Production Possibilities and Opportunity Costs
advertisement

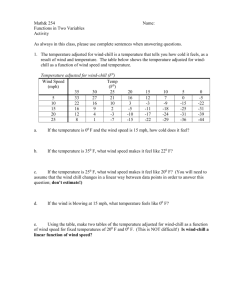
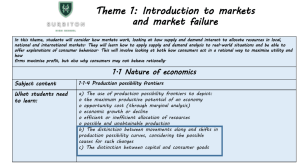
Production Possibilities and Opportunity Costs What is a Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)? A graph that shows the maximum combinations of goods that can be produced when resources and technology are used efficiently Scarcity & the PPF Economics involves choice since limited resources means that there will be a limited output. A PPC will show that as tradeoffs are made, sacrifice or opportunity costs are incurred. A Quick Review of Terminology Opportunity Cost is defined as the value of the next best alternative. So…opportunity cost measures the sacrifice we make when we are forced to make choices due to scarcity. For simplicity, lets take a world with only 2 products Lets use cola and pizza (perhaps the flat pizzas we serve at lunch) Cola A typical PPF has the following shape: The curve has a negative slope. The curve is concave to the origin. Pizza Cola All points on the curve correspond to full use of resources. A B Pizza Cola Points outside the PPF are not feasible with existing resources. .A Pizza Cola Periods of unemployment or inefficiency in production correspond to points under the PPF. .A Pizza Shape of the PPF? Why Concave? If PPF has a straight line, we have constant opportunity costs If PPF concave, we have increasing opportunity costs Consider a straight line PPF Cola given up, the opportunity cost, remains constant (10 colas forgone for every additional pizza produced). Cola 40 30 20 10 1 2 3 4 Pizza Concave shape, increasing opportunity costs. Cola given up, the opportunity cost, is increasing Cola 40 30 20 10 1 2 3 4 Pizza What is the Law of Increasing Costs? The opportunity cost of producing a good increases as more of the good is produced Why does the Law of Increasing Opportunity costs hold? Because resources are not perfectly adaptable to all products … example next page. Say this is a company that can produce colas or pizzas, and let’s say that they begin by producing all colas and no pizzas. When they decide to produce their first pizza, they take away some of their resources from producing colas. In terms of labor, the firm will take away those resources that can easily produce pizzas as well as colas. But when we begin to make more pizzas, we start to take Cola 40 away resources that were REALLY good at producing colas, and are not so good at producing 30 pizzas. 20 10 1 2 3 4 Pizza How do we have more of everything? By increasing our resources, either land, labor, capital, or entrepreneurship Cola Economic growth indicates an increase in the total output of an economy. The PPF shifts to the right ! Pizza Causes of rightward shifts in PPF’s? Increase in resources Increased productivity Improved technology Can a PPF shift inward (to the left)? YES!! For just the opposite reasons as an outward shift such as a loss of resources 19 Capital goods Economic growth and the Capital Consumer goods tradeoff: A From which point would an economy grow faster, A or B?? Answer is A, with more capital goods B Consumer goods What should a country specialize in producing? In those goods and services that it has a comparative advantage What is Comparative Advantage? A country’s ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than the country which it trades What is Absolute Advantage? A country’s ability to produce a good using fewer resources than the country with which it trades Example: 2 people, 2 jobs, time required Job A Job B Judy 60 min. 75 min Sam 90 min 150 min In the table, Judy is absolutely advantaged at both tasks – she can work either job faster than Sam. But what is her comparative advantage? What is Sam’s comparative advantage? Judy’s comparative advantage is at job B, and Sam’s comparative advantage is at job A To see why, look at the ratios in the table- Judy can do job A in 2/3 the time of Sam, but she can do job B in ½ the time, so she is relatively more efficient at job B. Theory of comparative advantage Argues that output is greater when resources tend to specialize in their greatest comparative advantages Problem With the same quantity of resources, Euphoria can produce 100 barrels of cola to Extasia’s 50 barrels, and Euphoria can produce 150 pizzas to Extasia’s 100. According to comparative advantage, what product should Extasia tend to specialize in? What about Euphoria? ANSWER: Extasia should specialize in pizzas, Euphoria in cola production Conclusion Production-possibility frontiers (and curves) help us to be able to analyze opportunity costs and tradeoffs. The analysis of opportunity costs can lead us to be able to extend our analysis even further into absolute advantage, comparative advantage, and specialization. Be sure to review these fundamental concepts, and ask questions for clarification in cases where you are not understanding.