File
advertisement

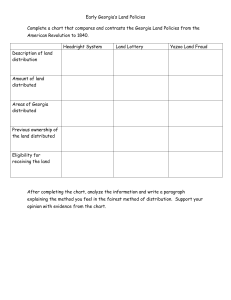
The Age of Expansion Day 1 Manifest Destiny The people of the US felt it was their mission to extend the boundaries of freedom to others, to impart their beliefs in democratic institutions and self-government. There was also an economic drive to expand the riches of the nation by moving west. Changes after the Revolutionary War Along with their hunger for independence from Great Britain, many Georgians developed a huge appetite for LAND!!!! Cherokee Lands Creek Lands Headright System During the settlement of the colony, much of the land east of the Oconee River belonging to the Indians was given to settlers by the Headright System. Each white male counted as a “head” of a family. They had the “right” to receive up to 1,000 acres. Land Lottery Replaced the Headright System in 1803. When public domain lands (lands owned by the state or federal gov’t) were opened for settlement, Georgia surveyed land lots of different sizes. Located west of the Oconee River. For a small fee, any white male 21 years or older could buy a chance to spin a wheel and win land. What Is Fairness? Free from bias, dishonesty, or injustice Give examples of a time when you felt someone was unfair to you (without using names). What is Fraud? Deceit, trickery, sharp practice, or breach of confidence, perpetrated for profit or to gain some unfair or dishonest advantage. Yazoo Land Fraud Georgia’s western borders were the Mississippi River and one of its tributaries – the Yazoo River. Both South Carolina and Spain claimed some of this same land So, the matter went to court... However, before a settlement could be made, 4 land companies approached ... Governor George Mathews & members of the Georgia General Assembly... They bribed the Legislators to pass a bill allowing the companies to buy the western lands. The Assembly passed a bill allowing them to purchase between 35 – 50 million acres of land for $500,000 – about 1 ½ cents per acre. The public quickly learned of this bargain basement sale, and there were protests all over the state. Newspapers printed articles telling what the legislators had done. Grand juries met to look into both the law and the land sales. Citizens called for the resignation of the legislation involved. As a result, the legislators involved were voted out of office. The new legislature repealed the law. All records of these land sales were burned in public at Louisville (the state’s capital at the time). Georgia Cedes Western Land Lost land and a lot of money because of the Yazoo Land Fraud. Ceded (Gave Up) land west of the Chattahoochee River to the federal gov’t for $1.25 million. Louisiana Purchase Thomas Jefferson became the 3rd president (succeeded John Adams). Bought the Louisiana Territory from France for $15 million in 1803. Doubled the size of the United States. Western Border = Rocky Mountains Economic Growth in Georgia Cons Pros State has no money to pay for war debt. Mechanized Farming Tools Many Tories left with the British and took money, slaves, and indentured servants with them. Few citizens had money to pay taxes. Steamboats Railroad Engines Advances in Industry, Business, and Commerce Farming 2 Main Crops cotton Cotton became “king” in the South. tobacco Eli Whitney Invented the cotton gin which separated the cotton fibers from the seeds Before the cotton gin Worker could separate 6 – 7 pounds of cotton seed per day. After the cotton gin Worker could separate 50 pounds of cotton seed per day. Mechanical Reaper Inventor = Cyrus McCormick Fastened wooden paddles to the harness of a horse. As the paddles turned, it would cut the grain. These time and labor-saving devices helped Georgians to work larger and more profitable farms. Panic of 1837 After this period of a strong economy with these new inventions, Georgia suddenly experienced a period of depression (a sharp economic downturn). Businesses Failed Farmers & Planters Lost Land Banks Failed Transportation horses Before Railroads stagecoaches boats Transportation After Railroads... Freight was sent to market by... Riverboats Ferries Wagon Trains Roads The federal government built some major highways in the early 1800s. Called Turnpikes because they had “pikes” or gates. Travelers had to pay a fee at each pike to remain on the road. Ferries Unique horse-drawn log rafts carried travelers across the rivers at their shallowest points. In the deepest river waters, the ferries used a pulley and cable system – required a strong back and arm as the ferry operator pulled the raft across the river. Railroads At first, rail travel was the least favored means of transportation. Most of the track in Georgia belonged to the Western and Atlantic Railroads. Started near Chattanooga, Tennessee and ended at Terminus (end of the railroad line/today’s Atlanta) Dramatically shortened travel time for passengers and freight.