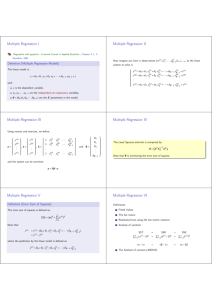
a. R 2
advertisement

Multiple Choice 1) When the estimated slope coefficient in the simple regression model, ̂ 1 , is zero, then a. There is a strong relationship between X and Y b. There is a moderate relationship between X and Y c. Y cannot be explained by X. d. The intercept is zero 2) In the simple linear regression model, the regression slope a. indicates by how many percent Y increases, given a one percent increase in X. b. when multiplied with the explanatory variable will give you the predicted Y. c. indicates by how many units Y increases, given a one unit increase in X. d. represents the elasticity of Y on X. 3) The OLS estimator is derived by a. connecting the Yi corresponding to the lowest Xi observation with the Yi corresponding to the highest Xi observation. b. making sure that the standard error of the regression equals the standard error of the slope estimator. c. minimizing the sum of absolute residuals. d. minimizing the sum of squared residuals. Interpreting the intercept in a sample regression function is a. not reasonable because you never observe values of the explanatory variables around the origin. (x=0) b. reasonable because under certain conditions the estimator is BLUE. c. reasonable if your sample contains values of Xi around the origin. d. not reasonable because economists are interested in the effect of a change in X on the change in Y. 5) The OLS residuals a. can be calculated using the coefficient of determination from the regression function. b. can be calculated by subtracting the fitted values from the actual values. c. are unknown since we do not know the population regression function. d. should not be used in practice since they indicate that your regression does not run through all your observations 6. When the estimated slope coefficient in the simple regression model, ̂ 1 , is zero, a. R2 = Y . b. 0 < R2 < 1. c. R2 = 0. d. R2 > (SSR/TSS). 7. The regression R2 is defined as follows: 𝑆𝑆𝐸 a. 𝑆𝑆𝑇 b. 𝑆𝑆𝑅⁄𝑆𝑆𝑇 c. 1 - 𝑆𝑆𝑅⁄𝑆𝑆𝑇 d. 8. 9. SSR n2 Which of the following statements is correct? a. SST = SSE + SSR b. SSE = SSR + SST c. SSE > SST d. R2 = 1 – (SSR/SST) The regression R2 is a measure of a. whether or not X causes Y. b. the goodness of fit of your regression line. c. whether or not ESS > TSS. d. the square of the determinant of R. Analytical questions 1. 2. A company administers an aptitude test for all new sales reps. Management is interested in the extent to which this test is able to predict the eventual success of the new reps. Particularly with regards to their weekly sales. A sample of 16 new reps. Produced the following results: = 9247 = 82,408 SSx = 298,377 SSy = 3,732,540 SCxy = 738,725 a. obtain the least square regression equation and interpret your equation b. As a car dealer, you are interested in knowing the factors that influence the number of cars sold per month. Having taken a course in economics, you inserted the variables, number of cars sold (y) and the average price (x) into spreadsheet software. The regression output is as follows: Regression Output Constant (intercept) 100.1206 Std. Error of Estimate 8.316073 R-Squared 0.738124 Degrees of Freedom 22 X-Coefficient (B1 hat) Std. Error of coefficient a. b. -3.68022 0.467353 state the ordinary least squares linear regression equation what percentage of the changes in car sales per month is explained by the changes in price 3. In a regression analysis, n=25, X = 75 Y = 50, X2 = 625 Y2 = 228, XY = 30 Find: a. the regression equation and interpret it 4. Consider the regression model : Yi = 0 + 1 Xi + i , where Yi denotes average test scores from fifth-grade classes (TS, measured in percentages) and Xi denotes the data on fifth grade class size (CS) . You collected data on 100 classes with class sizes ranging from 25 to 36 a. What does the term I represent? Suppose the regression above yields the following: ̂ = 520.5 − 5.82𝐶𝑆 𝑇𝑆 R-squ = 0.653 b. Interpret the estimated regression equation fully. c. Interpret the R2. What are the units of measurement for the R2? d. A classroom has 22 students. What is the regression prediction for the classroom’s average test score? Is this prediction reliable? Why or why not? c. The sample average class size across the 100 classrooms is 29.4. What is the average test scores across the 100 classrooms? 5. Sir Francis Galton, a cousin of James Darwin, examined the relationship between the height of children and their parents towards the end of the 19th century. It is from this study that the name “regression” originated. You decide to update his findings by collecting data from 110 college students, and estimate the following relationship: Studenth = 19.6 + 0.73×Midparh, R2 = 0.45, Se = 2.0 where Studenth is the height of students in inches, and Midparh is the average of the parental heights. (Following Galton’s methodology, both variables were adjusted so that the average female height was equal to the average male height.). SER is the standard error of regression (a) (b) (c) Interpret the estimated equation. Is the estimated intercept meaningful? Why or why not. What is the meaning of the R-squared value in this problem? Given the positive intercept and the fact that the slope lies between zero and one, what can you say about the height of students who have quite tall parents? Who have quite short parents?