Organic Chemistry Lab 5 – N.46 – Distillation
advertisement

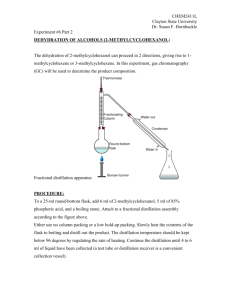
DISTILLATION PROCESS Distillation:An important organic process used to separate two or more than two liquids having different boiling points from a liquid mixture. An organic process used to separate a liquid organic compounds from a solid substance. According to the differences in boiling points between the liquids, distillation process classified into four types:1-Simple distillation. 3-Steam distillation. 2-Fractional distillation. 4-Vacuum distillation. Simple distillation:* The most common process used to separate two liquids whose boiling point differs at least by about 50 °C. Example:Separation diethyl ether (B.P=34°C), from dioxane (B.P=101°C). Separation chloroform (B.P=60°C), from an oil (B.P=220°C). * Separation of a liquid substances from the solid substances in a mixture. Example:Separation H2O (B.P=100°C), KMnO4 (B.P ≥ 240°C). Simple distillation components:Any simple distillation system composed from the following main parts:1-Heating source. 2-Distillation flask. 3- Thermometer. 4- Condenser. 5- Receiving flask . Separation of mixture by simple distillation:1- A mixture composed from A&B with boiling point (70 & 140) °C respectively is heated. 2- The lowest boiling point (A) will vaporized and ascended (elevated) from the solution till it reach the top of the system, with recording its real b.p. with the help of thermometer. 3- The ascended vapor will converts to the liquid form by the action of the condenser, then collect at the receiver. 4- Finally the highest boiling point will remain at the distillation flask. Simple Distillation Video FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION Fractional Distillation:Second technique of the distillation process, used to separate two liquids having close (near) boiling points (Lower than 25 °C). Example:Separation of ethanol (78) °C from water (100) °C . Fractional distillation components:Fractional distillation system composed from the following main parts:1- Heating source. 2- Distillation flask. 3- Fractional column. 4- Thermometer. 5- Condenser. 6- Receiving flask . Fractional Distillation Set-up Distillation Setups Distillation Process • • Liquid-Vapor Composition Diagram When a mixture AB of a specific composition is heated, the total vapor pressure (composed of the contributions of PA and PB) will rise until it is equal to the external vapor pressure. The mixture will begin to boil. The vapor which first forms is enriched in the more volatile component. This behavior is shown at right, •Assume a two component mixture with a composition of 30%A:70%B (point W). The boiling point of this mixture is found by drawing a vertical line from W to where it intersects the lower curve (point X). A horizontal line drawn from X to where it intersects the vertical axis (the temperature) gives the bp of composition W. From the point (Y) where this horizontal line intersects the upper curve (vapor) drop a vertical line to intersect the lower axis (the composition). Point Z gives the composition of the vapor which is in equilibrium with a liquid of composition W at its boiling point. Fractional Distillation AB at composition of 5% A boils at temperature L1 and the vapors with composition V1 enter the column at that temperature. The vapor will condense to a liquid with composition V1. The condensate L2 has a lower boiling point (because it has more of the lower boiling liquid A) and will thus vaporize at a lower temperature (warmed up by coming in contact with the additional vapors from below) to give vapors of composition V2. These vapors will condense somewhat farther up the column to give a condensate L3. If the column is long enough or contains sufficient surface area that many successive vaporizationcondensation steps (theoretical plates) can occur, the distillate that comes over the top is nearly pure A. Distillation yielding pure A continues until all of A is removed, after which the temperature at the thermometer rises to the boiling point of B. Distillation Efficiency •The efficiency of a fractional distillation is determined by the amount of “pure” liquid components obtained. Keep in mind that if a liquid is “pure” it will have a constant boiling point. The temperature of vapors in equilibrium with liquid at the boiling point will be constant. A plot of temperature vs. time for a pure liquid will look like A below. •The efficiency of a fractional distillation can be demonstrated graphically by plotting the change in temperature of the distillate over time (or over volume of distillate, as in this experiment). In a fractional distillation with low efficiency, separation will be poor. There will be little or no “pure” component as distillate. The composition of the distillate will be constantly changing and the bp of the vapor in equilibrium with liquid will be constantly changing. It will give a plot such as B. •An efficient distillation will give pure components which will have constant boiling points. Such a process is shown below in plot C. The relatively “flat: horizontal regions at the beginning and end of the plot indicate “pure” components A and B are obtained. The closer to this ideal sigmoid shape the better the fractional distillation. Proper Thermometer Depth