Downlaod - OAKHEIGHTS COLLEGE
advertisement

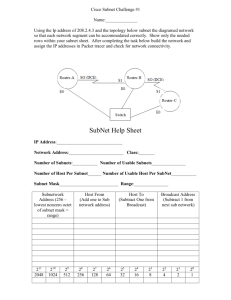
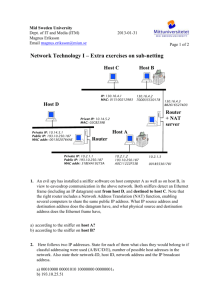
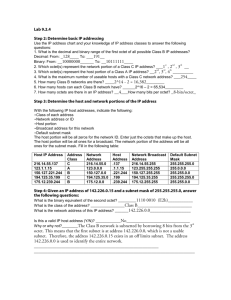
IP ADDRESSING AND CUSTOM SUBNETTING, READ ONLY DOMAIN CONTROLLERS, FUNCTIONAL LEVELS & OPERATION MASTERS IP Table Let us first study the IP table IP Address Classes CLASSES NETWORK ID SUBNET MASK NETWORK HOST CLASS A 1-126.0.0.0 0 255.0.0.0 126 16,777,214 CLASS B 128-191.0.0.0 10 255.255.0.0 16,384 65,534 CLASS C 192-223.0.0.0 100 255.255.255.0 2,097,152 254 Class A Loopback Address 127.0.0.1 Private IP Address Class A 10.0.0.1 – 10.255.255.254 Class B 172.16.0.1 – 172.31.255.254 Class C 192.168.0.1 – 192.168.255.254 Automatic Private IP Addressing APIPA, mostly happens when the DHCP server is down. Microsoft use it as host for client that are unable to receive IP address. Class C 169.254.0.0/24 Again Before we proceed, we need to get familiar with Binary to Decimal break-down 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Explanation will be done in class Custom Subnet ting We will try to wrap up subnet ting by dealing with 3 to 4 examples Example 1: Class C Network ID 192.168.1.0 Minimum subnet host required 50 Minimum subnet required 4 Calculate the Custom subnet mask, Maximum host per subnet, Maximum subnet, Subnet ID, Host ID ranges Solution: a. Network ID = 192.168.1.0 You first write out the default subnet mask which is 255.255.255.0 And its equivalent is 1111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 because 11111111 = 255 and 00000000 = 0 Now you need 2x > 50 (minimum subnet host required), you then find x Here x is 6 because 26 = 64 > 50 so x = 6 We now count at the last octet 6 zeros for the host i.e. the last octet now becomes 11000000 Meaning we have 2 network and 6 host, therefore each of the network falls under 128 & 64 Now we add 128 + 64 = 192 Our custom subnet mask now becomes 255.255.255.192 b. the maximum host per subnet is 26 = 64 – 2 = 62 (because it cannot be all zeros and all ones cos all ones are used for broadcasting) c. the maximum subnet is 22 = 4 i.e. 2 raise to power of the network which is 2 bit = 4 d. Our subnet ID now increments by 64 i.e. 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.64 192.168.1 128 192.168.1.192 e. The host ID ranges now becomes 192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.62 192.168.1.65 - 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.129 - 192.168.1.190 192.168.1.193 – 192.168.1.254 Example 2: Class C Network ID 223.1.1.0 Minimum subnet host required 29 Minimum subnet required 6 Calculate the Custom subnet mask, Maximum host per subnet, Maximum subnet, Subnet ID, Host ID ranges Solution: a. Network ID = 223.1.1.0 You first write out the default subnet mask which is 255.255.255.0 And its equivalent is 1111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 because 11111111 = 255 and 00000000 = 0 Now you need 2x >29 (minimum subnet host required), you then find x Here x is 5 because 25 = 32 >29 so x =5 We now count at the last octet 5 zeros for the host i.e. the last octet now becomes 11100000 Meaning we have 3 network and 5 host, therefore each of the network falls under 128 & 64 &32 Now we add 128 + 64 + 32 = 224 Our custom subnet mask now becomes 255.255.255.224 b. the maximum host per subnet is 25 = 32 – 2 = 30 (because it cannot be all zeros and all ones cos all ones are used for broadcasting) c. the maximum subnet is 23 = 8 i.e. 2 raise to power of the network which is 3bit =8 d. Our subnet ID now increments by 32 i.e. 223.1.1.0 223.1.1.32 223.1.1.64 223.1.1.96 223.1.1.128 223.1.1.160 223.1.1.192 223.1.1.224 e. The host ID ranges now becomes 223.1.1.1 - 223.1.1.30 223.1.1.33 - 223.1.1.62 223.1.1.65- 223.1.1.94 223.1.1.97– 223.1.1.126 223.1.1.129 - 223.1.1.158 223.1.1.161 - 223.1.1.190 223.1.1.193 - 223.1.1.222 223.1.1.225 - 223.1.1.254 Example 3: Class C Network ID 223.1.2.0 Minimum subnet host required 2 Minimum subnet required 61 Calculate the Custom subnet mask, Maximum host per subnet, Maximum subnet, Subnet ID, Host ID ranges Solution: a. Network ID = 223.1.2.0 You first write out the default subnet mask which is 255.255.255.0 And its equivalent is 1111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 because 11111111 = 255 and 00000000 = 0 Now you need 2x >2 (minimum subnet host required), you then find x Here x is 2 because 22 = 4 >2 so x =2 We now count at the last octet 2 zeros for the host i.e. the last octet now becomes 11111100 Meaning we have 3 network and 5 host, therefore each of the network falls under 128, 64,32,16,8,4 Now we add 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 = 252 Our custom subnet mask now becomes 255.255.255.252 b. the maximum host per subnet is 22 = 4 – 2 = 2 (because it cannot be all zeros and all ones cos all ones are used for broadcasting) c. the maximum subnet is 26 = 64 i.e. 2 raise to power of the network which is 6bit =64 d. Our subnet ID now increments by 4 i.e. 223.1.2.0 223.1.2.4 223.1.2.8 223.1.2.12 ………………… 223.1.2.248 223.1.2.252 e. The host ID ranges now becomes 223.1.2.1 - 223.1.2.2 223.1.2.5 - 223.1.2.6 223.1.2.9- 223.1.2.10 ………………………………… 223.1.2.249– 223.1.2.251 223.1.2.253 - 223.1.2.254 Example 4: Class B Network ID 172.16.0.0 Minimum subnet host required 500 Minimum subnet required 14 Calculate the Custom subnet mask, Maximum host per subnet, Maximum subnet, Subnet ID, Host ID ranges Solution: a. Network ID = 172.16.0.0 You first write out the default subnet mask which is 255.255.0.0 And its equivalent is 1111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 because 11111111 = 255 and 00000000 = 0 Now you need 2x >500 (minimum subnet host required), you then find x Here x is 9 because 29 = 512 > 500 so x =9 We now count at the last octet 9 zeros for the host i.e. the last octet now becomes 11111110.00000000 Meaning we have 7 network and 9 host, each of the network falls under 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, and 2 Now we add 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 = 254 Our custom subnet mask now becomes 255.255.254.0 b. the maximum host per subnet is 29 = 512– 2 = 510 (because it cannot be all zeros and all ones cos all ones are used for broadcasting) c. the maximum subnet is 27 = 128 i.e. 2 raise to power of the network which is 7bit =64 d. Our subnet ID now increments by 512 i.e. 172.16.0.0 172.16.2.0 172.16.4.0 172.16.6.0 ………………… 172.16.252.0 172.16.254.0 e. The host ID ranges now becomes 172.16.0.1 - 172.16.1.254 172.16.2.1 - 172.16.0.0 172.16.4.1 - 172.16.0.0 ………………………………… 172.16.252.1 – 172.16.0.0 172.16.254.1 - 172.16.0.0 Example 5: Class A Network ID 10.0.0.0 Minimum subnet host required 220 Minimum subnet required 118 Calculate the Custom subnet mask, Maximum host per subnet, Maximum subnet, Subnet ID, Host ID ranges Solution: a. Network ID = 10.0.0.0 You first write out the default subnet mask which is 255.0.0.0 And its equivalent is 1111111.00000000.00000000.00000000 because 11111111 = 255 and 00000000 = 0 Now you need 2x >220 (minimum subnet host required), you then find x Here x is 8 because 28 = 256 > 220 so x =8 We now count at the last octet 8 zeros for the host i.e. the last octet now becomes 11111111.11111111.00000000 Meaning we have 18 network and 8 host, each of the network falls under 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 Now we add 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 255 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 255 Our custom subnet mask now becomes 255.255.255.0 b. the maximum host per subnet is 28 = 256 – 2 = 254 (because it cannot be all zeros and all ones cos all ones are used for broadcasting) c. the maximum subnet is 216 = 65, 536 i.e. 2 raise to power of the network which is 6bit =64 d. Our subnet ID now increments by 256 i.e. 10.0.0.0 10.0.1.0 10.0.2.0 10.0.3.0 ………………… 10.0.255.0 10.1.0.0 10.1.1.0 10.1.2.0 ………………… 10.254.255.0 10.255.255.0 e. The host ID ranges now becomes 10.0.0.1 - 10.0.0.254 10.0.1.1 - 10.0.1.254 10.0.2.1 - 10.0.2.254 10.0.3.1 – 10.0.3.254 10.0.4.1 - 10.0.4.254 ………………………………… 10.0.255.1 - 10.0.255.254 10.1.0.1 - 10.1.0.254 10.1.1.1 - 10.1.1.254 10.1.2.1 - 10.1.2.254 ………………………………. 10.254.255.1 - 10.254.255.254 10.255.255.1 - 10.255.255.254 Read only Domain Controllers Read only Domain Controllers is a domain controller that never talks back, it only listen to instructions. It can only read information from other domain but can’t write e.g. editing accounts, resetting password and so on What you need to know before installing read only domain controller It is a read only copy of the directory database Only password is omitted in the active directory objects Update replicated to RODC from RWDC Locations where you might want to use RODC o Small branch offices because you might not have full infrastructure to install RWDC o No IT staffs o Less Secure Location Administrator Role Separator is a special roles that are assigned to read only domain controller, what it does is to Delegate Admin role to any User usually with the dcpromo answer file Applies only to one RODC so it doesn’t matter if you make them an enterprise admin Admin user can o Install updates, drivers o Perform admin task Prerequisite for RODC installation PDC emulator windows server 2008 Receives updates from windows server 2008 not 2003 DFL/FFL can be Server 2008 or 2003 One RODC per domain per site Now you can now install the RODC by running dcpromo in an advanced option…I You now run dcpromo /unattend:rodcinstall.txt in the administrative command prompt. Installation will be done in class. Operation Masters Operation Masters Roles or FSMO roles-Flexible Single Master Roles are predefined roles, the roles are 1. Forest a. Domain Naming- is a mechanism in charge of domain naming, Name change etc. it check if domain exit in place of a new one b. Schema- is responsible for all text area, check boxes, dialing characteristics, radio buttons and all different things you can fill within the active directory especially active directory users and computers. It is the skeletal structure of Active Directory 2. Domain a. Infrastructure- it keeps across domain references straight from one domain located inside of a security group to another b. RID Master- This role really relates to the thing called SID e.g. if you do a whoami /user in the command prompt, it gives you a user name and a SID number is a unique identifier & unique account of the domain, no other domain in the world should have the SID. So the reason why all this is possible is because of the RID Masters Role. c. PDC Emulator- the most critical of all of the domain role is PDC emulator, all other roles can actually goes down without being noticed but not in PDC because it’s in charge of i. Password Authority ii. Group Policy Object iii. Domain Master Browser iv. Master Time Source………explanation in class Proper explanation of each roles will be done in class. Domain Functional & Forest Functional Level-Functional Levels It gives you various capabilities within your domain, the highest the domain functional level, the more features of active directory you get. Same in Forest functional level. Windows Server 2003 Domain Functional Level We have You must install WS 2003 or 2008 DC Rename User password and last logon stamp Selective authentication Constrained Delegation Windows Server 2008 Domain Functional Level DFL 2003+ DC=2008 Last Logon Fine-grained Password Windows Server 2003 Forest Functional Level Forest Trust Domain Rename RODC Deactivate/ Redefine of schema objects Windows Server 2008 Forest Functional Level Nothing New, New Domain just need be Windows server 2008…Comprehensive explanation in class.