**** 1 - bugilsocialstudies
advertisement

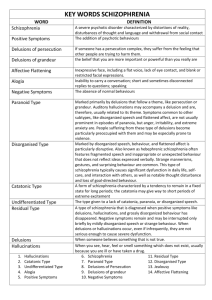
Which psychological disorder? If depression is the common cold of psychological disorders, chronic ___ is the cancer. Nearly 1 in 100 people will develop ___, joining the estimated 24 million across the world who suffer one of humanity’s most dreaded disorder (WHO). August Natterer (German artists)’s Witch’s Head Louis Wain •Conventional, naturalistic •Vibrant, erratic Schizophrenia APA: n. a psychological disorder characterized by disturbances in thinking(cognition), emotional responsiveness, and behavior. DSIM-IV-TR: a disorder that lasts for at least 6 months and includes at least 1 month of active-phase symptoms (two [or more] of the following: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior, negative symptoms) Diagnostic Criteria A. Characteristic Symptoms: Positive Symptoms two (or more) of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a 1-month period (or less if successfully treated): (1) delusions (2) hallucinations (3) disorganized speech (4) grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior (5) negative symptoms 1. Positive Symptoms Delusions 2. Hallucinations 3. 4. 5. Erroneous beliefs that involve a misinterpretation of perceptions/experiences Themes: persecutory, referential… Distortions in perception (auditory, visual, olfactory, gustatory, tactile) Not consider normal / religious experiences in certain cultural contexts Disorganized Thinking ★★★★★ Distortions in thought and language processes Derailment/tangentiality/incoherence Grossly disorganized behavior Distortions in self-monitoring of behavior Catatonic motor behaviors A decrease in reactivity to the environment 1. Negative Symptoms Affective flattening Restrictions in the range / intensity of emotional expression Facial expression, eye contact, body language 2. Alogia Restrictions in the fluency / productivity of thought and speech Brief replies, unwillingness to speak 3. Avolition Restrictions in the initiation of goal-directed behavior Little interest in participating in work /social activities B. Social/occupational dysfunction: one or more major areas of functioning (work, interpersonal relations, or self-care) are markedly below the level achieved prior to the onset Education, work, marriage, social contacts C. Duration: Continuous signs of the disturbance persist for at least 6 months. Must include at least 1 month of symptoms. D. Schizoaffective and mood disorder exclusion: b/c either (1) no Major Depressive, Manic, or Mixed Episodes have occurred concurrently with the active-phase symptoms, or (2) if mood episodes have occurred during active-phase symptoms, their total duration has been brief relative to the duration of the active-phase symptoms. E. Substance/general medical condition exclusion: the disturbance is NOT b/c direct physiological effects of a substance or a general medical condition. F. Relationship to a pervasive developmental disorder: if there is a history of Autistic Disorder or another Pervasive Developmental Disorder, the additional diagnosis of Schizophrenia is only if prominent delusions or hallucinations are also present for at least 1 month (or less if successfully treated). Subtypes 1. Paranoid A preoccupation w/ delusions or hallucinations Unless the Catatonic or Disorganized Type is present 2. Disorganized Disorganized speech, disorganized behavior (NO Catatonic Type present) 3. Catatonic Motoric immobility, excessive motor activity/negativism, peculiarities of voluntary movement 4. Undifferentiated Criterion A + No Paranoid/Disorganized/Cataonic Type 5. Residual Continuing evidence of the disturbance, but the criteria for the active-phase symptoms are no longer met. The Etiology – WHY? 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 1. Brain Abnormalities Dopamine overactivity Abnormal brain activity: frontal lobe, thalamus, amygdala Materal virus during midpregancy Genetic Factors Identical twins / adoption studies Specific genes: dopamine, neurotransmitters, myelin Nutritional /oxygen deprivation at brith Psychological Factors Social support, family problem-solving “refrigerator mothers” Age, Culture, Gender General: adults 0.5%~1.5%, urban-born Age: late teens~the mid 30s Culture Cultural differences (hallucinations, disorganized speech) Overdiagnose certain ethnic groups Gender Male: higher incidence Median age of 1st episode: mid 20s(M), late 20s (F) Possible Preventions? Cognitive-behavioral therapy Needs-based supportive therapy Supportive society, family, school Healthy life (exercise) Conservatorship Formal diagnosis at UCLA Medical Center Was hospitalized for psychiatric evaluation after setting fire in Californian neighborhood MCQ 1. A false belief that a person believes that he is being watched or tormented by others is known as a: ① Delusion of reference ② Persecutory delusion ③ Religious delusion ④ Somatic delusion ⑤ Grandiose delusion MCQ 2. The most common type of hallucination is: ① Olfactory ② Visual ③ Auditory ④ Tactile ⑤ Somatic MCQ 3. Which of the following is NOT a positive symptom of schizophrenia? ① Delusions ② Hallucinations ③ Disorganized speech ④ Alogia ⑤ Catatonic motor speech MCQ 4. Which of the following is NOT a subtype of schizophrenia? ① Undifferentiated ② Active ③ Residual ④ Disorganized ⑤ Paranoid MCQ 5. People with schizophrenia who have poverty of speech, inability to express their emotion and initiate a goal are said to be experiencing ______symptoms ① Positive ② Negative ③ Extrusive ④ Intrusive ⑤ Residual AP Style FRQ 1. 2. Schizophrenia is a psychological disorder that results in serious forms of suffering. Hence, psychologists have worked to identify its nature and origins. Identify three characteristic symptoms that are primarily used to diagnose schizophrenia. Discuss possible etiology for schizophrenia. Bibliography Amanda bynes' secret twitter account reveals possible schizophrenia symptoms & violent threats!. (2013, 10 1). Perezhilton. Retrieved from http://perezhilton.com/2013-06-05-amanda-bynes-secret-twitter-accountreveals-schizophrenia-symptoms/ American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author. American Psychological Association. (2007). APA dictionary of psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. Helicon. (2013, March 1). Re: Louis Wain: the effects of schizophrenia on the perception of the artist [Web log comment]. Retrieved from http://heliconbristol.blogspot.kr/2013/03/louis-wain-effects-ofschizophrenia-on.html Mash, Eric. J., & Barkley Russell A. (Eds.). (2003). Child psychopathology. New York: The Guilford Press. Myers, D.G. (2010). Psychology.(9th ed). New York: Worth publishers. Smith, M. (2013, 10 2). Amanda bynes new diagnosis bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Las Vegas Guardian Express. Retrieved from http://guardianlv.com/2013/10/amanda-bynes-new-diagnosis-bipolardisorder-and-schizophrenia/