File - Jose Banuelos 411
advertisement

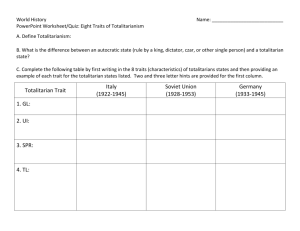
Jose Banuelos 1 Jose Banuelos Manos EDSS 300 Thurs. Lesson Plan for Totalitarianism, Fascism, and Communism Unit: Post World War I Europe Grade: 10th World History 10.7 Students analyze the rise of totalitarian governments after World War I. Analyze the rise, aggression, and human costs of totalitarian regimes (Fascist and Communist) in Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union, noting especially their common and dissimilar traits. ELD Standard Beginning: Identify terms such as dictator, totalitarian, fascisms, Nazism, and communism. ELD Early Intermediate: Identify which leader controlled which country and define what type of government the dictator ran. ELD Standard Intermediate: Explain with detailed sentences how the totalitarian regimes differentiated between one another and at least a couple of characteristics of each dictatorship. Objective: Students will be able to define and explain the characteristics of a totalitarianism government as well as be able to differentiate between fascist and communist rule. Language Objective for Beginning Student: Students are able to copy facts of totalitarian rule from the power point. Language Objective for Early Intermediate Students: Students are able to identify the major idea of totalitarian rule. Language Objective for Intermediate Students: Students are able to distinguish facts of totalitarianism government and fascist/communist rule. Anticipatory Set: Ask the class to think how government has oppressed people in the past. They will write up a quick list and then they will share with their Jose Banuelos 2 neighbor their ideas of governmental tyranny. After everyone has shared, we will have a quick classroom discussion to make sure everyone has an idea of the ways government has negatively affected their people. Purpose: This lesson will help students understand how Hitler, Mussolini, and Stalin came to power and gave rise to their respective totalitarian government and oppressed the people in their country. Input: I will show the students a power point with information from the textbook, and then give quick info about what is totalitarianism and the characteristics a totalitarian government, fascism, and communism. I will pass out a Totalitarian chart I created and the students will use their textbooks and power point to fill in the boxes. Differentiation: For students that need extra literacy help, I will give them help with matching words. For example, Fascism will match with Hitler and Mussolini. To further this activity, students will describe the governments with the power point slides. (worksheet provided) Modeling: Using the textbook, I will model how to fill in the worksheet sheet. We will do the first couple of sections of the chart together. Check for Understanding: I will ask the students how comfortable they are with the chart and textbook by giving me thumbs up or thumbs down. The students with thumbs up will then work on it in pairs or groups. If the students give a thumbs down, I will do a couple more boxes Guided Practice: Students will work in pairs use their to fill in the rest of the totalitarian chart. After everyone has finished and shared their totalitarian chart with their group students will write on the back of the worksheet. Their write up will answer, “What are differences and similarities between Fascism and Jose Banuelos 3 Communism,” “Which dictator took the most advantage of their power and why?” and “Who do you believe had the most control and rule of their respective country and why?” Differentiation: If students need extra literacy help, the students will receive a separate worksheet with a word bank that belongs to the totalitarian chart. For example, Jews would be in the word bank and belongs in the Germany was oppressed box. This would better help students, because it will make easier to define the characteristics. To further this activity, the back of the worksheet will be used to write sentences to describe totalitarianism. The students would use their matching working from before to help them frame a sentence. (worksheet provided) Closure: To finish the lesson students will come up to the board and fill in my totalitarian chart with their answers on the white board. We will have a class discussion, reviewing the worksheet, along with totalitarianism, fascism, and communism. Independent Practice: If a Students finish early, then they would make a quick write up on how different is a totalitarian government when compared democracy. Students will also describe the differences of the American leaders and totalitarian leaders as well. Bibliography 1. Roger B. Beck, Modern World History: Patterns of Interaction, (McDougal Little) Jose Banuelos 4 Worksheet for input differentiation: MATCH THE WORDS TO THEIR TYPE OF TOTALITARIAN GOVERNMENT BY DRAWING A LINE Communism STALIN HITLER NATIONALISM TOTALITARIANISM CHARISMATIC LEADERS SPEECHES CLASSLESS SOCIETY Fascism INTERNATIONALISM Jose Banuelos 5 Word box for chart Fascism Economic problems Italy S oviet U. Anyone against fascism Mussolini Feared revolt Attacked Italian communist and socialist Support from middle class and industrial leaders Germ any Stalin totalitarian Revolution; Lenin dies Controlled all media: newspapers, radio, etc. Religion, noncommunist Communism Wanted to keep non-communist idea out Control of education prevents other learning Jews Scapegoat for Germany’s problems Hitler Media (posters and speeches) making racist remarks towards Jews. Fascism/Nazism Germany facing a Great Depression Military tactics Jose Banuelos 6