Latin America
advertisement

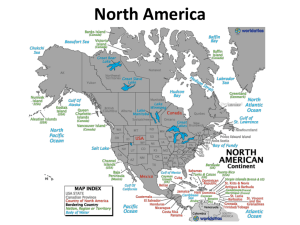
Latin America Coach McFarland 1 Physical Geography Mountains of South America Andes • World’s longest mountain chain above sea level • 4,500 miles • Stretching from Cape Horn to Panama Guianna Highlands Brazilian Highlands 2 Physical Geography Mexico consist mostly of a high central plateau with mountains along each side. Many areas of this region experience wet summers and dry winters. 3 Physical Geography 3 major river systems drain the eastern side of South America. The Amazon River The Orinoco River The Parana River 4 Historical Geography 3 great Native American civilizations Olmecs – 1st people to build religious pyramids Mayas – considered the most advanced culture Aztecs – centered around present day Mexico City • Warfare and disease brought by Europeans contributed to the decline of these civilizations. 5 Historical Geography Spanish and Portuguese colonists settled in Central America. The French, British, and Dutch acquired lands the Spanish had not colonized. Ex. - Smaller islands of the Caribbean, as well as Jamaica and Haiti. 6 Historical Geography All colonies based on plantation agriculture. Major crops • Sugarcane • Indigo • Bananas Slaves provided most of the labor 7 Historical Geography Because there were few women colonists, Europeans often married Native American or African women. Mestizos – people of Native American and European descent. Mulattos – people of African and European descent. 8 Economic Geography Natural resources: Gold Silver Copper Petroleum 9 Economic Geography Agriculture is divided into 2 categories: Traditional agricultural systems (large estates, called haciendas) and subsistance agriculture. Modern commercial and plantation agriculture. 10 Economic Geography Largest industrial region is between Rio de Janeiro, Brazil and Buenos Aires, Argentina. Tourism is a growing industry, particularly in the Caribbean Islands. 11 Regional Issues Middle and South America is experiencing large population growth. Lack of economic development has contributed to political instability. The region has challenges similar to other parts of the world Cutting of rain forests. Growing and trafficking of illegal drugs. 12 Mexico More than ½ of Mexico’s workers are employed in industrial and service jobs. Its most rapidly growing industrial centers are the cities along the U.S. border American and foreign companies have established factories in these cities. Products are assembled and exported to the U.S. and other nations. This is, in part, due to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). 13 Mexico City 14 Mexico Mexico City, the nation’s capital, is one of the most populated cities in the world, holding nearly 1/5 of the country’s pop. Monterrey and Tijuana with San Diego, California are beginning to merge into a metropolitan area. The Yucatan peninsula is famous for Cancun and Cozumel, resort cities on the Caribbean coast. 15 Cancun Cozumel 16 Central America The mountainous isthmus between North and South America separating the Caribbean and Pacific Ocean. Coffee is the primary export. 17 Central America Guatemala One of the most populous countries in Central America. 18 Central America Belize Visitors here are attracted by beautiful coral reefs. 19 Central America Honduras About 90% of the people are Mestizos. 20 Central America El Salvador During much of the 1980’s, the country was wracked by civil war. 21 Central America Nicaragua In 1979, the country began a period of dramatic political change. 22 Central America Costa Rica Has the highest standard of living and literacy rate in Central America. 23 Central America Panama The Panama Canal allows ships and trade to travel more quickly and safely between the two oceans. 24 South America Colombia Colombia is world famous for its coffee. Bogota is the nations capital and a modern city. Much of the country’s recent violence is related to a large illegal drug trade. 25 South America Venezuela Caracas is the capital. Rural poverty is wide spread. Oil provides about 80% of export income. Venezuela helped found OPEC, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries. 26 South America The Guianas Guyana – Tension between 2 major ethnic groups: those of South Asian descent (over ½ the pop.) and Africans/Mulattos. Suriname – Violent ethnic political disputes are common. French Guiana – The largest of France’s overseas territories. 27 South America Brazil Largest country in South America, and covers over half of the continents land area. Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro are major economic centers. Brasilia is the nation’s capital The Amazon River carries more water than any other river in the world. Destruction of the Amazon Rain Forest has become a global issue. 28 South America Argentina The 2nd largest country in Middle and South America. Competes with the U.S., Canada, and Australia in selling beef. Sheep grazing is a chief industry. Buenos Aires is the Capital. Has claimed the Falkland Islands for a long time. However, Britain has ruled the islands since 1833 29 South America Uruguay Montevideo is the business and government center of the country. 30 South America Paraguay A landlocked country. Hydroelectric projects make future development promising. 31 South America Ecuador Equator passes directly through Ecuador. Quito is the capital. The Galapagos Islands served as the laboratory for Charles Darwin. 32 South America Peru Lima is the capital. Every 5 to 10 years the country experiences El Nino, the weather pattern that warms the ocean near the coast, causing fish to flee and the coast to flood. 33 South America Bolivia La Paz is the capital, the highest in the world at 12,001 feet. 34 South America Chile Santiago is the capital. After years of political turmoil, Chile now has a stable democratic government. 35 The Caribbean Islands (West Indies) Contains 3 major island groups Greater Antilles Lesser Antilles Bahamas Beautiful beaches and sunny weather have made tourism the most rapidly growing industry. 36 Greater Antilles Cuba One of the world’s largest sugar exporter. 90 miles off the coast of Florida. 1959 Fidel Castro came to power. (Bro. Raul is now leader in 2008) Havana, the capital is the largest city in the Caribbean. 37 Greater Antilles Haiti Occupies the western 1/3 of the island Hispaniola. Poorest and most densely populated country in the Americas. Capital is Port-auPrince 38 Greater Antilles Dominican Republic Occupies the eastern part of Hispaniola. Santo Domingo, the capital, was the 1st permanent European settlement in the Western Hemisphere. 39 Greater Antilles Puerto Rico U.S. territory Citizens can serve in the military, but cannot vote in U.S. presidential elections. There is debate whether the country should remain a commonwealth, become independent, or become a U.S. state 40 Greater Antilles Jamaica A huge tourist attraction. 41 Lesser Antilles Virgin Islands Politically divided between the U.S. and the United Kingdom. Martinique – French possession Guadeloupe – French possession Aruba – Dutch territory Bonaire – Dutch territory Curacao – Dutch territory 42 Lesser Antilles Barbados Trinidad Tobago 43 Bahamas In the Atlantic Contains more than 700 islands 44