Parts of the plant and their functions
advertisement

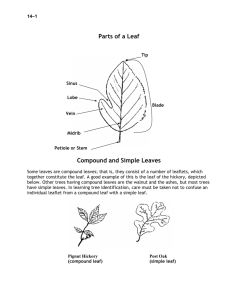
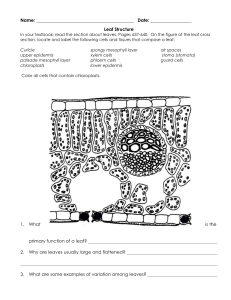
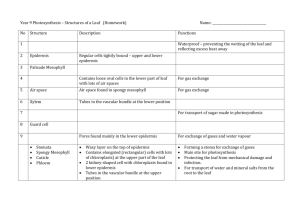
Complexity and Shapes of Leaves AGR 161: Unit C Found on Internet: Unknown Source Created By: Jennifer Stewart Objectives Recognize the complexity of Leaves Identify leaf shapes Principal Tissues of the Leaf Epidermis Cuticle Waxy substance covers the leaves and stems Waterproof layer that keeps water in plants Principal Tissues of the Leaf Epidermis (cont) Stomata Openings in the epidermis mainly located on underside of leaves Exchange of gases Principal Tissues of the Leaf Epidermis (cont) Guard Cells Two cells located on each side of stomata Open and closes stomata Allows gas exchange Principal Tissues of the Leaf Mesophyll layer Palisade mesophyll Primary site of photosynthesis Spongy mesophyll Contains air and chloroplasts Site of photosynthesis and gas exchange Principal Tissues of the Leaf Veins or vascular bundles In spongy mesophyll Phloem tissues conduct food from photosynthesis to rest of plant Xylem tissues conduct water and minerals up to cells in leaves and stems What is the difference between a simple leaf and a compound leaf? simple leaf = 2 parts (leaf blade and petiole) Leaf Blade Petiole What is the difference between a simple leaf and a compound leaf? Compound leaf: leaf blade divided into leaflets What are the different types of compound leaves? Palmately compound What are the different types of compound leaves? Pinately compound What are the different types of compound leaves? Trifoliate (alfalfa) Shape and size of leaves vary among plants used for identification of plants Review What is the difference between a simple leaf and a compound leaf? Review What type of compound leaf is this? Review What are the three parts of the epidermis? What is the cuticle? What are the guard cells? What are the three different leaf shapes?