The 6 Kingdoms of Life POWER POINT
advertisement

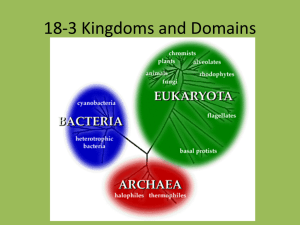
THE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE 6 KINGDOMS OF LIFE Alive? • To be considered living, an organism must… – Contain all 7 characteristics of life • • • • • • • DNA Reproduce Use energy Adapt Respond to Stimuli Made of cells Grow and Develop Leopard Gecko Leaf Tailed Gecko Kingdom Anamalia Anamalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Reptilia Reptilia Squamata Squamata Family Gekkonidae Gekkonidae Genus Eublepharis Uroplatus Species Macularius Phantaticus Class Order WHY CLASSIFY? To know how many known species there are in the world To know the characteristics of each species To know the relationships between species 7 Kingdom = Largest Group 6 Phylum 5 Class 4 Order 3 Family 2 Genus 1 Species Animal Kingdom * Food – Cannot make their own food. * Multi-cellular organisms * They have a nucleus (eukaryotic) * Can move on their own. Reproduction – Asexual and sexual Examples – Humans, crustaceans, spiders, insects, fish, birds, mammals, sponges, hydras, coral, worms, etc. Examples of Animals Sea horse Sea anemone hydra butterfly Poison Dart frog Great White Shark human Plant Kingdom * Food – make their own food by photosynthesis. *Multi-cellular * They have a nucleus (eukaryotic) * Cannot move on their own. Reproduction – Sexually and asexually Examples – rose, cactus, grass, daisy, ferns, trees Examples of Plant Kingdom Kingdom Fungi * Food – do not make their own food. Decomposers * Unicellular and multicellular. * Have a nucleus (eukaryotic) * Cannot move Reproduction – Sexual and Asexual Examples – yeast, mushrooms, mold, mildew, athletes foot, ringworm Examples of Fungi Athletes Foot Bread mold mushroom Foot Fungus yeast ringworm Bread mold magnified Kingdom Protists * Food – Some make their own food (plantlike); others cannot (animal-like). * Unicellular and Multi-cellular * They have a nucleus (eukaryotic) * Some can move on their own. Reproduction – Asexual & Sexual Examples – Euglena, paramecium, amoeba, slime mold, volvox, algae,diatoms, giant kelp Examples of Protists Paramecium Algae Amoeba Volvox Euglena Fission Stentor Red algae KINGDOM EUBACTERIA *Food – Some can make their own food: other cannot. * Unicellular organisms. * No Nucleus (prokaryotic) * Some move and other do not. Reproduction – asexual Roles: decomposers, food makers, help digest food, clean oil spills, makes nitrogen rich soil(helps plants grow), etc. Examples of Eubacteria Anthrax Bacteria help digest food Strep E. Coli Binary Fission Blue green algae Kingdom Archaebacteria This hot, sulfur-rich, acidic pool in Yellowstone National Park is home to species of Archea, including Sulfolobus. Some archaens live 1000’s of miles deep in the ocean near superheated volcanic vents. KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA * Food- Some cannot make their own food; others do. * Unicellular organisms * No Nucleus (prokaryotic) * Some can move and other cannot Reproduction – asexual Three main types – salt loving, heat loving, and methane makers, harsh environments Let’s Practice Which kingdom does each organism belong? Eubacteria Animal Protists protists plant Fungus Animal animal Fungus Eubacteria Archaebacteria BELLRINGERS 1. Define: living, dead, nonliving. 2. Give examples of living, nonliving and dead objects. 3. Describe how you would know if an object is living or nonliving? 4. Define: multicellular, unicellular, autotroph, heterotroph 5. Define: prokaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell 6. Define: taxonomy, classification, kingdom, organism Bellringer: Define: classification, taxonomy List 3 ways humans use classification every day. Classification of living things THE SCIENCE OF CLASSIFICATION Humans naturally like to put objects into groups in order to make sense out of the world around us. For example, at home you organize your socks from your pants, your forks from your cups. Classification Taxonomy - Grouping objects according to their similar characteristics. The science of classifying living things. WHY CLASSIFY? To know how many known species there are in the world To know the characteristics of each species To know the relationships between species SCIENTISTS BEHIND TAXONOMY Aristotle was the first person to come up with a classification system for living things. He divided animals into three groups: those that walked, those that swam and those that flew. Why was this not the best classification system for animals? NOT SO FAST ARISTOTLE!!! In the 1700’s, Carolus Linnaeus disagreed with Aristotle’s classification system. He invented the modern classification system we use today. It is called BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE. Today, scientists group organisms not only by their physical characteristics BUT by their evolutionary relationships (ancient ancestors). LINNAEUS’ SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION Binomial Nomenclature – A naming system that gives every living thing a TWO word name. This unique two word name is called the SCIENTIFIC NAME. Uses LATIN the language of scientists. Scientific names are always written in italics if typed or underlined if handwritten The first word is the GENUS and is always CAPITALIZED. The second word is the SPECIES and is always LOWER CASE. 7 LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION 1. Kingdom 2. Phylum 3. Class 4. Order 5. Family 6. Genus 7. Species **A scientific name is the genus and species. Katie Put Cream On Fresh Green Strawberries WHY TWO NAMES FOR EVERYTHING? Because people speak in more than one Because people give objects more than for example: language one name. What is the name of this cat? Mountain lion All are correct but its ONE scientific name puma cougar is Felis concolor American Lion LET’S PRACTICE Which scientific names are written correctly? HOMO SAPIEN Tyrannosaurus rex panthera leo Canis Lupus Felis domesticus elephas Maximus LOOKING FOR RELATIONSHIPS Remember that one of the goals of classification is to find out how certain living things may be related to one another. What makes a living thing part of the Animal Kingdom? Cannot Eukaryotic Multicellular Locomotion make its own food ARE ALL OF THESE ANIMALS? 7 LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION 1. Kingdom 2. Phylum 3. Class 4. Order 5. Family 6. Genus 7. Species **A scientific name is the genus and species. Katie Put Cream On Fresh Green Strawberries KINDOM ANIMAL PHYLUM CHORDATA CLASS MAMMALIA ORDER CARNIVORA FAMILY FELIDAE GENUS Panthera SPECIES leo Phylogeny – the evolutionary history of an organism PHYLOGENY OF MAN Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata (having a spinal cord) Class - Mammalia (have hair, give milk) Order - Primates (walk mostly on 2 legs) Family - Homindae (advanced brain that can think and reason) Genus - Homo Species - sapien PHYLOGENY OF THE WOLF Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata Class - Mammalia Order - Carnivora Family - Canidae Genus - Canis Species - lupus