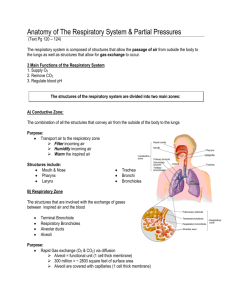
physiology_lec23_16_3_2011
advertisement

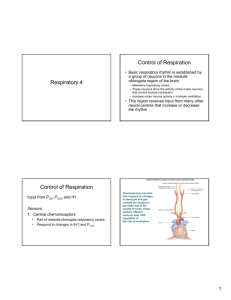
Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 physiology regulation of respiration we will talk about “control of breathing” Control of breathing aims to maintain normal O2 and CO2 in the blood. We have : respiratory center system(respiratory controller system) “which maintain homeostasis of co2 and o2” Therefore if u alveolar ventilation then Po2 will up tO 150mmHg (plateau). -Increase ventilation means “hyperventilation” The purpose of hyperventilation is to make the composition of alveolar air close to the composition of atmospheric air>>>(O2 and CO2 PAO2 ) PACO2 PACO2 P A O2 V Which means the more ventilation co2 “coz ur push out co2 from ur body” . 1|Page the less the alveolar Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 physiology regulation of respiration You make the alveolar air near the atmospheric air “so the co2 is low” VA PCO2 THE EFFECT OF CO2 ON VENTILATION More co2>>more ventilation( pco2 >>>>ventilation ) In the blood when co2 is high this will stimulate the respiratory controller system to drive ventilation more,therefore you push co2 out more. If p02 decreases in the blood there is an increase in ventilation to return po2 normal in the blood… ( 2|Page po2>>>>>> ventilation ) Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology 1 : 100% ventilation 2: double ventilation “hyperventilation” .5: 50% ventilation “hypoventilation N.B: po2 with vA is not linear relation WE NOTICE THAT: When PO2 increases in the bld more than 100 mmHg , it will not suppress V.(so 100 is the level that if pco2 reach it ,V is not affected means there is no contenious decreasing on v) . But if pco2 increases >>>v will increase “vice versa” 3|Page Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration Note that when p02 reach 60mmHg >>>> steap decline starts. ”steap curve” If Po2 < 60 mmhg … STOP >>>there is “ HB” HB “in RBcs” tells Po2 that : if u get down below 60 “I start loosing control” So if po2 < 60 “HB START TO LOOSE CONTROL” When po2 fall down from 100 to 60 >>> HB still holding po2 “not releasing 02) 90% : 18ml O2( 100%: 20 ml o2>>>15g × 1.34 ) From 18ml ,cells need only 5 ml (25% × 20) …so u still in agood shape When (p02 < 60 mmHg),,HB says: don’t worry >> So HB works …and respiratory center is at rest up to now . 4|Page physiology Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology keep ur respiratory center at rest ,don’t stimulate the respiratory center>>don’t do any hyperventilation >> don’t overload ur respiratory muscle “ I’m here I’m in a good shape” If po2 < 60 ,it will affect : 1. HB>>> bcoz o2 decrease. 2. CNS (there is asite which starts making firing impulses) Note : there is no contact between HB(its kinetic ,allosteric, interaction behavior and conformational changes …) & the respiratory center . Note : Respiratory neurons start working only if Po2 < 60 mmHg. _________________________________________________________ summarization The purpose of resp.center is maintaining po2,pco2 in the arterial bld gases>>>>> when we say,,we also involve H2, bcoz: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- +H+ ***CO2,is considered as an acid even it hasn’t (H+) NOW we can say that resp.system controls: 1. Po2 2.pco2 3.H2 Q: What stimulate the resp.crnter? A: - PO2, PCO2, H2 Q: Which do you think is a major controller or stimulator for the respiratory center, is it the (O2) 5 | POR a g e(CO2)??? Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology From (PO2 –HB) dissociation curve, we notice that if PO2 decreases from 100 to 60, it won’t affect>>>bcoz the curve isn’t linear>>>>>>>This means that O2 is NOT the major controller. BUT>>>> CO2: - The curve is linear, so any in PCO2 ,will be accompanied with in PO2 concentration . V PCO2 - IN hyperventilation>>>>> CO2 - IN hypoventilation>>>>>> CO2 6|Page pco2 VA Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology IN the Lung: Hyperventilated: PO2 ,,,, PCO2 apex Base Hypoventilated PO2 ,,,PCO2 When the contents of apex & base are mixed in the left ventricle as the follow: - If po2 in apex =130, po2 in base = 50>>>>>>the net po2 isn’t ((130+50)/2)>>>the result will be closer to 50!! So : we notice that the hyperventilation lung is unable to correct the hypoventilated lung>>>bcoz the shape of (O2HB) Curve isn’t linear , its sigmoidal. However……if the: PCO2 in apex =30,PCO2 in base= 50>>>>the net is (40)>>the curve is linear. so : 1. CO2 can correct itself (self compensatory). 2. Any or in PCO2 can affect the resp.center in order to maintain CO2. NOW,we can give an explanation for why PO2=95?? )21 (هدا السؤال ساله الدكتور في محاضرة 7|Page Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology Respiratory controller system: It s in the medulla oblongata... There are two groups of diffused neurons(in the respiratory crnter): 1. Dorsal respiratory group(DRG) 2. Ventral respiratory group(VRG) AT normal quiet breathing: -DRGs are working(active)>>>they send impulses to the phrenic neurons which located between (C3-C5)cervical (precervical 5) so it will be stimulated then>>>> it will stimulate the resp.muscles like Diaphragm . -VRGs are silent DRGs 1.inspirastory neuron (I) 2. AT normal quiet breathing: working(active) 3. they send impulses to the phrenic neurons which located between (C3C5)cervical (precervical 5) so it will be stimulated then>>>> it will stimulate the resp.muscles like Diaphragm . 8|Page VRGs 1. inspiratory & expiratory (I&E) 2. silent . 3. they can stimulate accessory inspiratory & expiratory muscle (internal intercostals& abdominal musle) Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology Note: if the collapsing tendency of the lung decreases like in ( COPD),where the elastic fibers are destroyed …now expiration is active . Pherinc neurons >>>>they lack automaticity ,they lack intrinsic ability to make there own AP. During exercise ,u may have both the VGR & DGR >BOTH r working In the medullary in different area,not with the respiratory center there is collection of neuron sensitive to chemicals (chemosensetive neurons)>>this chemical is H2. Above the medulla is the PONS,in the pons we have 2 accessory respiratory center One in the lower third of the pons we called it “Apneustic center” The other in the upper one third we called it “Pneumatoxic center” 9|Page Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology If we ask someone to stop his breath , ventilation (decrease)>>>CO2 WILL (INCREASE). From the cortex there is an inhibitory effect ..which inhibit neuron (pherinc)….then it will stop working >>no muscle contraction >>>no breathing >>co2 will increase in bld. Co2 reaches 50mmHg and bcoz co2 doesn’t have barrier so it will enter CSF >>where co2 combines to water (co2 + H2O-----> H2CO3---- HCO3- +H+ H+ >>>stimulate chemosensetive area in the medulla >>>its going to stimulate DGR>>>DGR will make strong stimulus on pherinc neuron. So until now: The pherinc neuron is under 2 different stimuli , one from the cortex(inhibitory),and the other from the medulla( stimulatory) The medullary stimuli is stronger than the cortical and thus stimulation of the diaphragm occur,therefore its not possible to anyone to suicide through stop breathing. *respiratory centers send sensory neurons (chemoreceptor) to sense po2 mainly and less exert to co2,H,in the aorta and carotid artery. So the sensory will go to aorta (the largest). 10 | P a g e Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology Po2=100,A Po2=40,V Po2=40 Po2=40 ARTERY The cell must sense the artery ,although it is surrounded by interstitial po2=40 In this work there is amiraculous manner Cells “chemoreceptor” The carotid & aortic bodies measure the chemoreceptor(po2) 3shan n5le el po2 elm7ee6 bl cell like el po2 elmwjood in the arterial aspect of the capillary 9ar fe m9’a3fe in arterial bld 3shrat elmrrat >>> mshan heek r7 tkoon el p02 mo 40 r7 tkoon btw 95-100 y3ne like el po2 in artery ****HOE DOESE THE INTERSTITIAL PO2 BECOME HIGH THAN NORMAL?? 1. Making the cells (don’t consume o2) metabolically inactive>>but this way cant be applied ,bcoz the cell which we talk about is the most active cell 2. Increase bld supply to this cell in which the cells whatever consume the result is (what is the left = what is dilever). The cells which have chemoreceptor these cells start 2 sending AP and stimuli to CNS (medulla),only if the po2 < 60mmHg so these cells don’t respond if the po2 is btw 60100….although these cells dn’t know about HB and its compliant. 11 | P a g e Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology Pco2 start affecting centrally Po2 start affecting peripherally Ventilation during exercise Exercise>>> ventilation What stimulate ventilation during exercise or wt stimulate the RSS during it??? PCO2 exercise VA During exercise the curve is shifted upward At rest if VA=1(100%),pco2= 40mmHg At exercise If the VA is doubled 5 times ,then the pco2 is also 40 this is bcoz as we know >> during exercise when amount of co2 “delivery “ amount of co2 “washed out” will the too. So ABG of pco2 still constant. - What drive muscle to contract during exercise ? - When stimuli come to muscle ,it also go to respiratory center >>>so when joints move >>they send impulse to the respiratory center to increase po2 ventilation. 12 | P a g e Lecture no.23 16-3-2011 regulation of respiration physiology For comatose person if he starts moving his legs he start hyperventilation So the same stimuli which drive muscle to contract ...they stimulate the ventilation tooo IF u go to high attitude place the % of po2 still constant”21%” but po2 will decrease then the peripheral stimulus will make more ventilation then co2 will decrease>>> this will suppress R.C SO there is 2 diff. “opposing stimuli” Co2 O2 >>>>suppression of R.C >>>>STIMULATION Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation: PH=6.1 + log (HCO3-/PCO2) - Any decrease in pco2 >>>increase in pH then the kidney starts excreating Hco3- in the urine so PH will back to normal.(no alkalosis neither acidosis)>>>there is no H+ inhibitory effect >>>so ventilation will increase. DONE BY:SUMAYA T. SHHADA This sheet is dedicated to my sisters: DR. Safeya shhada Aseel Dasan,Sumaya A.odeh,Aya Mhfooz,Nour Saddouq,Bayan saleh,Banan Mteir,Majd Madani,Rawan Hamdan,Rasha Al3wazim 13 | P a g e