Chem 10 CP Name: Unit 4 Study Guide In order to be adequately
advertisement

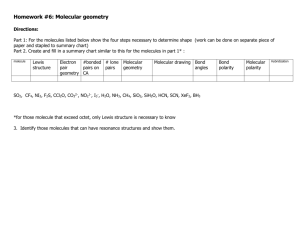
Chem 10 CP Name: _____________________________ Unit 4 Study Guide In order to be adequately prepared for your test, you will need to do the following: Study your notes Read relevant sections of the textbook Review all of the worksheets for this unit Go over your homework assignments for this unit 1. Draw a Lewis dot structure for carboxylic acid with the following molecular formula; C3H6O2 2. Draw a structural formula for an ester with the following molecular formula: C2H4O2. 3. Draw a Lewis dot structural for an amine with the following molecular formula: C3H9N. 4. Draw a structural formula for an alcohol with the following molecular formula; C4H10O. 5. In the following equation, label the reactant(s), the product(s) and decide if it represents a physical or a chemical change. 3 H2 + N2 2 NH3 6. What is the purpose of adding a catalyst to a chemical reaction? 7. Use structural formulas to write the reaction between propanoic acid (C3H6O2) and propanol (C3H8O). Be sure to include the structures for the resulting products. 8. Rewrite the above reaction using molecular formulas. 9. Write the structural formulas (with labels) for the following functional groups: Carboxyl, amine, ester, hydroxyl (alcohol) 10. With each functional group in the question above, give the related smell, and the appropriate ending for its name. 11. Define the term “electron domain”. 12. What is the electron domain theory? 13. What is the first step (after determining the molecular formula) you need to do in order to find the geometric shape of a small molecule? 14. How many electron domains surround each of the central atoms in the drawings shown below? 15. What is the geometric shape of each of the structures given in the previous question? 16. How many unbonded (lone pair) electron domains are in HF? Do any of them determine the shape of HF? Why or why not? 17. Determine the molecular geometry of the following molecules. CH3OH CH3NH2 PH3 C2H4 CH3Cl H2S HCN H2CO 18. How many electron domains are contained in a double bond? In a triple bond? 19. Is the geometry of the electron domains in a molecule always the same as the molecular geometry? 20. Consider the pentane molecule, C5H12. a. Draw the Lewis dot structure for pentane. b. How many electron domains does the molecule have? c. What shape would you predict for the C5H10 molecule? (explain why the carbon chain is not straight) 21. Relate the receptor site theory to the “lock and key” model? See pages 208 through 211 in the text. 22. What did the results mean (attraction to a charged wand or beading on wax paper) in regards to molecules in the “Attractions Between Molecules” activity? 23. What two things do we need to know about a small molecule in order to determine its polarity? 24. What are intermolecular forces? 25. A. Name and define the three types of bonding. B. Using dot structures, demonstrate what happens to the electrons involved in each type of bonding. 26. Define electronegativity? 27. What is a dipole? (Explain the two definitions.) 28. What does the symbol mean? 29. Determine the molecular geometry of the following molecules. Then label the molecules as polar or nonpolar. Where possible, use the arrow symbol to indicate the direction of the dipole. H2Se CO2 PBr3 CF4 Cl2 SF2