Structure and Function of Multi
advertisement

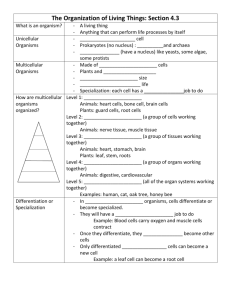
Structure and Function of Multi-celled Organisms Single-Celled vs. Multicellular Organisms Learning Target The student will distinguish between single cell and multicellular organisms. Single-Celled and Multicellular Organisms one cell. Some organisms are made up of only ________ Multicellular organisms are made up of ______ many cells. Often, cells in multicellular organisms are specialized to perform one task. These specialized cells must work together to keep the organisms healthy. What does specialized mean? Single-Celled Organisms Single-celled organisms are organisms that are made up of only one cell. Examples include bacteria, paramecia, and amoebas. Even though single-celled organisms are simple life forms, they still perform life functions. They move, find food, grow, and reproduce. Single-Celled Organisms Look at the amoebas below. Single-Celled Movement Amoebas move in the direction that their cytoplasm flows. These single-celled organisms eat by surrounding a food particle with streams of cytoplasm and then bringing the food into the cell. Some single-celled organisms have hair-like structures called cilia that help them move and feed. Others have tail-like structures called flagella that propel them forward. Food production and waste Other single-celled organisms have chlorophyll. Just like the chlorophyll inside plants, this chlorophyll allows the organism to transform the sun's energy into food for the cell. Single-celled organisms remove wastes by moving the wastes to the outside of their cell membranes. Single-Celled Organisms Reproduction Single-celled organisms also reproduce. Because they are made up of one cell, they reproduce by cell division. This kind of reproduction creates a new organism that is an exact copy of the parent. Multicellular Organisms Most of the plants and animals you see around you are multicellular organisms. This is because singlecelled organisms are usually very small and you need a microscope to see them. Dogs, cats, people, sunflowers, insects, sea stars, and worms are all made up of millions and millions of cells. Multicellular Cell Description Multicellular organisms are more complex than single-celled organisms, which are simple. Because of this, cells inside a multicellular organism perform specialized tasks. These cells all work together to keep the multicellular organism healthy. Multicellular Organisms For example, the cells that make up the heart work together to move oxygen and blood to all the other body tissues. A tissue is a group of cells that work together to perform a particular job. Multicellular Organisms Heart tissue along with other tissues all work together in the organ called the heart. An organ is two or more tissues working together to perform a job. The heart is one part of the circulatory system. The function of the circulatory system is to move oxygen and nutrients throughout an organism. The circulatory system is one example of an organ system. Multicellular organisms often have several organ systems. Multicellular Organisms Movement Multi-celled organisms can move on multiple ways. Animals can walk, crawl, slither, fly and swim. Plants movement by growing tall and also opening and closing its flowers. Multi-celled Reproduction Multi-cellular organisms can reproduce as well. Each unique cell goes through cell division (replication and reproduction)and is used for specific functions. 1. What is a group of cells that work together to perform a particular job called? a. a multicellular organism b. a single-celled organism c. an organ d. a tissue 1. What is a group of cells that work together to perform a particular job called? d. a tissue 2. Which of the following contains the most cells? a. a tissue b. an organ c. an organ system d. a single-celled organism 2. Which of the following contains the most cells? c. an organ system 3. Which of the following is not a life function of a single-celled amoeba? a. removing wastes from the cell b. moving c. collecting food d. making food from the sun's energy 3. Which of the following is not a life function of a single-celled amoeba? d. making food from the sun's energy