PowerPoint - Orbital Shape & Orientation
advertisement
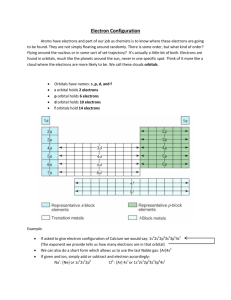
Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Bohr’s model… • Electrons are found in specific circular paths (orbits) around the nucleus. • The electrons have fixed energies called energy levels. (like rungs on a ladder) • The amount of energy required to move an electron to another energy level is called a quantum. The Quantum Mechanical model • It is based on the energy and possible location of an electron. • how likely it is to find an electron is described in terms of probability. (ie. Propeller blades) • Based on work done by Shrodinger… Atomic Orbitals • The energy levels of electrons are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n) • Each energy sublevel corresponds to an orbital of a different shape, which describes where the electron is likely to be found. Atomic Orbitals Shapes and Orientations of Orbitals 1s Orbital • Sphere around the nucleus The one tells you that the electron is in the orbital closest to the nucleus • S tells you about the shape 2s Orbital • Similar to 1s except the electron is most likely in the region farther from the nucleus p Orbitals • At the first energy level there is only the 1s orbital, after the second energy level there are 2p orbitals • Look like dumbbells • In the three directions Remember…. MAX NUMBER OF ELECTRONS IN AN ENERGY LEVEL ENERGY LEVEL MAX # OF ELECTRONS 1 2 3 4 5 2 8 18 32 50 Electron Configuration A detailed way of showing the order in which electrons fill in around the nucleus # of Electron Configuration sub level Symbols e in 2 1s Energy Level Sub Level (s, p, d, f ) We must follow 3 rules… • Aufbau priciple • Electrons occupy energy levels with lowest energy first. Pauli exclusion principle • If 2 electrons occupy the same energy level they must have opposite spins. Hund’s rule… • Electrons that occupy orbitals of the same energy will have the maximum number of electrons with the same spin. • 2p To start we will use orbital filling diagrams to help us with electron configurations…. • Example Boron- has 5 electrons Periodic table arrangement s (n) d (n - 1) p (n) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 f (n -2) • the quantum theory helps to explain the structure of the periodic table. • n - 1 indicates that the d subshell in period 4 actually starts at 3 (4 - 1 = 3). •Practice!!! Summary: p orbitals and d orbitals p orbitals look like a dumbell with 3 orientations: px, py, pz (“p sub z”). Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a clover shape. The last d orbital resembles a p orbital with a donut wrapped around the middle. st 1 Quantum # Principle Quantum # (n) Specifies the energy level that the electron is on. nd 2 Quantum # (l) Specifies the shape of the sub level . The 3rd (m) and 4th quantum numbers (s) … • Deals with the orbital within the sublevel and the spin of the electron. Four Energy Sub-Levels Energy Level Sub-level Type of sub s Sphere 2 # of Orbitals 1 p Dumbbell 6 3 d 4-Lobed 10 5 f 6-8 Lobed 14 7