POPULATIONS Definition
advertisement

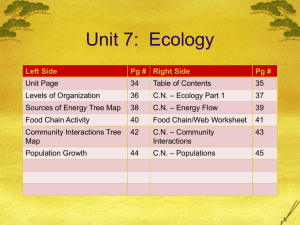
POPULATIONS Definition: All the members of a species that live in one place at one time. PROPERTIES of Populations Population SIZE Population DENSITY The number of individuals in a population Number of individuals per unit of area DISPERSION SPATIAL distribution of individuals within the population Uniform Random Clumped PROPERTIES of Populations Population Growth RATE Definition The amount by which a population’s size changes over time. Population Growth RATE Depends on: Birth + Death Emigration: movement of individuals OUT OF a population Immigration: movement of individuals INTO a population + 2 Types of Population Growth 1. 2. Exponential Logistic EXPONENTIAL Model of Population Growth Population increases rapidly with no limit “J” shaped curve What will a graph look like? Rare in nature. Why? Limit on the amount of resources (food / space) LOGISTIC Model ofAsPopulation populationGrowth reaches carrying capacity, death Accounts forincreases influence of rate limiting factors (like food, space) When at carrying capacity, What will the graph look birth like? rate is equal to death rate “S” WhenStretched populationout is small, birth rate is higher than death rate Population Growth Limited by Carrying Capacity Definition: The number of individuals the environment can support over a long period of time Population Size REGULATION 1. Density Independent Factors: reduce population regardless of population size Examples: Weather Fires Floods Population Size REGULATION 2. Density Dependent Factors: triggered by increasing population density Examples Food shortages Space limitations Waste accumulation Example of Exponential Growth Phase (JShaped Curve) Ex. Human Population Human population increased relatively slowly until about 1650. It then doubled in the next two centuries It doubled again in the next 80 years. Our population is now about 7 billion. This increases by 80 million/year This in an increase of 220,980/day. It takes 3 years for the world population to add the population equivalent of another US. Example of Exponential Growth Phase (JShaped Curve) Example of Exponential Growth Phase (JShaped Curve) How long will it be until we reach our carrying capacity? What will happen then? What factors increase our carrying capacity? Farming Medicines Better sanitation Example of Exponential Growth Phase (JShaped Curve) What impact does this stretching our carrying capacity have on other species. Endangers them or completely wipes them out. Example of Exponential Growth Phase (JShaped Curve) What are some consequences of human population growth? Global Warming Caused by the increasing burning of fossil fuels which lead to the greenhouse effect. Pollution Acid Rain Pile up of Waste Ozone Depletion The End!!