Chapter 13 Populations and sustainability
advertisement

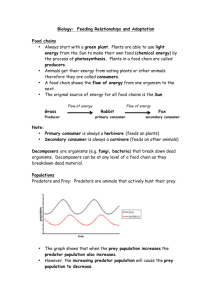
Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Populations and sustainability By the end of this session I should be able to: (a) explain the significance of limiting factors in determining the final size of a population; (b) explain the meaning of the term carrying capacity; (c) describe predator–prey relationships and their possible effects on the population sizes of both the predator and the prey; (d) explain, with examples, the terms interspecific and intraspecific competition; (e) distinguish between the terms conservation and preservation (HSW6a, 6b); Bacterial Growth Curve In a closed system, the organisms will eventually produce toxic by-products and die because the carrying capacity of the growth medium has been exceeded. http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/fox/growth_c.jpg World Population Density, 2012 www.nationsonline.org World Population Density – Another View National Geographic Atlas of the World, Eighth Edition WATCH! 2013 Population video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sc4HxPxNrZ0 Carrying Capacity • The population that an area will support without undergoing environmental deterioration. • The carrying capacity of an environment tends to limit population size. • Food availability, reproductive behaviour, and infectious diseases tend to keep animal (inc human) populations in check. WATCH ME! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BSVbdaubxxg In reality what does the carrying capacity look like? Abiotic factors are the non-living Components of the Environment • Abiotic factors include: – – – – – – Sunlight Water Temperature Wind Soil/substrate (edaphic) Special events such as: • • • • • Fires Hurricanes Floods Volcanic eruptions Tsunamis Biotic Factors A living organism is also affected by the living components of its environment. • Predators feed on members of the population. • Microbes can bring diseases. (If time travel were possible, and you could be transported to the Cretaceous Era to look at dinosaurs, don’t be afraid of Tyrannosaurus, fear the microbes. You would have no immunity to them!!) • There may be competition for nesting space. • Plants may compete for the light needed to carry out photosynthesis. • There are many other biological factors determining the success of an individual or species. • Competition exists for available food resources. Predator – Prey Relationships: A Description • WATCH ME! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CsfJL-IIVz4 (Madler, 1998) The predator’s abundance curve almost always lags behind that of the prey. WHY?? (2 marks) In reality the pattern is not always followed!! Circle areas on the graph where the is the case. Discussion pairs – 2 minutes Suggest reasons for the areas that you have circled on the graph where the typical predator prey pattern is not followed. (3 marks) Describe and explain the trend on the graph below. (5 marks) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1aRSeT-mQE Competition key terms 4 Minutes Key Term Compete Intraspecific Competition Interspecific Competition Niche Definition Plant example Animal example Sampling using transects Transects: LINE, BELT, CONTINUOUS, INTERRUPTED Procedures & equipment to consider when studying succession Distinguish between a line transect and a belt transect. Outline the advantages and limitations of using a frame quadrat. Outline the advantages and limitations of using a point quadrat. Studying succession – normally involves use of transects Describe how you would investigate plant diversity along a sand dune. For each scenario use pages 190 & 191 Scenario 1: Using a gridded quadrat along a line transect (8 marks) Scenario 2: Using a point quadrat along a belt transect (8 marks) Studying succession – normally involves use of transects Describe how you would investigate plant diversity along a sand dune. For each scenario use pages 190 & 191 Scenario 1: Using a gridded quadrat along a line transect (8 marks) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [8] ref to setting grid/area to be sampled; suitable reason for method chosen/ref line transect; ref to repetition of line transects; use of quadrats; use of appropriate sized quadrat; details of co-ordinates for quadrat placing; identify species/use of keys; presence or absence in quadrat;; measure % cover/use of appropriate scale; e.g.ACFOR ref to analysis of data/use of kite diagram; AVP; ref to relevant statistical analysis, e.g. Spearmans Rank Correlation max 7 QWC - clear well-organised answer using specialist terms 1 Studying succession – normally involves use of transects Describe how you would investigate plant diversity along a sand dune. For each scenario use pages 190 & 191 Scenario 2: Using a point quadrat along a belt transect (8 marks) • • • • • • • Details of positioning of belt transect (90 degrees from shoreline) Definition of belt transect Why a belt transect is suitable Description of placement of point quadrat (every 1m/5m) Description of use of point quadrat e.g. species present/not present under pin Identification of species (key) Reference to analysis of data e.g species frequency