The Production Possibilities Model.PPT
advertisement

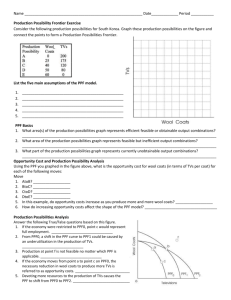
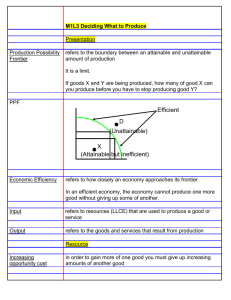
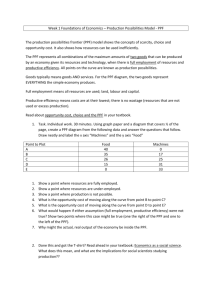
1.3 The Production Possibilities Model Consumer Product An item that gratifies people’s needs and wants Capital Good An item that is used to produce other products Production Possibilities Schedule A table that shows the possible output combinations for an economy Production Possibilities Curve A graph that shows the possible output combinations for an economy A society must choose among possible combinations of 2 goods. Production Possibilities Curve Production Possibilities Schedule Increasing Opportunity Costs Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs (OC): The concept that as more of one item is produced by an economy, the opportunity cost of additional units of that product rises You can see OC by moving from point to point along the PPF The “bowing-out” shape of the curve shows that as more of one product if produced, its OC in terms of the other product increases If a town starts if with 10,000 industrial machines (A), it cannot make any pizzas. If the town decides to make 100, 000 pizzas, it can now only make 9,000 industrial machines (B) The opportunity cost the first hundred thousand pizzas is one thousand industrial machines If the town decides to makes 200,000 pizzas, it can now only make 7,000 industrial machines (C) Notice: Opportunity Cost increased from 1,000 to 2,000 industrial machines for every 100,000 increase in pizzas Economic Growth Economic Growth An increase in an economy’s total output of goods and services This can happen due to: Rise in amount of available resources Improvement in technology Both these trends cause an outward shift in the PPF, thus, the amount of feasible output combinations expands Economic Contraction Just as an economy can grow, it can contract as well This can happen because: A society’s output of goods and services falls Drop in amount of available resources Explaining the reasons for economic growth and contraction is one of the main topics in macroeconomics EXAMPLE Computers – Capital Good Hamburgers – Consumption Good How does a society’s choice between the two affect the position of its future PPF? By choosing to produce more capital goods relative to consumption goods, a society can increase the amount of available resources Important to focus on capital resources to achieve good rates of economic growth in a country PPF Curve would shift outwards