Larynx Anatomy: Cartilages, Muscles, and Ligaments
advertisement
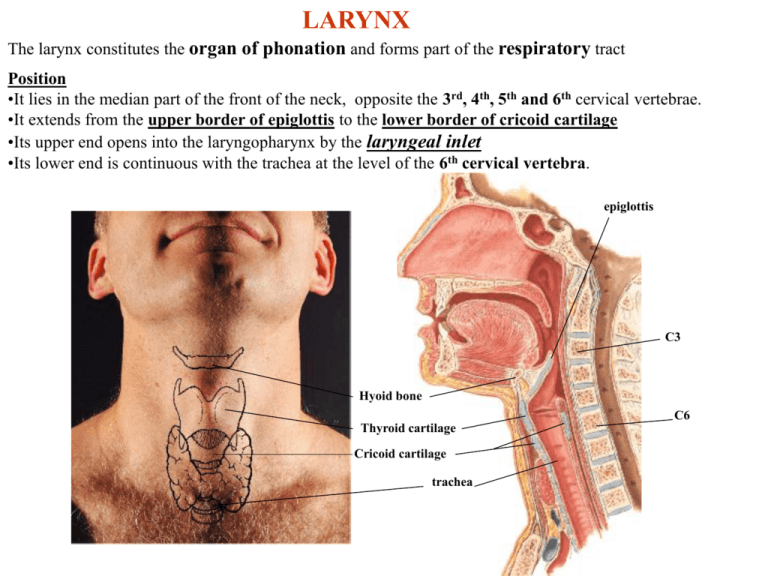
LARYNX The larynx constitutes the organ of phonation and forms part of the respiratory tract Position •It lies in the median part of the front of the neck, opposite the 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae. •It extends from the upper border of epiglottis to the lower border of cricoid cartilage •Its upper end opens into the laryngopharynx by the laryngeal inlet •Its lower end is continuous with the trachea at the level of the 6th cervical vertebra. epiglottis C3 Hyoid bone C6 Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage trachea Structure of the larynx The larynx is formed of a number of cartilages joined together by: • Ligaments • Membranes • Muscles • Synovial joints epiglottis Cartilago triticea Cartilages of the larynx Single cartilage: •Thyroid cartilage •Cricoid cartilage •Epiglottis Paired cartilages: •Arytenoid cartilages •Corniculate cartilages •Cuneiform cartilages Thyroid cartilage Cuneiform cartilage Corniculate cartilage Arytenoid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Thyroid cartilage • • • • The largest laryngeal cartilage Formed of 2 quadrilateral laminae which are fused anteriorly Posteriorly, the 2 laminae are separated by a wide gap The anterior border forms a median projection, the Superior thyroid notch Superior horn laryngeal prominence • The laminae present a median V-shaped notch, the superior thyroid notch • The posterior borders form upward and downward projections, superior & inferior horns • The outer surface of each lamina shows an oblique ridge, the oblique line • The oblique line extends between two tubercles, the superior and inferior thyroid tubercles Thyroid lamina Laryngeal prominence Oblique line Inferior horn Thyroid lamina Superior horn Superior horn Superior tubercle Oblique line Inferior tubercle Inferior horn Laryngeal prominence Thyroid lamina Posterior border Inferior horn Cricoid cartilage • Smaller, but thicker than the thyroid cartilage • Lies below and behind the thyroid cartilage • It has the shape of a signet ring with a quadrilateral lamina, posteriorly, and a narrow arch, anteriorly • Its lower border is horizontal • Its upper border is sloping Lamina of cricoid cartilage Posterior lamina of cricoid cartilage Upper border of cricoid cartilage Lower border of cricoid cartilage Arch of cricoid cartilage Epiglottis Median & lateral • A leaf-shaped lamella of elastic cartilage Glossoepiglottic folds • It projects upwards behind the tongue and hyoid bone • Has an upper broad free end and a lower tapering end • Anteriorly, it is connected to: 1.The root of the tongue, by the median and lateral glosso-epiglottic folds 2.The hyoid bone, by the hyoepiglottic ligament 3.The inner surface of the thyroid cartilage by the thyroepiglottic ligament Epiglottis (posterior view) Hyoepiglottic ligament Hyoid bone Thyroepiglottic ligament Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Epiglottis Arytenoid cartilage • A pyramid-shaped cartilage, with an apex, base and 3 surfaces: 1. Posterior surface 2. Anterolateral surface Corniculate cartilage 3. Medial surface • The apex is directed upwards and articulates with the Posterior surface corniculate cartilage • The base is directed downwards and articulates with Lateral (muscular) process the upper border of the lamina of cricoid cartilage • The lateral angle of the base projects to form the muscular process • The anterior angle of the base projects to form the vocal process Anterior (vocal) process Corniculate cartilage Lamina of cricoid cartilage Anterolateral surface Lateral (muscular) process Anterior (vocal) process Corniculate cartilage Posterior surface Lateral (muscular) process Cricoid cartilage Medial surface Anterior (vocal) process Corniculate cartilage • A small cartilage on the apex of the arytenoid cartilage • Enclosed in the aryepiglottic fold forming the Corniculate cartilage corniculate tubercle Cuneiform cartilage A small nodule enclosed in the aryepiglottic fold forming the cuneiform tubercle Aryepiglottic fold Cuneiform tubercle Corniculate tubercle Joints of the larynx Cricothyroid joints: • One on each side • A synovial joint between the inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage and the side of the cricoid cartilage Cricoarytenoid joints: • One on each side • A synovial joint between the base of arytenoid cartilage and upper border of the cricoid lamina Arycorniculate joints: • One on each side • A joint between the apex of the arytenoid cartilage and the corniculate cartilage Arycorniculate joint Cricothyroid joint Cricoarytenoid joint Cricothyroid joint Membranes and ligaments of the larynx Thyrohyoid membrane: • Extends from the upper border of thyroid cartilage to the upper border of posterior surface of hyoid bone • Separated from the posterior surface of hyoid bone by the hyoid bursa • The median part of the membrane is thickened to form the median thyrohyoid ligament • The membrane is pierced by the superior laryngeal vessels and the internal laryngeal nerve. • The posterior border is thickened to form the lateral thyrohyoid ligament • The lateral thyrohyoid ligament contains a cartilage nodule called the cartilago triticea. Lateral thyrohyoid ligament Cartilago triticea Foramen for sup laryngeal vessels & internal laryngeal n. Thyrohyoid membrane Median thyrohoid ligament Cricothyroid ligament: (conus elasticus) • An elastic band which lies below and on the inner aspect of the thyroid cartilage • It is connected to: • Thyroid cartilage • Cricoid cartilage • Arytenoid cartilage • Two parts of the ligament can be recognized: Median cricothyroid ligament: the anterior thickened part of the ligament which connects the adjacent borders of the cricoid and thyroid cartilages. - The ligament is overlapped by the cricothyroid muscle. Median cricothyroid ligament Median cricothyroid ligament Cricothyroid muscle Lateral cricothyroid ligament (crico-vocal membrane) this ligament is attached inferiorly to the upper border of cricoid cartilage superiorly, it has 2 attachments: to the inner surface of thyroid cartilage, anteriorly to the vocal process of arytenoid cartilage, posteriorly The free upper border of the crico-vocal membrane is called the Vocal Ligament “The vocal ligament is attached to the inner surface of thyroid cartilage (anteriorly) and to the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage (posteriorly)” Thyroid cartilage Thyrohyoid ligament Median cricothyroid ligament Vocal ligaments Lateral cricothyroid ligament Vocal process Upper border of cricoid cartilage Vocal ligament Arytenoid cartilage Posteroir lamina of cricoid cartilage Vocal process Cricoid cartilage Other ligaments of the larynx •Hyo-epiglottic ligament: connects the anterior surface of epiglottis to the hyoid bone •Thyro-epiglottic ligament: connects the lower end of the epiglottis to the inner surface of thyroid cartilage •Crico-tracheal ligament: connects the lower border of the cricoid cartilage to the first ring of trachea •Ligaments of the joints Epiglottis Hyo-epiglottic ligament Hyoid bone Thyro-epiglottic ligament Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Interior of the larynx Inlet of the larynx: - The opening of communication between the pharynx and larynx - The laryngeal inlet is directed upwards and backwards Boundaries of the inlet: • Upper border of epiglottis anteriorly • Aryepiglottic folds on both sides • Mucous membrane between the arytenoid cartilages posteriorly Inlet of the larynx Aryepiglottic fold: • A fold of mucosa extending between the apex of arytenoid cartilage and the side of epiglottis • It encloses the aryepiglottic muscle, cuneiform and corniculate cartilages Aryepiglottic fold Cuneiform tubercle Aryepiglottic muscle Corniculate tubercle Vocal fold: • A fold of mucous membrane extending from the inner surface of thyroid cartilage to the vocal process of arytenoid cartilage • The folds enclose the vocal ligaments (upper free border of lateral cricothyroid ligaments) • The fissure between the 2 vocal folds is called rima glottidis Vestibular fold: epiglottis Aryepiglottic fold Vestibular fold Sinus of larynx Thyroid cartilage Medial surface of arytendoid cartilage Cricoid cartilage • A fold of mucous membrane extending from the inner surface of thyroid cartilage to the anterolateral surface of arytenoid cartilage • It encloses a fibrous band called the vestibular ligament Vocal process Vocal fold Sinus of the larynx: • A recess between the vestibular and vocal folds Vestibule of the larynx: epiglottis • The upper part of the laryngeal cavity, between the inlet and the vestibular folds Mucosa of the larynx: • Lined by pseudostratified columnar ciliated epitheliuum containing goblet cells and mucous glands • The vocal folds are lined by non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium without submucosa or blood vessels • The vocal folds appear pearly white during laryngoscopy Thyroid cartilage Vocal ligament Vocal process Arytenoid cartilage Rima glottidis (glottis) The fissure between the two vocal folds anteriorly (inter-membranous part) and the two arytenoid cartilages posteriorly (inter-cartilagenous part) Vocal process Intermembranous part Rima glottidis (glottis) Intercartilagenous part Arytenoid cartilage Muscles of the larynx Extrinsic muscles of the larynx Intrinsic muscles of the larynx • Elevators of the larynx • Stylopharyngeus • Palatopharyngeus • Salpingopharyngeus • Depressors of the larynx • Sternothyroid • Thyrohyoid • Are muscles which connect the laryngeal cartilages together • All are paired EXCEPT the transverse arytenoid • They include: • Cricothyroid posterior • Cricoarytenoid lateral • Ary-epiglottic transverse • Arytenoid • Thyro-arytenoid • Thyro-epiglottic • Vocalis oblique Muscles of the larynx Cricothyroid: The only intrinsic muscle seen on the outside of the larynx The only muscle of the larynx supplied by the external laryngeal nerve O: outer aspect of the arch of cricoid I: inferior horn and lower border of thyroid cartilage A: a tensor of the vocal fold (lengthens the vocal fold) N: external laryngeal nerve Cricothyroid m. Vertical part Action of cricothyroid Lengthening (tightening) the vocal cords Cricothyroid m. oblique part Posterior Crico-arytenoid: Lateral Crico-arytenoid: O: posterior surface of cricoid lamina I: muscular process of arytenoid cartilage A: abduction of vocal cords O: upper border of arch of cricoid cartilage I: muscular process of arytenoid cartilage A: adduction of vocal cords Lateral cricoarytenoid Posterior cricoarytenoid Cricothyroid Posterior cricoarytenoid Cricoid lamina Lateral cricoarytenoid Muscular process Vocal process Cricoid arch Cricothyroid Thyroid cartilage Vocal cords Action of posterior cricoarytenoid Abduction of vocal cords Action of lateral cricoarytenoid Adduction of vocal cords MOVEMENT OF VOCAL CORDS Adduction of vocal cords: Abduction of vocal cords: •Lateral cricoarytenoid •Transverse arytenoid (also closes the rima glottidis) •Posterior cricoarytenoid Closure of laryngeal inlet: Widening of laryngeal inlet: •Oblique arytenoid •Aryepiglottic •Thyroepiglottic Relaxation of vocal ligaments: Tension of vocal ligaments: •Thyroarytenoid •Vocalis •Cricothyroid Closure of rima glottidis: •Transverse arytenoid Normal larynx during inspiration Normal larynx during phonation Functions of the larynx: • Respiratory function: it forms part of the respiratory airway • Phonation: (production of sound waves) • Raising the intra-abdominal pressure: by closing the rima labour) glottidis during expiration (ex. during Arterial supply of the larynx: • Superior laryngeal artery: from the superior thyroid artery (it pierces the thyrohoid membrane with the internal laryngeal nerve) • Inferior laryngeal artery: from the inferior thyroid artery (it ascends deep to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor with the recurrent laryngeal nerve) Venous drainage of the larynx: • Superior laryngeal vein: drains into the superior thyroid vein • Inferior laryngeal vein: drains into the inferior thyroid vein Nerve supply of the larynx: • Superior laryngeal nerve (from vagus), Divides into: • External laryngeal: supplies the cricothyroid m. • Internal laryngeal: supplies the mucous membrane above the level of the vocal folds • Recurrent laryngeal nerve (from vagus), Divides into motor and sensory branches • The motor branch supplies ALL intrinsic muscles of the larynx (except cricothyroid) • The sensory branch supplies the mucous membrane below the level of the vocal folds









