Electron Transport Chain
advertisement

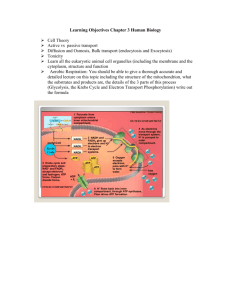
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation It all reduces down to water. Mitochondria • outer membrane relatively permeable • inner membrane permeable only to those things with specific transporters – Impermeable to NADH and FADH2 – Permeable to pyruvate • Compartmentalization – Kreb's and β-oxidation in matrix – Glycolysis in cytosol Most energy from Redox • electrons during metabolic reactions sent to NAD and FAD – Glycolysis • In cytosol • produces 2 NADH – Pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction • In mitochondrial matrix • 2 NADH / glucose – Krebs • In mitochondrial matrix • 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 / glucose Electron Transport Chain • Groups of redox proteins – On inner mitochondrial membrane – Binding sites for NADH and FADH2 • • • • On matrix side of membrane Electrons transferred to redox proteins NADH reoxidized to NAD+ FADH2 reoxidized to FAD 4 Complexes • • proteins in specific order Transfers 2 electrons in specific order – Proteins localized in complexes • • Embedded in membrane Ease of electron transfer – Electrons ultimately reduce oxygen to water • 2 H+ + 2 e- + ½ O2 -- H2O Electron Transport Chain Complex 1 • Has NADH binding site – NADH reductase activity • NADH - NAD+ – NADH ---> FMN--->FeS---> ubiquinone – ubiquinone ---> ubiquinone H2 – 4 H+ pumped/NADH Electron Transport Chain Complex II • succinate ---FAD—ubiquinone – Contains coenzyme Q – FADH2 binding site • • FAD reductase activity FADH2 -- FAD Electron Transport Chain Complex III • • • ubiquinone - ubiquinone ox while cyt C gets reduced Also contains cytochromes b – proton pump 4H+ • Adds to gradient 8 H+ / NADH 4 H+ / FADH2 Electron Transport Chain Complex IV • • • • reduction of oxygen cytochrome oxidase cyt a+a3 red ---> oxidized state oxygen ---> water – 2 H+ + 2 e- + ½ O2 -- 2 H2O – transfers e- one at a time to oxygen • Pumps 2H+ out – Total of 10 H+ / NADH – Total of 6 H+ / FADH2 Totals • Proton gradient created as electrons transferred to oxygen forming water 10 H+ / NADH 6 H+ / FADH2 Electron Transport Chain Generation of ATP • Proton dependant ATP synthetase – Uses proton gradient to make ATP – Protons pumped through channel on enzyme • From intermembrane space into matrix • ~4 H+ / ATP – Called chemiosmotic theory Totals NADH 10 H+ X 1 ATP = 2.5 ATP 4 H+ FADH2 6 H+ X 1 ATP = 1.5 ATP 4 H+ Total ATP from mitochondrial matrix • Pyruvate dehydrogenase – NADH ……………………………….2.5 ATP • Krebs 3 NADH X 2.5 ATP/NADH ……….7.5 ATP FADH2 X 1.5 ATP / FADH2……….1.5 ATP GTP X 1 ATP / GTP ……………..1.0 ATP (from a separate reaction) Total …………….12.5 ATP (Per glucose = X 2 = 25 ATP) What about NADH from glycolysis? • NADH made in cytosol • Can’t get into matrix of mitochondrion • 2 mechanisms – In muscle and brain • Glycerol phosphate shuttle – In liver and heart • Malate / aspartate shuttle Glycerol Phosphate shuttle • http://courses.cm.utexas.edu/jrobertus/ch339k/overheads-3/ch19_glycerol-shuttle.jpg Glycerol phosphate shuttle • In muscle and brain • Each NADH converted to FADH2 inside mitochondrion – FADH2 enters later in the electron transport chain – Produces 1.5 ATP Total ATP per glucose in muscle and brain • Gycerol phosphate shuttle – 2 NADH per glucose - 2 FADH2 – 2 FADH2 X 1.5 ATP / FADH2……….3.0 ATP – 2 ATP in glycoysis ……………………2.0 ATP – From pyruvate and Krebs • 12.5 ATP X 2 per glucose ……………..25.0 ATP Total = 30.0 ATP/ glucose Malate – Aspartate Shuttle • http://courses.cm.utexas.edu/emarcotte/ch339k/fall2005/Lecture-Ch19-2/Slide14.JPG Malate – Aspartate Shuttle in cytosol • In liver and heart • NADH oxidized while reducing oxaloacetate to malate – Malate dehydrogenase • Malate crosses membrane Malate – Aspartate Shuttle in matrix • Malate reoxidized to oxaloacetate – Malate dehydrogenase – NAD+ reduced to NADH • NADH via electron transport yields 2.5 ATP Total ATP per glucose in liver and heart • Malate – Aspartate Shuttle – 2 NADH per glucose - 2 NADH – 2 NADH X 2.5 ATP / NADH…………5.0 ATP – 2 ATP from glycolysis………………..2.0 ATP – From pyruvate and Krebs • 12.5 ATP X 2 per glucose ……………..25.0 ATP Total = 32.0 ATP/ glucose Summary • Total ATP / glucose – Muscle and brain 30.0 ATP • Uses glycerol phosphate shuttle – Heart and liver • Uses malate aspartate shuttle 32.0 ATP