File
advertisement

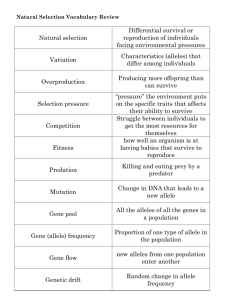
Gene Definition (a) A gene is the basic physical unit of heredity. Remember that heredity is the genetic transmission of characteristics (or traits) from parents to their offspring. Therefore a gene is the physical representation of this in the human body. (b) Genes are a form of DNA and each gene contains a particular piece of information that is required to make a protein for a cell. Therefore genes carry the information required to create a person’s physical appearance, kind of like a biological computer programming code. Half of a person’s genes come from their mother and the other half come from their father. Allele Definition (a) Some characteristics (or traits), such as eye colour or hair colour, can be controlled by a single gene. The same gene in a human has two copies that are not necessarily identical. Different copies of the same gene are called alleles. For example, the gene for eye colour has an allele controlling the blue eye colour and another allele controlling the brown eye colour. Dominant and Recessive Definition An allele can be dominant or recessive: (a) The trait that is controlled by a dominant allele will develop if the allele is present on one OR both chromosomes in a pair. However, (b) The trait that is controlled by a recessive allele will develop only if the allele is present on BOTH chromosomes in a pair. Homozygous and Heterozygous Definition While an allele can be dominant or recessive, an individual can be homozygous or heterozygous: (a) Individuals who are homozygous for a certain gene carry two copies of the same allele. Individuals can also be referred to as ´purebred´ for a certain characteristic if they carry two copies of the same allele (e.g. purebred tall if BOTH alleles inherited were tall). However, (b) Individuals who are heterogenous for a certain gene carry two different alleles. Phenotype and Genotype Definition (a) A phenotype is the physical appearance which results from the information actually inherited (if you have brown eyes then you have the phenotype brown eyes). Dominant alleles are expressed even if only one is present in a cell’s phenotype. However, this is not the case for recessive alleles. If only one recessive allele is present then it can become masked by the dominant allele in the phenotype. However, (b) A genotype of an organism demonstrates the alleles that are present for a particular characteristic, but does not indicate which characteristic is physically represented in an individual like a phenotype does. The genotype is the code for the phenotype.