1/4 th of work force worked shorter hours reducing their incomes
advertisement

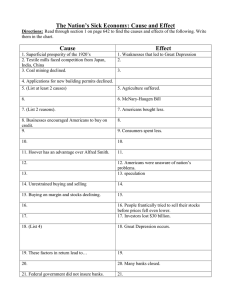
The Great Depression How was a decade of prosperity followed by a decade of hopelessness? The 1920s: “The Good ole’ Days” 1920s • jobs were plentiful • home ownership had doubled 1930s • Over ¼ unemployed – unemployment rate never dropped below 14 percent until 1941 • 1/4th of work force worked shorter hours reducing their incomes • Families were losing their homes, and many starving. “a permanent plateau of peace and prosperity.” 1920s 1930s • most home-owning families enjoyed amenities • Many families were going hungry. • 60% of all households had automobiles • 26% owned cars in 1920 • More teenagers were attending high school; fewer were working full time. • Children were riding around in freight cars, looking for work The Great Depression Causes of the Great Depression 1. Unequal distribution of wealth • 2% of people owned 60% of wealth • 50% of families lived below poverty level – Under $1500/yr • Unequal balance between production & distribution 2. Unequal distribution of corporate power • Government Policies benefited corporations and those who were wealthy • Abandoned anti-trust acts • 200 companies owned 50 % of nation’s wealth 3. Poor Banking Structure • Small, local banks owned by larger city ban • Not backed up or regulated by government • Lent out more than they took in http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qu2uJWSZkck 4. High Tariffs and War Debts • European countries couldn’t pay WWI debt b/c hit by depression • Hawley-Smoot Tariff: placed a high tax on imports – countries retaliate and halt international trade 5. Overproduction in Industry & Agriculture • Purchase new machines with credit to increase production – Plan: pay off debt with “increased” income from “increased” sales 6. Buying on Credit • Americans bought most durable goods(refrigerators, washing machines, radios, cars…) on the installment plan: some money down at first, followed by a year of monthly payments + interest – By the end of 1920s American consumers bought the following on installment plans: * 65 percent of vacuum cleaners * 75 percent of washing machines 7. Playing the stock market • People hoped to make a quick buck by purchasing shares of businesses, also known as ______. – part ownership of a company so that when the company prospers so do you! – But…..if the business declines….you lose $$$$ Problems with playing the stock market STOCK SPECULATION – risky move to buy stocks at low price then sell at a high price BUYING ON MARGIN: paying 10-50% of the stock and borrowing the rest from a broker Example of Buying on Margin The Good • EXAMPLE – 1 share is $110 and you pay $10 – You owe stockbroker $100 with 10% interest per month – 2 months later the stock doubled ($200)….you sold it – You owe stock broker $120 but make $70 (80-10) The Bad • EXAMPLE – 1 share is $110 and you pay $10 – You owe stockbroker $100 with 10% interest per month – 10 months the stock didn’t move and the broker wants his money…you sell the stock for $100 – You owe stock broker $90 + $100 =$190……YOU LOSE Buying on margin The good • Stocks go up • Borrowers sell at high price • Pay off… – Loan – Interest + make extra $$$ The bad • High interest rates • Demand payment anytime • If stocks fall then don’t have money to pay back Short term trends that led to the Great Depression 1. WEDNESDAY, October 23rd – Dow Jones dropped 21pts in an hour before it closed – Dow Jones Industrial Average = an average of stock prices of major industries 2. BLACK THURSDAY October 24th –investors began to sell and stock prices fell. JP Morgan & banks tried to stabilize market 3. BLACK TUESDAY/THE GREAT CRASH October 29th , 1929 – FEAR led to selling stocks 16.4 million shares sold investors lost over 30 billion dollars Short term trends that led to the Great Depression The Ripple Effect Caused by the Crash 4. Bank Failures – People are unable to pay loans to banks - More banks close - Fear leads to bank runs (people rushed to the banks to withdraw) 5. Savings wiped out – By 1933 nine million savings accounts vanished Short term trends that led to the Great Depression The Ripple Effect Caused by the Crash 6. Cuts in production – Businesses have no money to produce. Lack incentive due to lack of demand. 7. Businesses shut down - By 1933 100,000 business closed down 8. Rise in unemployment – As businesses cut back on production, workers are laid off. - went from 1.6million(3%) to 15million(25%)