Kingdoms Plantae and Animalia and rest of Classification Notes
advertisement

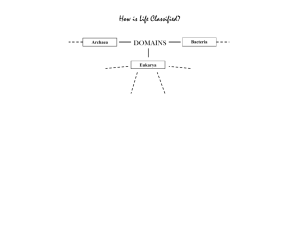
Kingdoms Plantae and Animalia and rest of Classification Notes Kingdom Plantae • Characteristics: – Eukaryote – Multicellular – Autotrophic (photosynthesis) – Cell wall – Mostly terrestrial Kingdom Plantae Examples • Mosses Kingdom Plantae Examples • Ferns Kingdom Plantae Examples • Conifers Kingdom Plantae Example • Flowering plants Kingdom Animalia • Characteristics – Eukaryote – Multicellular – Heterotrophic (ingest) – No cell wall – Terrestrial and aquatic Kingdom Animalia Examples • sponges Examples • Jellyfish Examples • Mollusks Examples • Round worms Examples • Flat worms Examples • Segmented worms Examples • Arthropods Examples • Starfish Examples • Fish Examples • Amphibians Examples • Reptiles Examples • Birds Examples • Mammals Phylogeny • (evolutionary history) • Phylogenetic trees are branching diagrams showing how organisms are related • Also called family trees • Fossil records help establish relationships on a phylogenetic tree • Organize living things based on their evolution Phylogenic Tree • Common ancestor is shown at the base of the tree • Most modern organism shown at the tips of branches • Each time a branch divides into a smaller branch, a new species evolves Cladograms • Show how organisms are related based on shared, derived characteristics such as feathers, hair, scales, etc. THREE DOMAIN SYSTEM • Based on comparing sequence of ribosomal RNA in different organisms to determine ancestry. • All organisms placed into 3 broad groups called DOMAINS Three Domain System Three Domain System • Domain Archae: (Kingdom Archaebacteria) contains chemosynthetic bacteria living in harsh environments. • Domain Bacteria or Eubacteria: (Kingdom Eubacteria) contains all other bacteria including those causing diseases. • Domain Eukarya or Eukaryota: (Kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia) contains all eukaryotic organisms •The end of these notes