. Page B. Page B. Page B. Page When practicing the hands on skills with the stethoscopes, make sure participants wipe down their stethoscope before touching the volunteer. Emphasize the importance of direct skin contact to prevent extraneous sounds. Make gloves available for those that request it. Allow time for reflection after each task is done. Rubric for Assessment of Stethoscopy Skills This rubric is an assessment that can be used throughout a module by the instructor and the student for self-evaluation and for feedback on their progress towards skill mastery. Scoring Mastery - 4 Competent - 3 Progressing - 2 Beginning - 1 Identifies parts of the stethoscope Uses stethoscope properly Can easily identify all the parts of the stethoscope and can elaborate on the differences between scopes Can identify all the parts of the stethoscope without prompting Easily uses the stethoscope correctly and with confidence Can correctly identify all breath sounds correctly on one breath every time Wears and uses properly with some hesitation and deliberate movements Knows how to wear it properly, but need more practice to use properly Does not know how to wear a stethoscope or how to use it Can correctly identify all breath sounds correctly after a few breaths Can identify some of the parts of the stethoscope with some prompting Cannot identify an of the parts of the stethoscope Correctly Identifies breath sounds Can identify many but not all of the breath sounds correctly Cannot correctly identify any breath sounds I chose mastery at the top and beginning at the bottom. As a minimum, I want providers to achieve the competent level. To be considered competent, the student has to meet the objectives. Some will achieve the mastery level, the highest rating. Those that achieve mastery are expected to perform easily and with confidence, on their own without help. I tried to select the scoring based on a student’s progress towards mastery. The progressing phase is the students that has learned the skill but is in need of further practice. The beginning section is the student that has just started learning the skill as a baseline. Sounder Skills Practice When practicing the sounds with the sounder device, play the sounds for at least 15 seconds each. Allow time for a self-description and reflection of the sounds. Mention the correct name of the sound played before, during and after the sound. During the sounds practice, have the students assess each other using the rubric provided. The can get feedback from each other and help each other to obtain the minimum level of competency. The review assessment will be done using the clickers, their stethoscopes, and the sounders. Sounds will be played, the students will have 15 seconds to correctly identify the sounds they hear. Evaluation Plan: Pre-course Evaluation At the beginning of the class, I will use audience polling to determine the baseline attitude of my students towards their knowledge of stethoscopy skills and training in general. This will be done with clickers that each student will have. Questions will appear on the screen and students will answer with their devices. This type of polling is anonymous to the students but I can see the results via a bar graph on my screen giving me instant knowledge and feedback as to their responses. The questions will be general opinion questions based on the objectives I plan to cover in the course. The information gained from this polling will allow me to improve my delivery and content based on the feelings of the group. I will know what areas to emphasize and which do not need that much time spent it. Covering things the audience already knows well will not benefit the learner and will diminish the overall impact of the course. This also will help me to evaluate the success of the course design by spotting opinion changes in the pre and post course evaluation. The purpose of this type of formative evaluation is to try to measure the learner’s pre and post course opinions on their understanding of the information presented. I will use the following questions to measure their opinions before the class begins as a baseline for a comparative evaluation Audience instructions. After carefully considering the following statements, please respond with your clicker with the number that corresponds with your answer. 1. Strongly Agree 2 Agree 3 Neither agree or disagree 4 Disagree 5 Strongly disagree Statements 1 I feel I am completely competent is my skill in using a stethoscope. 2 I received sufficient training in using a stethoscope in my primary EMS course. 3 I listen to breath sounds on every patient. 4 I can easily recognize normal breath sounds by location heard 5 I can easily recognize and name adventitious breath sounds. 6 I am aware of the proper procedure for auscultating breath sounds. 7 I have access to a lab that I practice listening to breath sounds. 8 I need more practice in using a stethoscope. 9 I need more practice in identifying the various breath sounds. These questions are a baseline because I really want to see their response to the statements after having the opportunity for hands on and “ears” on learning sessions. Overall Summative Post-Course Evaluation The overall summative course evaluation will query anonymously the learner’s opinions of the instructor’s effectiveness and their thoughts on the learning techniques used and their desire to continue to learn. I really want to see how they will process the session and get to the “now what” phase. I will use the following questions in the post- course summative evaluation. Audience instructions. After carefully considering the following statements, please respond with your clicker with the number that corresponds with your answer. 1. Strongly Agree 2. Agree 3. Neither agree or disagree 4. Disagree 5. Strongly disagree 1. The instructor covered the stated objectives adequately. 2. The instructor encouraged questions 3. The instructor provided adequate feedback 4. The instructor used effective teaching techniques 5. The hands on use of the stethoscope drill was helpful to me 6. The ears on simulator experience was helpful to me 7. I would like more practice listening to the breath sounds 8. This class will change my practice using a stethoscope 9. After the class, I feel more confident using a stethoscope Using the Data from the Evaluation I will use the data from this post course evaluation to alter the methodology and delivery style of the material until the learning objectives and the behavioral objectives are met. Since this is relatively new or infrequently assessed skills, Questions 1-4 are designed to evaluate the instructor’s ability to establish a great learning environment. One that is conducive to learner’s engagement in the course. Since a course like this may seem to make the learner feel like they are ill prepared or hesitant to divulge their own weaknesses to the material, an open and honest approach to feedback and questioning is essential. This part of the evaluation should help to improve this important part for future classes by exposing weakness or areas for improvement. It is equally important to provide feedback to instructors doing a great job as well. The heart of the program is the “hands and ears” on approach to this skill. A considerable amount of time and practice goes into skill mastery of any given skill. Although this is not a very long course, the time spent should be based upon the learner’s feedback. Question 7 evaluates the learner’s need for more practice in a lab like this. When compared with pre-course evaluation on whether this training is actually available to the student, a new business opportunity for self run program similar to the lab can be explored. Another outcome is adding to the time for the course. How long is too long? The learner feedback here is vital. The practice labs should be of value to the learner. Questions 5-6 evaluate the effectiveness of the two main labs. Feedback from this will directly impact how future courses are tweaked. A simulator has the ability to make things easy or difficult for the learner. The feedback will allow the instructor to customize their delivery of this station to suit the learner’s needs. Many times in skill stations, advanced learners may indicate that it wasted their time. This evaluation should gauge that and changes be put into the course to accommodate advanced learners. The data gathered in the pre-course evaluation can help identify these learners at the start of the class. Final Analysis I want the learner to be able to value the importance of using the stethoscope correctly. It is through the knowledge gained and skill mastery that this goal will be achieved. Questions 8-9 evaluate the overall effectiveness of the course based upon a self-assessment of their confidence level in performing the skill. The impact of this course overall is increase the learner’s confidence and make the student reflect and process the information which will lead to future changes in their practice. I am also hoping that it will lead to different instruction design and techniques in teaching this skill on a larger scale. Web Page Link: http://www.multileadmedics.com/www.multileadmedics.com/Stethoscopy.html Follow this link to learn more and to download the handout for the course. NEW! In response to learner feedback and polls, Bob has developed a tool called a Lung Sounds Tutorial for the learner to continue practicing the skill after class in over, designed to take them to mastery level. More details are found on this web site: https://www.pinnacletec.com/medical-products-catalog/shop/breath-sounds/