Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel
advertisement

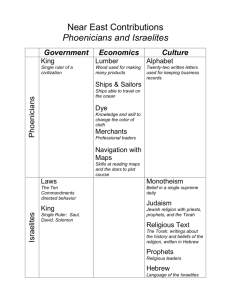
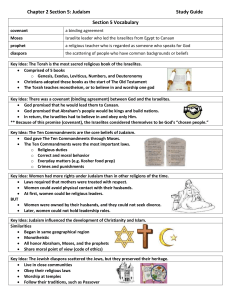
Chapter 3 The Ancient Israelites Chapter 3, Section 1 The First Israelites (Pages 80–85) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: • What did the Israelites believe? • Where was the Promised Land of the Israelites, and how did they return there? Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Chapter 3, Section 1 The First Israelites Terms to Know ►monotheism: belief in one god; ►tribe: a unit of society made up of family groups; ►Torah: Jewish religious law; ►covenant: a formal agreement Chapter 3, Section 1 The Promised Land Terms to Know ►alphabet: a group of letters that stands for sounds Chapter 3, Section 1 The First Israelites People to Meet ►Abraham: the father of the Israelites; ►Jacob: grandson of Abraham and father of the 12 tribes of Israel; ►Moses: man who led the Israelites out of slavery in Egypt Chapter 3, Section 1 The Promised Land People to Meet ►Phoenicians: group of Canaanites who lived in cities along the Mediterranean; ►Deborah: Israelite judge who defeated King Jabin and his army Class Notes & Discussion The Early Israelites ► The Israelites built a kingdom in Canaan, along the Mediterranean Sea in southwest Asia, in 1000 B.C. Today, Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan occupy the land that was once Canaan. ► Israelites believed in one god. The belief in one god is called monotheism. ► The Israelite faith became the religion of Judaism. Judaism influenced Christianity and Islam and helped shape the beliefs of European and American societies. The Early Israelites The Early Israelites ► Israelites spoke Hebrew and wrote their history and beliefs in what later became the Hebrew Bible. ► The Israelites believed they were descended from a man named Abraham. The Israelites believed God told Abraham to settle in Canaan and worship the one true God. ► Abraham’s grandson, named Jacob, raised 12 sons in Canaan. Their families became the 12 tribes of Israel. 12 Tribes of Israel The First Israelites ► After 100 years in Canaan, the Israelites suffered a long drought. To survive, some Israelites went to Egypt. ► The Egyptian pharaoh enslaved the Israelites. To prevent the Israelites from rebelling, the pharaoh ordered all baby boys to be thrown into the Nile River. The pharaoh’s daughter found a baby boy in a basket on the riverbank, and she named him Moses. Baby Moses The First Israelites ► When Moses grew up, he herded sheep in the hills outside Egypt. In those hills, he saw a burning bush and heard a voice. He believed it was God telling him to lead the Israelites out of Egypt. The Early Israelites ► The Hebrew Bible says that God sent 10 plagues to trouble Egypt. The last plague killed all the firstborn children, except for those Israelites who marked their doors with lamb’s blood. The plague convinced the pharaoh to let the Israelites leave Egypt. The First Israelites ► After the Israelites left, the pharaoh changed his mind. He sent soldiers after the Israelites. The Hebrew Bible says that God parted the Red Sea, so the Israelites could pass. The water flowed back when the soldiers tried to cross, and they drowned. The First Israelites ► On the way back to Canaan, Moses went to the top of Mount Sinai and received laws from God. These laws were known as the Torah, which became the first part of the Hebrew Bible. The First Israelites ► The Ten Commandments – what God believes to be right and wrong – are an important part of the Torah. The Ten Commandments helped form the basic moral laws of many nations. Chapter 3, Section 1 The First Israelites ►What Sum It Up covenant was described in the Torah? ►The Torah described God’s agreement with the Jewish people—his promise to return the Israelites to Canaan if they followed his laws. Chapter 3, Section 1 The First Israelites Reading Strategy As you read pages 81–85 in your textbook, complete this sequence chart to trace the movement of the Israelites. Mesopotamia Canaan Canaan Egypt Sinai Desert Chapter 3, Section 1 The Promised Land Sum It Up ►Who led the Israelites into Canaan, and what city did they conquer under his leadership? Joshua led the Israelites into Canaan. They conquered Jericho. Chapter 3, Section 1 Section Wrap Up What did the Israelites believe? ►The Israelites believed in one god and followed the laws from the Torah, including the Ten Commandments. Chapter 3, Section 1 Section Wrap Up ►Where was the Promised Land of the Israelites, and how did they return there? ►The Israelites returned to Canaan, their Promised Land, when God delivered them from slavery in Egypt. Chapter 3 Section 2 – The Kingdom of Israel Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel (Pages 86–92) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: • Why did the Israelites choose to follow kings instead of judges? • Who was King David and why was he important? • Why were the Israelites conquered? Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel Terms to Know ►prophet: person who claims to hear and speak words from God Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel People to Meet ►Philistines: strongest people living in Canaan; enemies of the Israelites; ►Saul: Israel’s first king; ►David: shepherd chosen by God to replace Saul as king Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel Academic Vocabulary ►instruct: to teach, to direct Class Notes & Discussion Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel Sum It Up ►Why did the Israelites want a king? ►The Israelites wanted a king to unite and lead them against their enemies, the Philistines. Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Summarizing As you read, complete the following sentences. Doing so will help you summarize the section. 1. David defeated the giant Philistine named ______________ with a Goliath ______________. As David won more slingshot victories ______________ became Saul jealous and plotted to ______________ kill David. 2. David took over the throne in about ______________, when Saul and his sons 1000 B.C. were ______________ in battle. killed Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Summarizing 3. David created an empire and established the capital of ______________. His son Jerusalem ______________ built a great temple Solomon there. 4. When Solomon died, the 12 tribes broke into two nations: ______________ and Israel ______________. Judah Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Terms to Know ►empire: a nation that rules several other nations; ►tribute: money or enslaved persons given to a stronger ruler; ►proverbs: wise sayings Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Places to Locate ►Jerusalem: the capital of Israel established by David, later became the capital of Judah; ►Judah: smaller kingdom that broke away from Israel, founded by two tribes in the south Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Academic Vocabulary ►expand: to make bigger; ►symbol: an image or object used to represent something else Chapter 3, Section 2 David and Solomon Sum It Up ►Why did Solomon tax the people so heavily? Solomon taxed the people so heavily in order to pay for the temple and other buildings he built in Jerusalem Chapter 3, Section 2 A Troubled Time Sequencing ► As you read, place the following events in the correct order by numbering them in the spaces provided. ____ 3 The Egyptians conquer Judah ____ The Jews unite with the Egyptians to fight the 5 Chaldeans ____ 6 King Nebuchadnezzar captures Jerusalem 1 The Assyrians conquer Israel and scatter the 10 tribes ____ 7 Nebuchadnezzar takes the Jews into captivity in ____ Babylon 2 The Assyrians become known as Samaritans and ____ eventually worship Israel’s God 4 The Chaldeans conquer Egypt ____ Chapter 3, Section 2 A Troubled Time People to Meet ►Nebuchadnezzar: Chaldean king who defeated Judah and captured Israel Chapter 3, Section 2 A Troubled Time Academic Vocabulary ►route: a road or way for travel Chapter 3, Section 2 The Kingdom of Israel Reading Strategy Location Israel Judah Capital City North South Date Conquered 772 B.C. 620 B.C. Conquered By Assyrians Egyptians Chapter 3, Section 2 A Troubled Time Sum It Up ►Why did the Assyrians and Chaldeans want to control the land belonging to the Israelites? The Assyrians and Chaldeans were building their own empires in southwest Asia. They wanted to control trade routes that ran through the Israelite kingdom. Chapter 3, Section 2 Egypt’s Old Kingdom Section Wrap-Up Now that you have read the section, write the answers to the questions that were included in Setting a Purpose for Reading at the beginning of the lesson. Why did the Israelites choose to follow kings instead of judges? ►Israelites choose to follow kings instead of judges because they wanted a strong leader to unify them and protect them from their enemies. Chapter 3, Section 2 Egypt’s Old Kingdom Section Wrap-Up Who was King David and why was he important? ►King David is considered the greatest king of Israel. He conquered neighboring nations, created an empire, and established the capital of Jerusalem. Chapter 3, Section 2 Egypt’s Old Kingdom Section Wrap-Up Why were the Israelites conquered? ►The powerful Assyrians and Chaldeans threatened the weakened Israelites. They wanted to control the trade routes through Israel. The Israelites were conquered by the Assyrians in 722 B.C. Chapter 3 Section 3 – The Growth of Judaism Chapter 3, Section 3 The Growth of Judaism (Pages 93–102) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: • How did Judaism grow in the period following their exile? • Why did the Romans destroy the temple and exile the Jews? Chapter 3, Section 3 The Growth of Judaism Reading Strategy As you read page 96 in your textbook, complete this diagram to describe the Maccabees. Led by priest named Judas Maccabeus Rebelled against Antiochus and fled Formed an army called the Maccabees Drove the Greeks out of Judah and destroyed all traces of Greek gods in their temple Restored their temple to worship of their God Remembered in the celebration of Hanukkah Became new ruler of Judah Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Outlining I. Why Did Jews Return to Judah? The Persian king Cyrus allowed A. ___________________________ the Jews to return to Judah. B. ____________________________ Persians controlled the government, so Jews looked to their religion for leadership. Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Outlining II. What Is in the Hebrew Bible? Thirty-nine books including A. ___________________________ Jewish history and the Torah. B.____________________________ The Jews believed that God had a special role for them in history. Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Outlining III. The Jews Look to the Future The Bible describes God’s plans A. ___________________________ for a peaceful future. B. ____________________________ The Jews believed that good would ultimately triumph over evil. Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Terms to Know ►exile: forced removal from a native country; ►Sabbath: weekly day of worship and rest; ►synagogue: Jewish place of worship Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Places to Locate ►Babylon: Jews the land of exile for the Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Academic Vocabulary ►series: objects or events that come one after the other; ►symbol: an image or object used to represent something else Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Terms to Review ►Scribe: A Jewish scribe named Ezra helped write the first five books of the Torah. Chapter 3, Section 3 Exile and Return Sum It Up Who allowed the Jews to return to Judah? Cyrus allowed the Jews to return to Judah. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Greeks Questioning ► As you read, write three questions about the main ideas presented in the text. After you have finished reading, write the answers to these questions. ► Student questions should be based on the main ideas in the text, including the influence of the Greeks on the Jews, the Diaspora, the Maccabees, and Hanukkah. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Greeks Terms to Know ►Diaspora: term referring to the scattered people of Israel Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Greeks People to Meet ►Judas Maccabeus: priest who led the rebellion against Antiochus and the new ruler of Judah Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Greeks Academic Vocabulary ►version: translation from another language; ►trace: visible evidence Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Greeks Sum It Up How did Alexander the Great affect the Israelites? ► Alexander the Great introduced the Israelites to Greek language and culture. Jews who learned Greek translated the Hebrew Bible. This helped people who were not Jews understand Jewish history and ideas. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jewish Way of Life Determining the Main Idea Jewish law set out rules for living Jews placed great importance on family Jews followed strict dietary laws Education was very important, including religious education for boys Jewish law forbade mixing some fabrics Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jewish Way of Life Academic Vocabulary ►affect: to cause a change or have an impact on; ►community: a group of people living in the same place Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jewish Way of Life Sum It Up Why were sons especially valued in Jewish society? ► Sons were especially valued in Jewish society because they carried on the family name and became head of the family upon the father’s death. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 1. What did Herod do as king? ►Herod was cruel. He made the temple very grand, ruled when Jesus was born, and he allowed Jewish rulers to run Judah. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 2. Why were the Jews unable to regain control over their Roman rulers? ►The Jews were unable to regain control over their Roman rulers because they were splintered into different groups. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 3. Who were the Pharisees? ►The Pharisees taught the Torah and how to apply it to daily life. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 4. Who were the Sadducees? ►The Sadducees were priests and scribes concerned with the law in the Temple. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 5. Who were the Essenes? ►The Essenes were priests who broke away from the temple and lived in the desert praying for God’s deliverance. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 6. What were the cause and results of the Jewish revolts? ►Jewish hatred of the Romans led to the revolts. The revolts led to the death of thousands, the destruction of the temple, and exile. The Romans renamed Judah Palestine. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Monitoring Comprehension 7. What role did rabbis play in Jewish society? ►Rabbis were teachers of the Torah who held an important place in Jewish society. They developed the Talmud to pass on teachings about the Torah. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Terms to Know ►messiah: a deliverer sent by God; ►rabbi: teacher of Jewish law ►Talmud: the combined teachings of the Torah Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans People to Meet ►Herod: Roman king who ruled over Judaea; ►Zealots: Jews who wanted to fight the Romans for their freedom; ►Johanan ben Zakkai: Jewish rabbi who founded a school in northern Palestine that became a center of Torah studies Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Academic Vocabulary ►expand: to make bigger; ►despite: in spite of Chapter 3, Section 3 The Jews and the Romans Sum It Up ►How did the Roman conquest affect the Jews? ►Ultimately, the Roman conquest resulted in loss of Jewish lives, as well as their homeland and temple. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Growth of Judaism Section Wrap-Up Now that you have read the section, write the answers to the questions that were included in Setting a Purpose for Reading at the beginning of the lesson. How did Judaism grow in the period following their exile? ► Jews who were scattered to other lands learned Greek and translated their Bible so that other people could learn about Jewish ideas. Chapter 3, Section 3 The Growth of Judaism Section Wrap-Up Why did the Romans destroy the temple and exile the Jews? The Romans destroyed the temple and exiled the Jews to crush the Jews spirit and prevent further uprising.