Design a network addressing system, with subnet and
advertisement

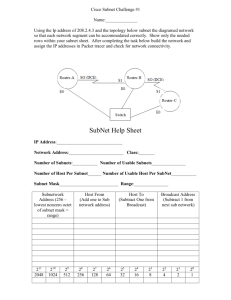
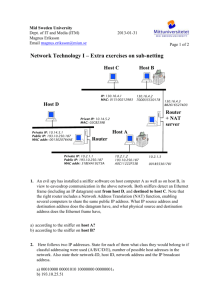
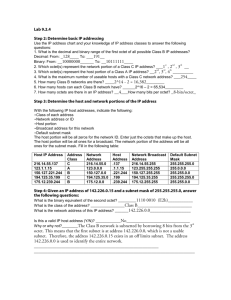
Exercise 3 Design a network addressing system, with subnet and host IDs including appropriate devices Network protocols are the rules that define the standards for communication between network hosts .Examples of protocols used in computer networking include: 1. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) 2. Network Basic Input Output System (NetBIOS) 3. NetBIOS Enhanced User Interface (NetBEUI). TCP/IP is a suite of protocols including Internet Protocol (IP) which provides network addressing. Each computer, network printer or other network host on your organization network will need a unique IP address – just the same as a letter that is mailed to you through Australia Post needs a unique address to be delivered to you. These IP addresses can be either configured manually at each device or assigned automatically by the network operating system. In this we will look at the format of IP addresses, and how networks are segregated from each other by using subnet masks. To fully understand how IP addressing works, firstly you need to be able to translate binary numbers such as 10001000 to decimal numbers (10001000 =136). An IP address is 32 bits long and made up of two components, a network portion and a host portion. The network address is used to identify the network and is common to all the devices attached to the network. The host (or node) address is used to identify a particular device attached to the network. The IP address is generally represented using the dotted-decimal notation, where 32 bits are divided into four octets. Each of the octets can be represented in a decimal format, separated by decimal points. When a computer is configured to use the same IP address each time it powers up, this is known as a Static IP address. In contrast, in situations when the computer's IP address is assigned automatically, it is known as a Dynamic IP address,The current version of the IP protocol is IP version 4 (IPv4) & IP version 6 (IPv6). Example of Ipv4 :-An Ipv4 address(dotted decimal notation) 10101100. 00010000.11111110.00000001 172 16 254 1 One byte = 8 Bits So, four byte = 8*4=32 Subnet allows network administrators to subdivide a single class of network addresses into multiple, smaller networks, allowing allowing the more efficient use of IP addresses. The basic idea of subnetting is to divide the standard class full host number field into two parts – the subnet ID and the host ID on that subnet. . In each of IP address first two bytes (172.16)are network address ,Third is subnet ID and fourth byte is host ID. Computer 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.1 Computer 172.16.1.2 Computer 172.16.1.3 hub router Computer 172.16.2.2 172.16.2.1 hub Computer 172.16.1.4 Computer 172.16.2.3 Computer 172.16.2.4 IP address Subnet 1 172.16.1.0/24 (subnet mask 255.255.255.0) Subnet 2 172.16.1.0/24 (subnet mask 255.255.255.0) To internet NOTE:-Subnet mask - Determine which bits in the host address are the subnet ID requires using 32 bit value. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------THE END ------------------------------------------------------------------------------