10.1 Radioactivity
advertisement

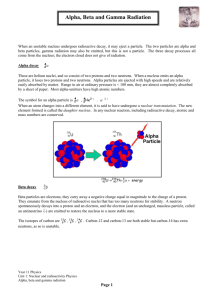
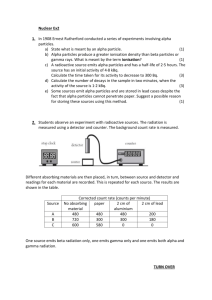
10.1 Radioactivity Nuclear Decay… • Atoms of one element can change into atoms of a different element altogether. • An unstable atom has excess internal energy, with the result that the nucleus can undergo a spontaneous change towards a more stable form. • Radioisotopes are atoms that contain an unstable nucleus and will change into another isotope over time. • Scientists can estimate the age of fossils by looking at nuclear decay. Radioactivity… is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy. 3 Types of Nuclear Radiation 1. Alpha Particles 2. Beta Particles 3. Gamma Rays Nuclear Radiation… charged particles and energy that are emitted from the nuclei of radioisotopes. • If an element decays and emits an alpha or beta particle, it becomes a new element. • Gamma rays are often emitted with alpha or beta radiation also, as the nucleus decays to a less excited state. Alpha Particle • Positively charged particle made up of two protons and two neutrons—the same as a helium nucleus. • When a uranium-238 sample decays, it emits alpha particles. • An alpha particle has a 2+ charge. • Symbol for alpha: Beta Particle • negatively charged radiation • electron emitted by an unstable nucleus • A beta particle is assigned an atomic number of –1. • Symbol for beta: Gamma Ray • Penetrating ray of energy emitted by an unstable nucleus. • Gamma radiation has no mass and no charge. • Like X-rays and visible light, gamma rays are energy waves that travel through space at the speed of light. •Symbol for gamma: Units of Radioactivity… • The amount of radioactive material is given in becquerel (Bq), a measure which enables us to compare the typical radioactivity of some natural and other materials. • A becquerel is one atomic decay per second. Radioactivity of some natural and other materials • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1 adult human (100 Bq/kg) 7000 Bq 1 kg of coffee 1000 Bq 1 kg superphosphate fertiliser 5000 Bq The air in a 100 sq metre Australian home (radon) 3000 Bq The air in many 100 sq metre European homes (radon) up to 30 000 Bq 1 household smoke detector (with americium) 30 000 Bq Radioisotope for medical diagnosis 70 million Bq Radioisotope source for medical therapy 100 000 000 million Bq (100 TBq) 1 kg 50-year old vitrified high-level nuclear waste 10 000 000 million Bq (10 TBq) 1 luminous Exit sign (1970s) 1 000 000 million Bq (1 TBq) 1 kg uranium 25 million Bq 1 kg uranium ore (Canadian, 15%) 25 million Bq 1 kg uranium ore (Australian, 0.3% 500 000 Bq 1 kg low level radioactive waste 1 million Bq 1 kg of coal ash 2000 Bq 1 kg of granite 1000 Bq Electromagnetic Radiation • Consist of electromagnetic waves • Most of these are harmless