Lab Exercise
advertisement

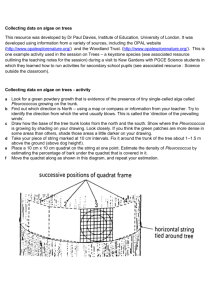
Lab Exercise. We need to distribute 3 Excel tables to the class for the quarterpoint data. 1: Columns = Transect, Point, SpeciesCode, TreeDBH [One for each tree stem] 2: Columns = Transect, Point, SpeciesCode [One for each sapling stem] 3. Columns = Transect, Point, Sapling distance, Tree distance [4 records/point] We need to distribute 2 Excel tables to the class for the quadrat data 4. Columns = Transect, Quadrat, SpeciesCode, TreeDBH [One for each tree stem] 5. Columns = Transect, Quadrat, SpeciesCode, stem number [One for each species in each quadrat] We need to distribute 1 table summarizing the overall stand [50,0-50,100-175,0-175,100] 6. Columns = Code, Species, Sap (N/ha), Trees (N/ha), BA(m 2/ha) E. The Assignment (a preview) Three datasets from the "Big Oak Woods" will be distributed: 1) Quadrat Method - Data from approximately 12 100 m 2 quadrats. 2) Quarter Method - Data from approximately 20 quarter points. 3) Complete Inventory - a summary of the tree and sapling data from a complete enumeration of the area sampled in 1) and 2) above. You will compare parameter estimates calculated from the sample data with "known" values of the parameters determined for the complete enumeration. Details will be explained when the data are distributed. Quarter method: 1. Prepare a new Excel table with columns for SpeciesCode, Sap (N), Tree(N), BA(m2). Recall that BA = πr2 = πd2 /4 2. Calculate total trees per hectare (density) by first calculating the mean distance, squaring the mean, and dividing into 10,000. 3. Calculate tree density/ha by species. First calculate relative density such that the species total 100, and then multiply the results by the [total trees per hectare / total trees observed] to give stems per hectare per species. 4. Repeat density calculations for saplings. 5. Calculate BA/ha. First calculate relative BA of each species such that BA totals 100. Then multiply the relative BA of a species by [total trees per hectare / total trees observed] Quadrat method: The only trick here is to remember that the area of a quadrat is 100 m 2. Thus, multiply everything by 100/n where n is the number of quadrat. Breifly comment on the degree of convergence of the results of each method with “truth”. Which is more accurate? Any thoughts on why? How does accuracy vary with species? The text portion of this report should not exceed 1 types page.