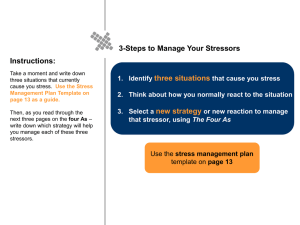
Physical signs stress
advertisement

Ch. 4 Lesson #1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Open: iSwifter APP Open the bookmarks tab and choose: “Glencoe chapter activities” Drop Down: “Chapter Activities” Choose: “Chapter 4” Open: “Interactive Study Guides” Open: “Lesson #1” http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0078726549/359991/InterActC h8Ls1.html Objective 1: Examine the causes and effects of stress. Objective 2: Differentiate how stress can affect physical, mental/emotional, and social health. Objective 3: Show how substance abuse harms mental/emotional health. Show video located on the “J” drive titled, “Help, I’m Stressed” 26 minutes in duration Try each of the 3 stress management techniques: 1. Exercise (for leisure) for a minimum of 20 min. 2. Listen to soft music for a minimum of 20 min. 3. Option: Choose 1 – warm BATH, massage, advice from a parent(s), reading a book for leisure (not for a class), drawing, playing a musical instrument for leisure. NEXT Answer the following questions for each technique (1, 2, & 3). This MUST BE TYPED A. What exactly did you do (use detail) B. After you were done, did you feel any stress relief? C. Would you use this relief technique again? WHY? The reaction of the body and mind to everyday challenges and demands Stress in Your Life Perception: is the act of becoming aware through the senses. One way to manage stress is to change how you perceive and react to events that cause it. Also, your reaction to stressful events depends on your previous experiences. Can have both a positive and negative effect. Question: What are some of the positive and negative effects? Stressor: is anything that causes stress. They can be real or imagined, anticipated or unexpected. What causes stress for you may not cause stress for someone else. Work with a partner and discuss the following: ACTIVITY: Share with each other what causes you stress. See if your partner also feels stress from that event/situation like you do. Three phases: 1. Alarm 2. Resistance 3. Fatigue When you perceive something to be dangerous, difficult, or painful, your body automatically begins the stress response. Example: when your camping and you hear an animal. Or, your younger and you watched a scary movie. Later in bed you hear noises in the kitchen. In the alarm stage, your body produces adrenaline. Adrenaline: Gives you a burst of energy and causes many changes in your body. The physical response is largely involuntary. Fight or flight response: The changes cause you to fight the stressor or “take flight” and escape. It’s not always possible to fight or take flight from the stressor. If exposure to a stressor continues, your body adapts and reacts to the stressor. The body may continue to function at a higher level for a brief period of time. Fatigue: If exposure to a stressor is prolonged, your body loses its ability to adapt. You begin to tire an lose the ability to manage other stressors effectively. ACTIVITY: physical & psychological responses to stress. Open the health web page and click on the link. Complete the Survey. When you are finished, I will put the results of the survey on the screen. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Physical signs stress Pounding heart Dryness of mouth Raised body temperature Lightheaded, dizziness, or faintness Trembling, shaking hands Speech difficulties Insomnia Grinding of teeth during the night Sweating Frequent urination Upset stomach Loss or increased appetite Increase substance abuse Accident proneness Frequent illness 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Psychological signs Irritability, tension, or depression Impulsive behavior Emotional instability Lowered self-esteem Reduced communication with others Avoidance of activities Forgetting things Decreased ability to perform tasks Inability to concentrate Nightmares Excessive work; omission of play The physical changes that take place in your body during the stress response can take a toll on the body. Prolonged stress can lead to Psychosomatic Response. Psychosomatic response: a physical reaction that results from stress rather than from an injury or illness. Some examples: Headache A weakened immune system High blood pressure Clenching the jaw or grinding the teeth Digestive disorders. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Open: iSwifter APP Open the bookmarks tab and choose: “Glencoe chapter activities” Drop Down: “Chapter Activities” Choose: “Chapter 4” Open: “Health Inventories” Open: “Chapter 4” http://www.glencoe.com/qe/qe148inv2007.p hp?qi=3457&state=na