Leaf Structure
advertisement

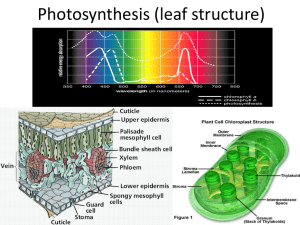
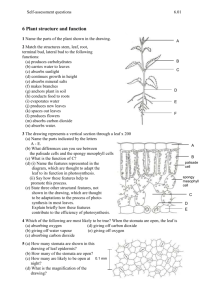
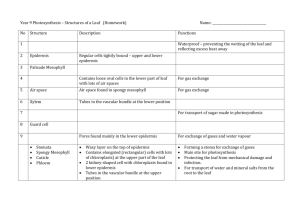
LEAF STRUCTURE B4a THE LEAF What might happen to leaf structure if climate change continues? OBJECTIVES Key Objective Describe the role of specialised cells in aiding photosynthesis Describe how the main features of the plant are linked to photosynthesis (E-G) Explain how leaves are adapted for efficient photosynthesis (C/D) Explain how the structure of a leaf palisade cell is related to its function (C/D) Identify the process by which gases travel in and out of the plant (C/D) Explain how the cellular structure of a leaf is adapted for efficient photosynthesis (A/B) PRACTICAL Designing leaves for different environments PLENARY Draw this diagram of a Marram grass leaf. MARRAM GRASS IS FOUND ON SAND DUNES. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Add the two missing labels (D) What does the waxy cuticle do? (C) How does the position of the stomata help this plant? (C) Why are there no stomata on the outer surface of the leaf? (B) Explain the function of the hairs on the inner surface of the leaves? (A) Explain how having sunken stomata will affect gaseous exchange in the plant, and why this would be an advantage to the plant. (A*) FOR G-E: Identify the chloroplasts, vacuole and cell wall in a plant cell. State that chloroplasts absorb light energy for photosynthesis. State that photosynthesis occurs mainly in the leaves. Describe the entry points of materials required for photosynthesis: water through roots; carbon dioxide through leaf pores. Describe the exit point of materials produced in photosynthesis: oxygen through leaf pores. KEY WORDS: chlorophyll; cuticle; guard cell; lower epidermis; palisade mesophyll; spongy mesophyll; stomata; upper epidermis; vein FOR C/D Name and locate the parts of a leaf: Explain how leaves are adapted for efficient photosynthesis: cuticle; upper and lower epidermis; palisade and spongy mesophyll layers; stomata and guard cells; veins. broad so large surface area; thin so short distance for gases to travel; contain chlorophyll to absorb light; have a network of veins for support and transport; stomata for gas exchange. State that the exchange of gases is by diffusion. Explain how the structure of a leaf palisade cell is related to its function: contains many chloroplasts. FOR A*-B: Explain how the cellular structure of a leaf is adapted for efficient photosynthesis: epidermis is transparent; palisade layer at the top containing most of the chloroplasts; air spaces in the spongy mesophyll allow diffusion between stomata and photosynthesising cells; internal surface area / volume ratio very large.