FIT L Ch17-18 Condit..
advertisement

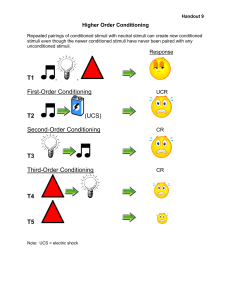
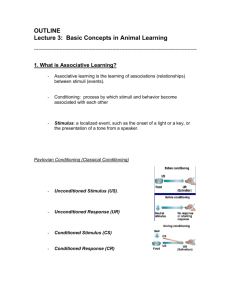
Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Addendum: 17A. Stimulus Combinations in Conditioning Overshadowing and Blocking Inhibitory Stimuli in Compounds Sensory Preconditioning and Second-Order Conditioning Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Some Examples • • • The effects of diet sodas, in the days when they were new Conditioning effects on physiological reactions such as responses to heat and cold The origins of drug overdoses in the conditioning effects of the user’s environment Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance \ Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Autoshaping • • • In autoshaping, a skeletal response, the pigeon’s key-peck, functioned as a conditioned response If the delivery of food reliably followed the lit key and the pigeon ate the food, it would soon start also to peck the key It did not learn to stop pecking when its pecks prevented food delivery Autoshaping • • • In autoshaping, a skeletal response, the pigeon’s key-peck, functioned as a conditioned response The conclusion: whether a response is motor or autonomic doesn’t tell you whether you can expect to see operant or respondent changes in behavior The physiology is not a reliable predictor of behavioral function Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli Addendum 18A: Biological Constraints on Learning Sensory Constraints Motor Constraints Constraints on Consequences Preparedness Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli The Example of Conditioned Suppression Basics to Applications From Electric Shocks and Conditioned Suppression to the Pediatric Burn Unit Effects of Pre-Aversive Stimuli • With no pre-aversive stimulus, the effects of the aversive stimulus disrupt behavior throughout the session • With a pre-aversive stimulus, behavior is disrupted during that stimulus, but the rest of the time is safe time • The time without a pre-aversive stimulus functions as a safety signal Effects of Aversive Stimuli • As the Burn Unit usually works, painful and intrusive procedures can occur at any time, and the child is stressed at all times • When procedures are signalled, the child is stressed when the signal occurs, but the rest of the time is safe time Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli Respondent Behavior: Conditioning Conditional Reflexes The Role of Elicited Responses Types of Conditioning Conditioning and Contiguity Contiguity and Consequences Autoshaping and Automaintenance Operant-Respondent Interactions: Emotion Conditioning and Emotion The Language of Emotion Preaversive and Preappetitive Stimuli Recapitulation Kinds of Contingencies and Contingent Stimuli